You've used too much, and now we have to charge you more... a lot more.
No matter where you live, work or play — be it Seoul, Korea, Manchester in England, or Oklahoma City — there is one thing consumers in all three cities will readily agree on: hatred of broadband data usage caps.
Those are the findings of a brand new survey conducted by GfK NOP in association with Reuters News in Britain.
Nearly 1,000 consumers were asked what they would do if confronted with their Internet provider implementing usage limits and other Internet Overcharging schemes. More than half said they would be shopping for a new provider.
Not surprisingly, regardless of whether a consumer uses wired or mobile broadband, few believe usage caps are anything more than price gouging by providers to rake in additional revenue. Many of these company’s biggest-spending-customers are unhappy to learn their provider is back looking for more money in return for less service.
The survey found users of smartphones such as the Apple iPhone care more about their mobile data allowance than they do about their choice of operator or even handset brand.
The survey found that users of the iPhone, Google Android phones or Research in Motion’s BlackBerry — typically, those who spend the most — are far more likely to switch operators to find better data deals.
More than half the users of these devices said they would switch to get a higher mobile data allowance.
Adjusted to take account of the fact that consumers do not always do what they say they will, GfK NOP esimated that 24 percent of contract customers using smartphones would actually switch operators.
Such a stampede would ring panic alarms inside any wireless carrier, but one company in particular faces some serious consequences for delivering years of bad service at high prices.
According to market research firm Morpace, nearly one-half of AT&T’s iPhone customers will seriously consider jumping ship if and when Verizon offers their own version of the wildly popular Apple smartphone.
At least 34 percent of current iPhone owners are resisting upgrade offers from AT&T that require a two-year contract renewal. They’d rather wait until the iPhone is available on any network other than AT&T.
 Even worse, should Verizon introduce their version of the iPhone in the coming year, nearly a quarter of AT&T customers (including those without the iPhone) are “somewhat or very likely” to dump AT&T immediately and head for Verizon.
Even worse, should Verizon introduce their version of the iPhone in the coming year, nearly a quarter of AT&T customers (including those without the iPhone) are “somewhat or very likely” to dump AT&T immediately and head for Verizon.
In addition to complaints about lousy network performance, AT&T smartphone owners who spend the most with the carrier absolutely loathe AT&T’s new data usage limits implemented this past June.
“Experienced smartphone users who understand the benefits of using the Internet on the move and use services to help them in their day-to-day lives simply can’t live without mobile data,” says GfK/NOP analyst Ryan Garner, one of the report’s authors.
“They don’t want to be thinking about their data allowance and possible costs of over-running every time they open their browser or click on an app.”
Although AT&T told their customers and the media the new data-limited plans were going to save many customers money and have no impact on the rest, that is not what AT&T’s Chief Financial Officer Rick Lindner told Wall Street bankers and shareholders on a conference call last month.
“We believe over time, based on how much data they use, they will then begin to migrate up to [more costly] higher tiered plans,” Lindner said.
AT&T is well aware customers are already packed and ready to abandon ship, which is why the wireless provider has introduced a series of impediments to keep customers anchored in place. Waived upgrade rules permitted most iPhone owners to upgrade to the latest iPhone 4 model this summer at the promotional price, in return for a two-year contract extension. Customers seeking an end to their relationship with AT&T will find divorce an expensive proposition. The company nearly doubled the contract early termination fee for smartphone owners June 1st. Your exit price: up to $350.

Why construct more of these if providers can get you to use less and pay more in the process?
Reuters notes the biggest driver towards the introduction of Internet Overcharging schemes like usage caps is the quest for additional revenue.
Most Western carriers have frozen or cut capital expenditure in the last two years as they prioritise maintaining the dividends prized by investors — meaning the modernisation of networks has been largely put on ice.
Meantime, they say they can no longer afford physically or financially to support unlimited data usage, and are banking on the fact that most consumers will barely notice data caps that are in any case far more generous than average data usage.
Stop the Cap! has been reporting that fact for at least two years now. Usage limits are never about saving money for customers or making consumers pay for what they use. They are about increasing profits at the same time providers continue to reduce investments to maintain and upgrade their networks. Providers routinely report they are spending countless billions on network infrastructure, but neglect to mention those investments are not keeping up with subscriber growth and, in many cases, are actually decreasing year-by-year. The self-perpetuating problem of network congestion that inevitably follows then becomes an excuse to charge customers more money for usage-limited service.
Reuters confirms that many western carriers have business plans that would be familiar to any neighborhood drug dealer – hand out plentiful cheap samples, get customers hooked, and then gradually reduce the supply while also raising the price.
In Europe, Scandinavian operator TeliaSonera is betting that the superiority of its next-generation LTE network, the world’s first, will allow it to offer premium services — at premium prices.
“When a service like this is entering the market, you normally more or less give it away for free, and so we did with mobile data,” Hakan Dahlstrom, the company’s head of mobility services, told investors last month.
“After a while… to meet the customer’s need for cost control; that is when you have flat rate. And then after some time the user understand how these services work and how it suits them, and you start charging for speed and volume.”
 Yet not every provider has found success in alienating and overcharging their customers for increasingly important connectivity.
Yet not every provider has found success in alienating and overcharging their customers for increasingly important connectivity.
Reuters found Japan and Korea’s more advanced and mature data networks have already been down the road of usage restrictions, and found they didn’t solve network congestion issues — only provider investments in upgrades did:
Japanese operators NTT DoCoMo, KDDI and Softbank have stuck to flat rates — with discounts for months in which customers use less data — while encouraging them to use more Wi-Fi to take pressure off the mobile networks.
In Korea, carriers are returning to unlimited data plans because of heightened competition while investing heavily to upgrade their networks — a move that Western counterparts are unlikely to be able to avoid for much longer.
SK Telecom, South Korea’s top mobile carrier, last month said it would offer unlimited data services and free mobile Internet calls for customers paying 55,000 won ($46.40) and over in monthly service charges.
Of course, both Korea and Japan maintain more oversight by public officials over critical network infrastructure vital to both nations’ economies. Neither government allows unregulated monopolies or duopolies in their midst — convinced they’ll deliver the least amount of service they can for the highest possible price they can get away with. In other words — today’s marketplace model in much of Europe and North America.
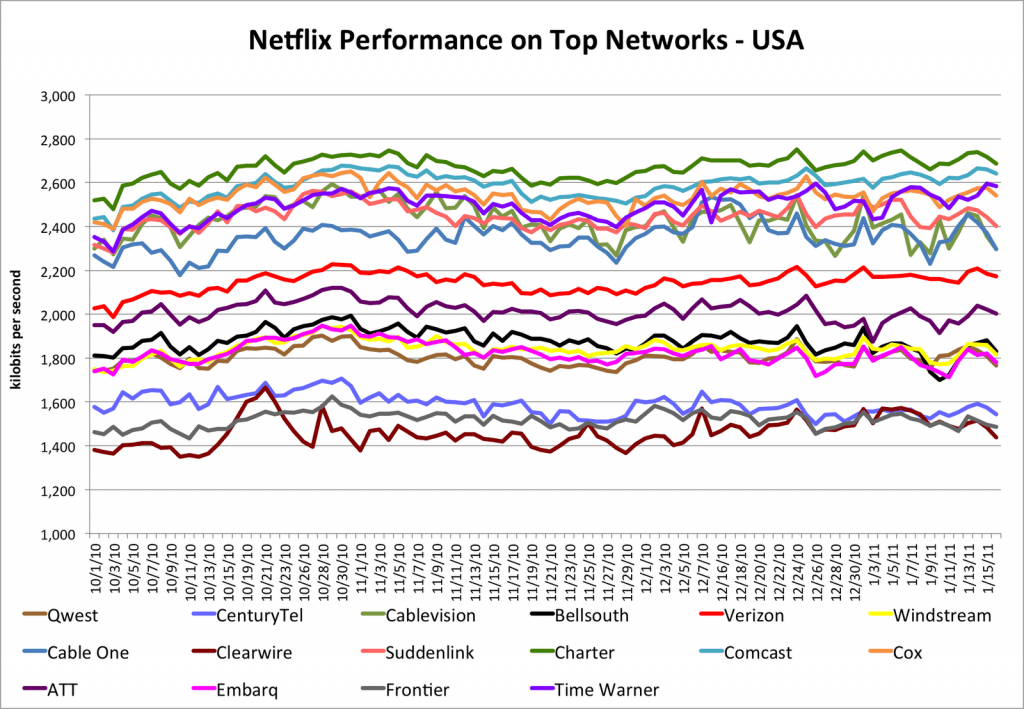
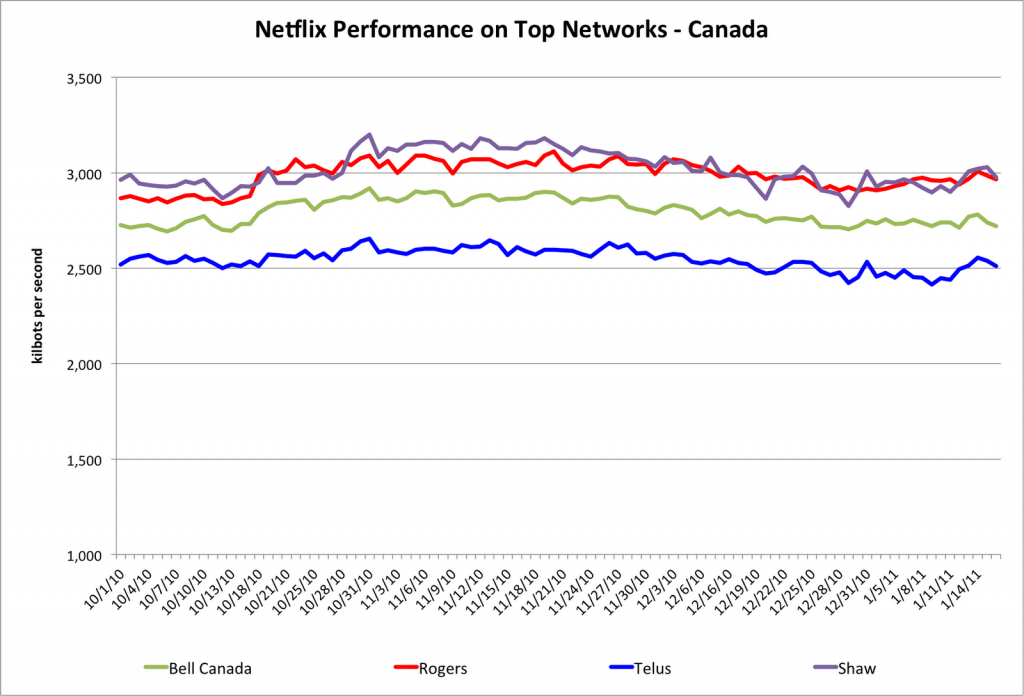
 Netflix today released statistics showing Frontier Communications was America’s worst ranked wired Internet Service Provider, ranking at the bottom for quality and speed when using Netflix’s streamed content.
Netflix today released statistics showing Frontier Communications was America’s worst ranked wired Internet Service Provider, ranking at the bottom for quality and speed when using Netflix’s streamed content.

 Subscribe
Subscribe