Mid-Rivers Communications, a Montana-based telecom co-op, wants everyone to believe their mandatory, usage-based broadband scheme that charges $19.95 a month + $0.20 per gigabyte is popular with their customers.
Mid-Rivers Communications, a Montana-based telecom co-op, wants everyone to believe their mandatory, usage-based broadband scheme that charges $19.95 a month + $0.20 per gigabyte is popular with their customers.
After the company noticed that fewer than 20% of customers were responsible for more than 90% of Mid-Rivers’ network traffic, it decided to ditch its traditional usage-capped, speed tier plans in favor of a compulsory usage-based billing scheme that included the maximum speed available, sometimes as high as 1Gbps, with no usage allowance.
To listen to Michael Candelaria, Mid-Rivers CEO and general manager, people have lined up at the doors just waiting to sign up, according to an interview published by Telecompetitor:
Initially the company tested usage-based pricing as an option in one CLEC market. But considering that 80% of customers opted for usage-based pricing within one year of its introduction, Mid-Rivers moved completely to usage-based pricing and launched it throughout all four CLEC markets.
Mid-Rivers has been particularly proud of the response it has received from local businesses. Candelaria noted that local hotels have seen occupancy drop after the area experienced an oil-related boom, followed by a bust. Nearly-empty hotels were paying $500 to $1,000 a month for high-bandwidth connections from competitors but only using a fraction of the capacity. The Mid-Rivers usage-based broadband offering was perfect for them.
During certain months, the hotels’ bills are dramatically lower than they were before.
“When the hotel is full, their bill goes up and they know why,” Candelaria said.
Meanwhile, as businesses that were not Mid-Rivers customers heard about the usage-based offering, “they came to us” after “we beat on their door for 20 years,” he noted.
 But as news of the interview spread, it seems more than a few customers are not happy with Mid-Rivers’ new broadband pricing, and accused the company of propagandizing its usage based pricing scheme and censoring social media to suppress customer backlash.
But as news of the interview spread, it seems more than a few customers are not happy with Mid-Rivers’ new broadband pricing, and accused the company of propagandizing its usage based pricing scheme and censoring social media to suppress customer backlash.
Candelaria admitted the company used to take a lot of heat from customers that called up and asked for the cheapest internet plan available, which was $40 a month for 1.5Mbps service. At those speeds and prices, customer slammed the company’s Facebook page.
“This is where Candelaria time traveled a bit on his answer,” reflects Dan Corey, a customer rebutting Candelaria’s case. “Before the usage-based internet [plans], the tiers Mid-Rivers [offered] were 8, 12, and up to 50Mbps. There has not been a 1.5Mbps speed at Mid-Rivers for years.”
These days, Candelaria claims, complaints about speed and pricing are mostly gone.
“Of course they are gone,” responds customers J.P. and Kyle Jones, who jointly shared their feelings with Stop the Cap! “Mid-Rivers now censors their social media after taking a lot of heat so complaints are never publicly seen on their Facebook page.”
“Mid-Rivers must approve any comments made on their Facebook page, so 90% of the complaints are never seen unless Mid-Rivers has a full (even if not accurate) response ready to post along with it,” adds Corey. “No dissatisfied customers would know of others because of the control. Their Facebook page used to show all comments when posted, but that changed once they got a better understanding of how to control the flow of comments.”
Jones points out that the reason “80% of customers opted for usage-based pricing” is that any account change automatically forced the customer onto a usage-based pricing plan whether they wanted it or not. Most customers, including himself, do not want data caps or usage pricing, but he didn’t get a choice in the end.
“Put yourself in the shoes of a customer that used to be enrolled in Mid-Rivers’ Preferred Plan, which cost $59.95 a month and includes 600GB of usage at 12/1Mbps speeds,” writes J.P. “People don’t live in Montana for the social life so we spend a lot of time streaming video at home. Under Mid-Rivers’ new plan, if I used 500GB a month, I’d pay $20 for the account and $100 in usage charges — double what I paid a month earlier just for faster speed I could have paid more to get if I wanted or needed it. How many people do you think are enthusiastically waiting to pay double what they used to for internet?”

Mid-Rivers new usage-based plan.
For Candelaria, “Wide Open Wi-Fi” is about selling fast internet access for less, and customers should only pay for what they use.
“People have been paying for utilities by usage for some time,” he told Telecompetitor. “Customers don’t tally up how much electricity they use and then order a 30-kilowatt plan and they don’t count how many showers they take to determine what kind of water plan they need. Why should the internet be any different? Everybody should have good internet. It doesn’t matter if you’re rich, poor, you should be able to afford fast internet.”
Customers like J.P. agree with wanting fast and affordable internet, but argue this isn’t that. Where available, “Wide Open Wi-Fi” quickly becomes the only option Mid-Rivers offers, he claims.
“The reason for the [high] ‘take rates’ is that if you attempt to change or upgrade service, you are forced onto the usage-based service,” adds Corey. “There is no choice, so the take rates are very misleading. Customer satisfaction would increase for those that don’t use the service as of now. However, with more and more of the world going to internet, those customers will feel the squeeze soon enough.”
For customers that avoid calling Mid-Rivers and keep their heads down to keep their current plan, that doesn’t stop the company from eventually notifying customers their plan was changing whether they liked it or not.

Mid-Rivers older tiered plans.
“You will be ‘offered’ the Wide Open internet shortly I’m sure. Just like we in the cable modem towns were,” noted BigSkyGuy. “However, once not enough people switch to it, or it’s been some pre-determined amount of time, you’ll be forced onto it like the rest of us. Then you can enjoy the larger bills. Just like your forced router unfortunately.”
Mid-River sells its “Wide Open” service as a great way to get rid of data caps and tiered plans, and includes a free Wi-Fi router:
- Virtually unrestricted speeds
- Connected Home Wi-Fi included!
- No more tiered plans! You automatically get the fastest speed!
- No more data caps
- Pay for only what you use
- Your speed and experience will be greatly enhanced
- Your perfect plan – whether you need the fastest speeds or the most affordable option
- You as the customer will have control over your Internet bill*
 That asterisk points to fine print that explains for $19.95 a month, you get no data allowance. You are billed $0.20 per gigabyte in one gigabyte increments. Don’t like the high bill that results?
That asterisk points to fine print that explains for $19.95 a month, you get no data allowance. You are billed $0.20 per gigabyte in one gigabyte increments. Don’t like the high bill that results?
“Your bill can be controlled by monitoring how much data you are using, use less and your bill will decrease,” the company explains.
But for most internet users, using less isn’t an easy option, especially as cord-cutting shifts more viewing towards the internet. Once Netflix, Hulu and similar services detect the faster speeds available on Mid-Rivers’ metered plan, their players increase video bandwidth to match available speed unless the customer intervenes. If they don’t, streaming can get very expensive.
“I have been hit with that Wide Open internet scam […] and unless you change your settings in [Netflix, Hulu, CBS, etc.] it’ll run you up to 7GB an hour, especially when it reads that speed setting from the Wide Open. In essence, Mid-Rivers is making you pay $1.40 per hour of Netflix,” writes BigSkyGuy. “Now granted, you can go in and change your settings, but how many people really know you can do that?”

The meter is lurking.
Candelaria argues the majority of Mid-Rivers customers use less than 100GB a month and their bill is less than $40, which is nearly $5 less than Mid-Rivers’ cheapest plan at $44.95, which includes a 300GB data allowance. He also claimed ‘the change to usage-based broadband has increased customer satisfaction and take rates – and while margins initially dropped, profitability was back to its previous level within six months.’
To accomplish that, either the company has signed up more new customers under the plan than it expected or usage charges from heavier users are covering the lost revenue. For Candelaria’s statement to remain true, “most customers” would have to use less than 100GB of usage a month for their bill to remain under $40. Lighter use customers may benefit from the faster speeds and continue to pay less as long as their usage stays at or near 100GB a month. But as average internet use continues to increase, so will customers’ bills.
Jones says the news isn’t all good for Montana businesses either.
“In areas where Charter/Spectrum offers business internet service, their bills are a fraction of what Mid-Rivers is charging if that business tends to run up a lot of usage, and there are no surprise bills from Mid-Rivers’ traffic charges,” Jones notes. “The problem is that Mid-Rivers is charging sky-high usage fees of $0.20/GB while other ISPs pay at most pennies per gigabyte. In fact, most ISPs buy bandwidth based on meeting demand during peak usage times, not traffic alone. During off-peak times, using your connection costs Mid-Rivers next to nothing, but Mid-Rivers keeps charging $0.20/GB day and night.”
BigSkyGuy notes other ISPs in the area are offering customers a better value proposition with flat-rate internet that will quickly be the envy of many Montanans facing future Mid-Rivers’ usage charges:
- RTC/Reservation Telephone Cooperative: (100/100Mbps) UNLIMITED DATA $55/month
- Midco/Midcontinent Communications: (75/5Mbps) UNLIMITED DATA $56/month or (25/3Mbps) UNLIMITED DATA $42/month
- Nemont: (10/10Mbps) UNLIMITED DATA $71/month
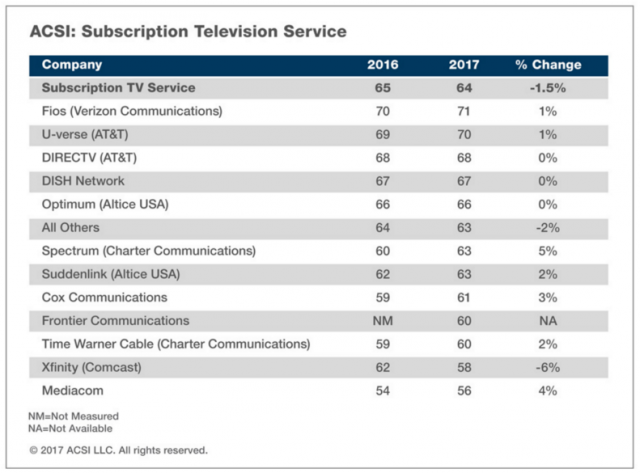
 Nearly 200 people turned out for a packed public meeting in Lexington, Ky. to complain about Charter Communications and its Spectrum cable television service.
Nearly 200 people turned out for a packed public meeting in Lexington, Ky. to complain about Charter Communications and its Spectrum cable television service. “Spectrum has increased my bill twice while I’m still on the package,” complained customer Loney Burns. When she tried to cut back on her package to save money, Burns was told, “if you want to take them off, we will increase your bill.”
“Spectrum has increased my bill twice while I’m still on the package,” complained customer Loney Burns. When she tried to cut back on her package to save money, Burns was told, “if you want to take them off, we will increase your bill.”

 Subscribe
Subscribe