Friday is the last day to submit your views on Net Neutrality with the Federal Communications Commission. Although there may be some future opportunities to comment, it’s important to make your voice heard with the FCC today. Almost 650,000 Americans have done so to date, and we need to see this number rise even higher to combat the influence and power of Big Telecom companies looking to turn the Internet into a corporate toll booth.
Friday is the last day to submit your views on Net Neutrality with the Federal Communications Commission. Although there may be some future opportunities to comment, it’s important to make your voice heard with the FCC today. Almost 650,000 Americans have done so to date, and we need to see this number rise even higher to combat the influence and power of Big Telecom companies looking to turn the Internet into a corporate toll booth.
If you recall, FCC chairman Tom Wheeler is promoting a scheme where big ISPs like Verizon, AT&T and Comcast can divide up the Internet and introduce toll lanes allowing preferred paid traffic to travel on the Internet at faster speeds, usually at the expense of unpaid traffic that will get relegated to an Internet slow lane. It’s pay to play, and customers of these ISPs are already getting a preview of the new corporate road map for the net. Netflix viewers on ISPs that don’t have a paid agreement to handle video traffic suffer from rebuffering and lower quality video. But ISPs collecting tolls from Netflix don’t subject their customers to a degraded online video experience. Of course, before ISPs realized they could make money selling fast lanes, Netflix worked fine on virtually all of these providers.
Wheeler’s proposal would extend the two-tiered Internet to other websites and service providers, allowing big telecom companies to hand-pick winners and losers and discriminate in favor of their own Internet traffic. Comcast does that today with online video on certain game consoles. If that video comes from Comcast, it doesn’t count against any usage caps. If it doesn’t, it could get rough sticking to Comcast’s arbitrary usage allowance.
The FCC is in way over its head, unaware of the creative ways ISPs can find loopholes large enough to drive through any well-intentioned consumer protections. There is only once certain way to keep ISPs honest — reclassify them as what they should have been all along – a telecommunications service subject to common carrier rules. That would guarantee ISPs could not meddle with your Internet service for financial gain, could not artificially slow down “non-preferred” traffic to make room for paid traffic, and would guarantee that Internet applications of the future will succeed or fail on their merits, not on how much money they are willing to spend.
Since the FCC website is jammed today, we recommend e-mailing the Commission by this Friday at: [email protected]
Our friends at Free Press have published some sample comments they are getting, which may help you formulate yours. Here is ours as well:
Dear Chairman Wheeler,
Although we believe your intentions are good, your proposed Net Neutrality rules simply do not afford enough protection to preserve a free and open Internet. Troubling signs are already clear as providers test how much they can get away with meddling with Internet traffic. The wireless experience is replete with examples of selective speed throttling, usage caps, and traffic discrimination that allows some content to escape the usage meter and throttle while competitors cannot.
The Internet is a transformative experience for many Americans because for the first time in a long time, entrepreneurs can build online businesses that are judged on their merit, not on how much money they have to spend to achieve and maintain prominence. Anything that allows an ISP to collect additional funds for a “preferred” traffic lane will come at the detriment of others who have to share the same broadband pipe. This is especially evident in the wireless world, which escaped even the light touch regulatory framework of your predecessor. Providers promptly began creating new schemes to further monetize growing data traffic, bandwidth shortage or not. Almost none of these changes really benefit customers — they are simply new revenue-making schemes.
A foreshadowing of what is likely to happen under your proposal is also apparent with Comcast and Netflix. For several years subscribers had no trouble accessing online video. But when the issue of traffic compensation was reintroduced by Internet Service Providers, the upgrades to manage natural Internet growth largely stopped and the Netflix viewing experience on these ISPs deteriorated. Verizon, AT&T and Comcast all argue that a paid traffic deal would adequately compensate them to enhance the viewing experience customers already pay good money to receive with or without a paid peering arrangement with Netflix.
Money drives these debates. If an ISP properly managed their broadband infrastructure, there would be no incentive for any company to contract for a better online experience on a so-called “fast lane” because existing service would perform more than adequately. When a company cuts back on those upgrades, a market for paid prioritization appears. Customers will ultimately pay the price, primarily to ISPs that already enjoy an enormous margin selling broadband service at inflated prices.
A rising tide floats all boats, so your focus should not be as short-sighted as allowing ISPs to divide up the limited broadband highway. The FCC should instead focus on setting the conditions to hasten new competition and force existing providers to upgrade and maintain their networks for the benefit of all subscribers and content producers. The FCC must also move swiftly to cancel state bans on community broadband networks, eliminate regulations that deter broadband start-ups, and maintain enough oversight to guarantee a level playing field on which all can compete.
There is only one way to effectively accomplish all that. Reclassify broadband service the way it should have been classified all along: as a telecommunications service subject to common carrier regulations. Canada has been very successful requiring ISPs to open their last mile networks to competitors, which have allowed people to avoid compulsory usage caps. Customers have a choice of multiple providers from their local phone or cable company, giving rise to much-needed competition.
With strong Net Neutrality, consumers can reach the websites they want without interference. Ignore nonsense suggesting Net Neutrality is a government takeover or censors the Internet — two provably false assertions. In fact, Net Neutrality is the opposite.
I urge you to move with all speed towards reclassification, if only to prevent the inevitable legal challenges to any future policies built on the shakier ground of the current framework, which has not held up well under court scrutiny. I hope the voices of more than a half-million Americans contacting you on this issue will be more than enough to overcome industry objections. We are not asking for 1950s-style telephone regulations. We just want a legally affirmed platform that allows the Internet of today to continue being successful tomorrow.
Yours very truly,


 Subscribe
Subscribe The New York Public Service Commission needs to hear from you about the Comcast-Time Warner Cable merger. Unlike some of the southern and midwestern states that have utility commissions that basically rubber stamp the agenda of Big Telecom companies, New York’s PSC has a reputation for being tougher and more customer-oriented. But the PSC cannot act in your interest if you don’t share your views.
The New York Public Service Commission needs to hear from you about the Comcast-Time Warner Cable merger. Unlike some of the southern and midwestern states that have utility commissions that basically rubber stamp the agenda of Big Telecom companies, New York’s PSC has a reputation for being tougher and more customer-oriented. But the PSC cannot act in your interest if you don’t share your views.


 Powell and others made certain that Internet Service Providers would not be classified as “common carriers,” which would require them to rent their broadband pipes at a reasonable wholesale rate to competitors. The industry and their well-compensated friends in the House and Senate argued such a status would destroy investment in broadband expansion and innovation. Instead it destroyed the family budget as prices for mediocre service in uncompetitive markets soared. Today, consumers in common carrier countries including France and Britain pay a fraction of what Americans do for Internet access, and get faster speeds as well.
Powell and others made certain that Internet Service Providers would not be classified as “common carriers,” which would require them to rent their broadband pipes at a reasonable wholesale rate to competitors. The industry and their well-compensated friends in the House and Senate argued such a status would destroy investment in broadband expansion and innovation. Instead it destroyed the family budget as prices for mediocre service in uncompetitive markets soared. Today, consumers in common carrier countries including France and Britain pay a fraction of what Americans do for Internet access, and get faster speeds as well.
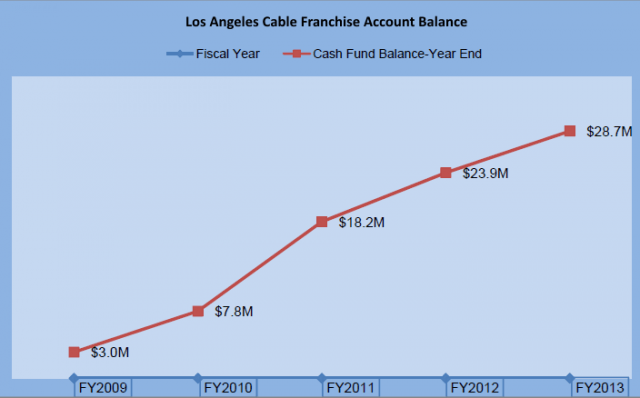
 AT&T and Verizon sold the legislation to the public as a red-tape cutter to bring Verizon FiOS and AT&T U-verse to millions of Californians without unnecessary bureaucratic delay.
AT&T and Verizon sold the legislation to the public as a red-tape cutter to bring Verizon FiOS and AT&T U-verse to millions of Californians without unnecessary bureaucratic delay.