 It is rare for AT&T and Verizon to feud in public, even rarer for one company to accuse the other of being anti-competitive, but that is precisely what happened last week in California as the two companies sparred over building a next generation wireless network for first responders.
It is rare for AT&T and Verizon to feud in public, even rarer for one company to accuse the other of being anti-competitive, but that is precisely what happened last week in California as the two companies sparred over building a next generation wireless network for first responders.
The First Responder Network Authority (FirstNet) is a government program to provide emergency responders with priority access to the first nationwide, high-speed wireless broadband network dedicated to public safety. AT&T won an extremely lucrative contract to build, operate and maintain the network in states that “opt in” to AT&T/FirstNet’s proposal. But AT&T is not building a separate wireless network apart from its existing wireless infrastructure. It is using $6.5 billion in public taxpayer dollars and free access to an extremely valuable segment of nationwide 700MHz spectrum, known as Band 14, to improve its existing wireless network for individual customers and the first responders that will get priority access in the event of an emergency.
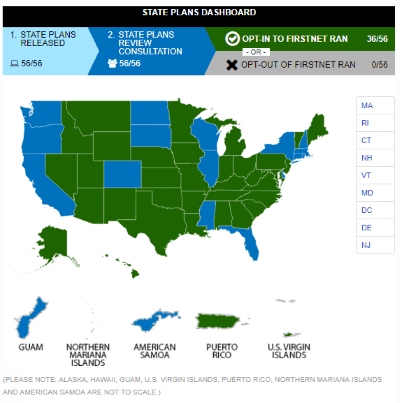
For AT&T to benefit the most financially, it has to convince each of 56 states and territories to “opt in” to its FirstNet deployment plan or do nothing at all, which will result in that state or territory automatically being enrolled in AT&T’s plan. If a state elects to opt out of AT&T’s plan, the wireless company cannot get free access to Band 14 or collect the taxpayer dollars designated for that area.
 FirstNet is one of AT&T’s most lucrative contracts in years, and the phone company is doing everything possible to win over state officials in hopes they will embrace the FirstNet plan. It has been a successful effort with more than 30 states, Puerto Rico and the U.S. Virgin Islands purposely opting in, and more than a dozen still studying AT&T’s offer. To date, no state has opted out.
FirstNet is one of AT&T’s most lucrative contracts in years, and the phone company is doing everything possible to win over state officials in hopes they will embrace the FirstNet plan. It has been a successful effort with more than 30 states, Puerto Rico and the U.S. Virgin Islands purposely opting in, and more than a dozen still studying AT&T’s offer. To date, no state has opted out.
Verizon, which did not bid on the original FirstNet contract, has not walked away from providing public safety communications and has spent a considerable amount of its advertising budget to promote Verizon’s own services to first responders, designed to assure they get first priority to clogged cellular networks in the event of an emergency. In August, Verizon announced it will privately finance its own “private network core” to directly serve police, fire, ambulance, and related agencies. Verizon’s first responder network will be separate from Verizon’s public network, but the company has also promised full priority access to its public LTE 4G network across the country.
Verizon’s counteroffer comes without taxpayer financing, yet will offer many of the same services as AT&T FirstNet, without costing the country more than $6 billion. Among the services Verizon will give away for free: priority/preemption access, which means in an emergency, first priority will go to emergency officials even if it means dropping your cell phone call or data session. Verizon is also bolstering its Push-to-Talk Plus service, which works with existing land mobile radio networks. This will allow first responders to use the “walkie talkie”-type features already a familiar part of their radio equipment.
 Verizon’s offer would seem to be a good deal for consumers and governments in states like New York and California that have yet to opt in to AT&T FirstNet, and in California, Verizon was invited to bid to create an alternative network in a potential “opt out” scenario. Verizon’s director of public-safety solutions group – David Wiederecht, promised the state Verizon would submit its bid by the state deadline, which was last Wednesday. By Friday, California officials leaked word Verizon had reneged on that commitment and did not participate, a fact Verizon later confirmed.
Verizon’s offer would seem to be a good deal for consumers and governments in states like New York and California that have yet to opt in to AT&T FirstNet, and in California, Verizon was invited to bid to create an alternative network in a potential “opt out” scenario. Verizon’s director of public-safety solutions group – David Wiederecht, promised the state Verizon would submit its bid by the state deadline, which was last Wednesday. By Friday, California officials leaked word Verizon had reneged on that commitment and did not participate, a fact Verizon later confirmed.
Verizon accused AT&T and FirstNet of colluding to rig the “Request for Proposals” process in California with requirements that were impossible for anyone except AT&T to meet.
“Vigorous competition that allows the industry and the marketplace to continue to grow and innovate is in the best interest of public safety and should be everyone’s shared goal,” Verizon said in a written statement. “Instead, we believe FirstNet and its corporate partner are rigging the game in order to stifle true competition.”
Urgent Communications reported that the among the most onerous requirements imposed by AT&T and FirstNet is that all emergency communications in an “opt out” state must be sent to the FirstNet LTE core network operated by AT&T. That would mean that regardless of who builds and operates the network, AT&T still remains at the core of FirstNet.
“We’re not prepared to have our public safety customers run on a network where we can’t control their ability to connect or their customer experience,” according to the Verizon spokesperson.
Verizon suggests the reason for 36 states to have opted-in to AT&T’s proposal may not be the result of love for AT&T, but rather the punishments the states and territories risk if they don’t sign on with AT&T.
Don Brittingham, Verizon’s vice president of public safety, testified at a Pennsylvania hearing regarding FirstNet and warned states could be effectively stuck with AT&T indefinitely.
“States should not be required to use the network core deployed by (AT&T) FirstNet, as such a requirement would put the state in the untenable position of being driven by the interests and decisions of FirstNet’s commercial partner—a condition that would be unattractive to any prospective state commercial partner,” Brittingham said.
AT&T has also borrowed from its customer preservation policies on the retail side with terms and conditions that could be financially devastating to states that decide to look elsewhere.
Because any competing provider is required to use AT&T’s network core to be a part of FirstNet, AT&T can set whatever price it chooses for third party access. But most onerous of all is the penalty imposed if a state opts out of AT&T FirstNet and chooses a vendor that does not meet every FirstNet guideline. In that case, a state would be required to come hat in hand back to AT&T/FirstNet for service that does meet the guidelines AT&T/FirstNet wrote. In California, that penalty fee would amount to as much as $15 billion, more than twice the amount taxpayers are paying AT&T to build out FirstNet in at least 36 states and territories.

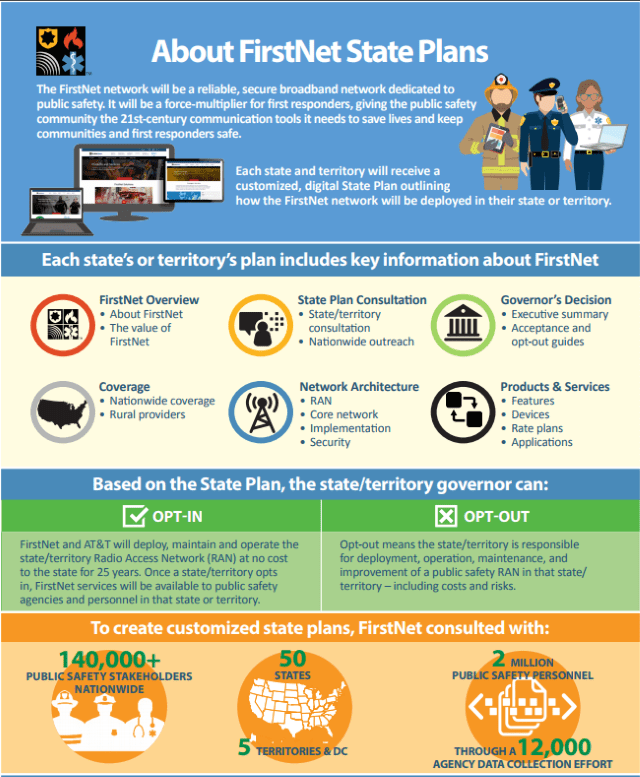
Taken from a FirstNet fact sheet.
AT&T defended the amount of the penalty fee, claiming it has to build or enhance its network to provide public safety communications for at least 25 years, but critics contend the penalty is so risky, most states will opt for the path of least resistance and legal exposure and sign on with AT&T/FirstNet.
Verizon’s complaints about the bidding process received a strong rebuke from AT&T.
“Building a state-of-the art network that meets the needs of first responders is hard. Clearly, AT&T is up for the task,” Chris Sambar, AT&T’s senior vice president for FirstNet, said in a statement provided to Urgent Communications. “We’re noticing a pattern: Verizon says they have public safety’s back, but when it comes to the heavy lifting, they are nowhere to be found.”
But then, neither are any competing providers.


 Subscribe
Subscribe

 Charter Communications has announced gigabit broadband is available on the Hawaiian island of Oahu for $104.99/month, thanks to DOCSIS 3.1 upgrades being tested in the state.
Charter Communications has announced gigabit broadband is available on the Hawaiian island of Oahu for $104.99/month, thanks to DOCSIS 3.1 upgrades being tested in the state.

 But Moffett is thinking even further ahead, by suggesting wireless carriers might be able to stop spending billions on building and expanding their competing 4G LTE networks when they could all share a single provider’s network in each city. That idea could work if providers agreed to creating local monopolies.
But Moffett is thinking even further ahead, by suggesting wireless carriers might be able to stop spending billions on building and expanding their competing 4G LTE networks when they could all share a single provider’s network in each city. That idea could work if providers agreed to creating local monopolies.
 Headquartered in Evansville, Ind., MetroNet provides internet, phone and television service across a 100% fiber optic network in 35 communities in the midwest — mostly in Indiana and the western suburbs of Chicago. The company started operations in 2005, wiring the community of Greencastle, Ind. Since then, it has grown with the financial support of billionaire investors including Microsoft founder Bill Gates and Nike’s Phil Knight. Oak Hill Equity Partners, a private equity firm, has a financial interest in MetroNet, along with investments in WOW!, Atlantic Broadband, Wave Broadband, and Cincinnati Bell.
Headquartered in Evansville, Ind., MetroNet provides internet, phone and television service across a 100% fiber optic network in 35 communities in the midwest — mostly in Indiana and the western suburbs of Chicago. The company started operations in 2005, wiring the community of Greencastle, Ind. Since then, it has grown with the financial support of billionaire investors including Microsoft founder Bill Gates and Nike’s Phil Knight. Oak Hill Equity Partners, a private equity firm, has a financial interest in MetroNet, along with investments in WOW!, Atlantic Broadband, Wave Broadband, and Cincinnati Bell.