Bray Cary, president and CEO of a group of West Virginia television stations enjoying advertising revenue from Frontier Communications, was back on his Decision Makers program to allow an opposing viewpoint to the puff piece interview he held earlier with Frontier’s Ken Arndt, Frontier’s Southeast region chief. This time, he invited Ron Collins, vice-president of the Communications Workers of America to give the CWA side. Cary’s Tea-‘N-Cookies Breakfast Club With Ken this was not. Cary decided to play hardball with Collins, leaving no viewer in doubt where Cary stood on the question of Frontier’s proposed purchase of West Virginia’s phone lines from Verizon.
Unfortunately, Collins was not completely prepared to rebut Cary’s pro-Wall Street, pro-deal propaganda and looked ill at ease at times during the interview. We’re not, and Cary’s “facts” deserve some investigation. After all, how hard should it be to rebut a guy who believes Wall Street and the banks have all the right answers for West Virginians’ phone service?
- Video No Longer Available.
Right from the outset, Cary wants to play “devil’s advocate” with Collins, asking why in the world the CWA is opposed to this deal. That was a major departure from his cheerleading session with Arndt.
“I’ve looked at this […] their stock has been extremely stable. Wall Street appears to be signaling their financial viability is okay. Why is the stock market not reacting negatively? If it’s good for stockholders, how can it be bad for their financial stability. Stockholders want financial stability,” Cary said in a series of statements about the deal, including mentioning a Moody’s report on the deal.
The Moody’s report Cary talks about is for shareholders who will reap the rewards or suffer the losses based on the success or failure of the deal. Moody doesn’t rate the deal’s impact on consumers who have to live with the results. What’s good for Wall Street is not necessarily what’s best for customers.
“What you don’t have is anyone in the financial community suggesting this is a bad financial deal,” Cary said December 13th.
Wrong. Almost a week earlier, on December 7th, D.A. Davidson, a respected Wall Street analyst said the opposite. In a story published in Barron’s: “Frontier Communications’ Shares Not Wired for Success,” the analyst firm argued the regional telecom’s acquisition of Verizon’s rural lines will be… wait for it… bad for the stock.
Cary’s claim that Wall Street is concerned with the long term viability of companies belies the growing reality that much of the investment culture in America has a long term obsession with short term results. Your company is only as good as your last quarter’s financial earnings statement, and several bad ones in a row are usually enough to bring a recommendation to dump shares. Frontier has kept its stock value stable largely as a result of their steady dividend payment. Collins claims Frontier has gone beyond reason, paying 125% of earnings in dividends. That may make the stock a popular choice for income investors, but is also eerily familiar.
FairPoint Communications also enjoyed a healthy stock price because of its high dividend payout. Wall Street only got concerned when they thought that deal might not go through. Morgan Stanley issued a report in 2007 suggesting the deal between FairPoint and Verizon to take control of landline customers in Vermont, New Hampshire, and Maine, was itself helping to prop up the stock’s value. We saw how far that got FairPoint when the company declared bankruptcy a few months ago.
Indeed, smaller independent phone companies commonly use high dividends to remain attractive to investors and stay viable in a tough market. Windstream is another such company and even CNBC’s Jim Cramer gave due diligence to the fact high dividends and stock value by themselves don’t necessarily predict the company’s long term success or failure.
Make no mistake, Frontier has sold this deal to investors based on dividend payouts, claimed cost savings, and a safe bet that any broadband in rural America will earn them increased revenue, especially where consumers have no other place to go for service.
Frontier will take on massive additional debt to finance the deal, but on paper it actually appears to reduce their debt ratio. That’s because when you add millions of new customers, the debt doesn’t look so big next to the increased revenue those additional customers will bring, assuming they stay with Frontier. Should Frontier’s performance underwhelm customers, they’ll drop service if they can. If mobile phone networks do a better job of reaching these rural customers, many will drop landline service anyway. When wireless broadband service becomes a more realistic option, customers might toss Frontier’s slow speed DSL overboard.
AT&T and Verizon have read the writing on the wall — an ongoing decline in landline service and the eventual death of the kind of service Frontier is providing its customers on its legacy network. Would you be better off with a company that recognizes the truth about the future of wired basic phone service, or the one that wants to buy up obsolete networks and hang on until the last customer leaves?
Cary’s concern starts and stops with shareholder value, not the individual long term needs of consumers across West Virginia.
“All of the bankers and all of Wall Street are saying financially this is a good deal financially for Frontier,” Cary argued.
“Good for Wall Street, bad for West Virginia,” Collins replied.
“Well, see I disagree… that has been a myth put out there, and the reason we don’t have any jobs in this state is companies don’t want to come here just because of that mentality. People need to make money. You look at where companies are flourishing, the workers flourish when they do,” Cary said.
Really. Then why are several of these telecommunications companies awash in revenue also continuing to reduce their workforce in their relentless effort to obtain “cost savings.” Someone is making money, just not the average employee. Every state has pro-business acolytes claiming businesses don’t want to come to their state because of regulation and a hostile business climate, even those with the fewest regulations, lowest taxes, and little protection for employees and consumers.
Cary does make one valid point: Verizon wants out of West Virginia and refuses to invest a dime in the state as it looks for a quick exit. Instead the company has diverted resources from serving smaller states’ phone service needs into its larger city FiOS fiber to the home system where it believes it can reap more revenue. Whether that disinvestment should be permitted in the first place is a question that needs to be asked.
Verizon is a regulated utility that is required to meet certain performance standards, and the company’s long history of operations under that framework, under which it profited handsomely, does require consideration. But the state can also provide additional incentives to make it more attractive for Verizon to commit more resources in the state, ranging from tax credits, public-private investment, rewards for performance and service improvements, etc. It can also find someone else to provide the service, or let local communities band together into cooperatives to run their own networks, should customers find that could deliver better service.
At the very minimum, Frontier should he held to strict conditions that require a fiscally responsible transaction for ratepayers, not just for shareholders and management. Verizon’s workforce, already cut to the bone, should not bear the brunt of “cost savings” either, both now and into the future. If Frontier wants to deliver broadband, they should commit to offering 21st century speed (not the 1-3Mbps service typical for their smaller service areas) without their draconian 5GB usage limit in their Acceptable Use Policy.
Cary doesn’t concern himself with those kinds of details, but consumers and small businesses in his state sure do.
Cary wants more jobs and more earnings for West Virginia. In the changing digital economy, high speed broadband isn’t an option — it’s a necessity. Verizon has a proven track record of being able to provide 21st century broadband — Frontier does not (sorry, 1-3Mbps DSL is more 1999, not 2010).
Cary makes an astonishing statement in the third segment of the interview which makes me question his ability to grasp the reality-based community most Americans live in today.
“I have great faith in the banking system in America, in Wall Street, to evaluate these things.”
That stunned Collins, who asked, “even after the 2008 crash?”
Cary seems to think “everything is back to normal.” Unfortunately, after the bailouts and big lobbying dollars being spent in Washington to preserve the status quo as much as possible, everything is back to normal… for Wall Street and the banks. The rest of the country, including West Virginia, is another matter.
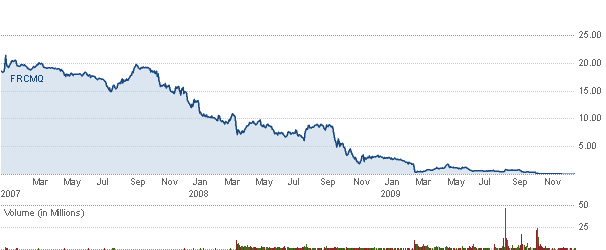
FairPoint's Stock Price from 2007, when it announced the deal with Verizon, to late 2009 when the company declared bankruptcy. By late 2008/early 2009, what seemed like a great deal for investors was apparently not, as the panicked rushed for the exits.
I’ll put my trust in the wisdom of West Virginians who want good service and reasonable prices. If Cary wants to read from the Good Book of the “paragons of virtue” like AIG, Bear-Stearns and Goldman Sachs, let him sell his TV stations to help finance the bailouts. Remember that when we went through this before with Hawaii Telecom and FairPoint Communications, the cheerleading session on Wall Street lasted only as long as the quarterly balance sheets looked good. At the first sign of trouble, they bailed on the stock and both companies ended up in bankruptcy.
For them, it represented just another roll of the dice in the giant financial casino we call Wall Street.
For the rural residents of states like West Virginia who ultimately have to live with the results, this is their phone and broadband service we are talking about. Before all bets are placed and the dice are thrown, isn’t it worth considering them?


 Subscribe
Subscribe