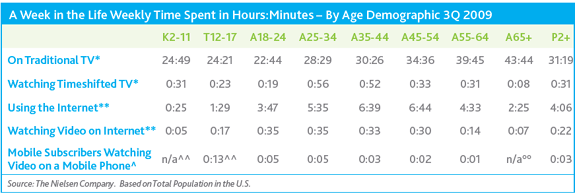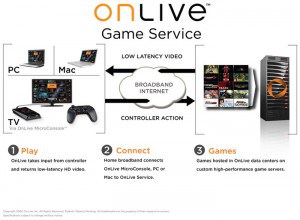
OnLive puts the processing power to render and play games on their end, and streams the result to you over your broadband connection (click to enlarge)
OnLive, the cloud-based videogame streaming service, was on display during a live dem0 of the service at Columbia University. The service, which literally streams game play across fast broadband networks, could seriously challenge the videogame console marketplace. Instead of using an expensive piece of hardware at home to play videogames such as w88, OnLive puts the hardware at their end and streams the results to any computer or television. If it works, it means consumers won’t need the highest performance videocards or latest new CPU. They’ll just need a fast broadband connection to let OnLive’s own servers do all of the processing.
The founder and CEO of OnLive, Steve Perlman, shows considerable enthusiasm for the concept, and several major investors including AT&T and Time Warner have backed the venture, which could help guarantee smooth passage on their broadband networks.
Still, a product that requires a minimum of a 5Mbps broadband connection for HD-quality streamed game play could consume an enormous amount of data — up to 2.25 GB per hour of gaming. Although cable and fiber-based broadband connections will suffice, many DSL customers don’t have service fast enough to support OnLive. Among those that do, any usage caps or allowances will significantly reduce the value of the service to potential subscribers. Frontier Communications’ infamous 5GB “acceptable use” per month, for instance, would allow just over two hours of use per month, assuming you did nothing else with your DSL service.
Even Comcast’s 250GB usage allowance cuts game play to a little over 100 hours per month. That’s a ludicrous amount of gaming for most of us, but not for some gaming addicts who may have tried games like 핑카지노. Besides, it also assumes you don’t use your Comcast broadband service to watch video or other bandwidth-intensive online services.
Time Warner Cable’s proposed 40GB usage limit, shelved indefinitely in April after consumer protests, would permit less than an hour of play per day, assuming your Road Runner service was for nothing but OnLive.
In short, assuming OnLive works as promoted, its biggest threat to success will come from external factors mostly outside of its control — namely cap-happy ISPs that could quickly make streamed cloud computing untenable for all but the wealthiest among us.
What could OnLive do to reduce its risk from caps? Partner with ISPs in a non-Net Neutral broadband world, of course. That investment from AT&T, for example, could theoretically pave the way for AT&T to exempt OnLive from any usage limits that come from its own Internet Overcharging experiments in Beaumont, Texas and Reno, Nevada. That would be a clear violation of Net Neutrality, if enacted into law.
Scenarios like this should drive consumers to support Net Neutrality policies. ISPs forming “preferred partnerships” with innovative services like OnLive might seem consumer-friendly at first, but not in the long-term because it spells the death of would-be “non-preferred” start-ups, and helps pave the way even faster to Internet Overcharging schemes letting broadband providers pick the winners and losers of the future.
[flv width=”484″ height=”292″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/OnLive Columbia University Demo.flv[/flv]
OnLive founder and CEO Steve Perlman demonstrates OnLive and talks about cloud-based, streaming game play at this gathering at Columbia University in New York. (49 minutes)
(If stream stops for buffering, pause it for a few minutes to let a significant amount of the file pre-load, which should reduce re-buffering problems.)


 Subscribe
Subscribe