Yesterday, the Federal Communications Commission formally introduced its omnibus National Broadband Plan to America, Congress, and the telecommunications industry. The FCC seeks nothing less that a transformation of broadband to better meet the needs of Americans for years to come.
The 376-page plan recognizes broadband is no longer a novelty. It’s now becoming one of the essential utilities of life — joining power, telephone and water service as something virtually every American will eventually have in their home. But while the Commission lays the general groundwork for future regulatory policy to help achieve that goal, it ignores the historical reality that made universal service for utilities possible.
I am a strong believer in reviewing past mistakes to avoid repeating them in the future. That is why Stop the Cap! occasionally turns back the clock and reviews history. Railroad robber barons, telephone company monopolies, and electric service providers all abused their positions and consumers paid through the nose for service until the government finally broke up the anti-competitive trusts that limited competition.
Just like today’s broadband players, in the early 20th century, electric companies asked for and received favorable treatment by Congress. The industry argued such treatment was required to make investors comfortable with the enormous amount of investment required to construct power generation facilities, run wiring to homes, and obtaining easy access to American streets and backyards. Regulations must be kept to a bare minimum, providers demanded. Anything else, they claimed, would discourage critical private investment, would create job losses, and slow deployment of service to millions of Americans. Sound familiar?
By the time the American public realized electric companies were abusing their monopoly positions to charge outrageously high prices, the half-measures legislators proposed to control rates and improve service were often ineffective.
Just as with electric service, any broadband plan that seeks to tinker around the edges of the problem will not solve the problem. Providers will find loopholes, lobbyists to help water down the provisions they dislike, and lawyers to mount endless legal challenges to stall reform.
The warning signs are already apparent in the FCC plan. The agency seeks to cooperate with some of the biggest players in the industry that are responsible for what the FCC calls “the critical problems that slow the progress of availability, adoption and utilization of broadband.”
That ultimately means working with existing providers instead of creating the right conditions to welcome new players into the market.
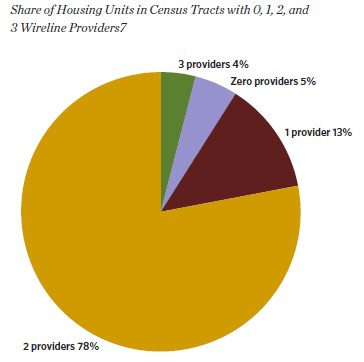
America's broadband duopoly - just four percent of Americans have more than two providers to choose from
The anti-competitive, de facto duopoly pricing power available to cable and telephone companies has created an enormous digital divide for rural Americans who cannot pass “Return on Investment” means tests, prices broadband service out of reach for many, and seeks even higher pricing while proposing to limit service with Internet Overcharging schemes like “usage-based billing” and “usage limits.”
Where one lives is often the most important factor when considering broadband speed and service quality. It’s the luck of the draw. A customer on one side of the street may have the option of Verizon FiOS, a true fiber-to-the-home service providing equal upstream and downstream speeds far higher than the national average. Across the street, a customer may only be served by another telephone company offering 1Mbps DSL with no alternatives.
Other Americans live within viewing distance of a utility pole where cable or telephone broadband service stops, giving them the choice of paying $10,000 to extend service, or living with dial-up or satellite fraudband.
Few phone or cable companies will ever consider invading another’s turf, even if customers begged.
But it gets worse.
The service customers can obtain from a provider varies even within its service area. Verizon FiOS and AT&T U-verse is available in some neighborhoods, but not others. What stops or slows service expansion? Anything from a management decision on a whim to concerns by private investors, market conditions, cost controls, or changing revenue expectations that inhibit uniform service across the community. Local governments used to manage this problem with franchise agreements that made approval conditional on supplying service across an entire community, but companies like AT&T lobbied their way to statewide franchising reforms that can eliminate local oversight.
The cable television industry has a better track record of providing uniform broadband service to customers in their respective service areas, but at what cost? Time Warner Cable COO Landel Hobbs recently told a group of investors pricing for its Road Runner service can be increased at the company’s whim. Comcast has already increased prices on its broadband service. Both companies have either tested or implemented usage limits and restrictions on their customers.
What makes these things possible? Limited competition and insufficient oversight.
The FCC’s solution to limited competition includes vastly expanding wireless frequencies available to mobile broadband providers. But here’s the problem. The government will auction those frequencies off to the highest bidders, which are most assuredly the dominant industry players AT&T and Verizon. For millions of Americans, that means no extra competition at all because their phone, broadband, video, and wireless service all come from these two companies. The only way smaller players can compete in a bidding war is through consolidating mergers, which reduce the number of competitive choices in many cities. If the government wants competition, it should provide incentives to spur its development.
Wall Street certainly won’t help much. They loathe heavily competitive markets now, because inevitable price wars limit their returns. Getting initial investment to construct new networks is problematic because investors don’t want excessive competition. Providers howl it’s unfair for government to help their competitors, but their incumbency provides them with built-in benefits unavailable to new entrants.
The FCC recognizes the importance of broadband service as America’s next utility, but is afraid to regulate them as such. They may have good reason not to try. Comcast is presently suing the Commission in federal court, claiming they don’t have jurisdiction over broadband policy. Should Comcast prove its case, the National Broadband Plan could be just another thesis for improved broadband, with no backing authority to implement its recommendations and regulatory changes.
That brings us to Congress. While the FCC may bring its best intentions to the table with the National Broadband Plan, it’s very likely lobbying will force changes to what finally gets implemented, if anything.
The telecommunications industry never has a problem finding financial resources to hire lobbyists and spread lavish campaign contributions all over Washington.
They’ve already bought and paid for an enormous astroturf group called Broadband for America with 200 member organizations, virtually every single one backed by AT&T or Verizon money or personnel, or equipment providers who stand to earn substantially from broadband improvement. They are running TV ads telling viewers private providers should be left alone to get the job done, something they’ve had a decade to accomplish with insufficient progress in key areas.
Many in Congress, especially on the Republican side of the aisle, will agree with BfA’s “hands-off” advocacy. Early reaction from Republicans regarding the Broadband Plan is not favorable. Rep. Cliff Stearns (R-Florida), the ranking Republican on the House Energy and Commerce communications, technology and the Internet subcommittee, told the Washington Post he wants the agency to stay focused on bringing access to people who don’t have it.
“I am concerned, however, that the plan may contain stalking horses for investment-killing ideas, such as so-called net neutrality mandates or a return to outdated, monopoly-era regulation,” he said.
Many Democrats with large telecommunications companies headquartered in or near their districts are likely also to advocate caution.
Regardless of what the FCC recommends, Congress will ultimately control the outcome.
Here are our recommendations you should consider sharing with your elected officials:
Congress and the FCC must be willing to stand up to the telecommunications industry which is not delivering world-class broadband service. The United States is falling behind in access, pricing, and speed. Simply accepting the provider argument that they should be left alone in an unregulated, duopoly marketplace is not an option;
Congress must deliver to the FCC clear authority to regulate broadband service and enforce Net Neutrality. Recent court cases argue the Commission presently lacks that authority. Congress should take every possible step to ensure the courts this isn’t the case.
Increased oversight of the broadband industry is essential. Why does an industry making billions in profits need to consider usage limits and usage-based billing designed to deter residential use of broadband service? Such limits are designed to protect cable-TV revenue that could disappear if Americans dump their television channel packages in favor of watching everything online on their existing broadband account.
Congress should not stand for an unregulated duopoly controlling a service that is becoming as essential as water, energy, and the telephone. As broadband becomes an essential utility, why is the government not stepping in when the COO of the nation’s second largest cable company — Time Warner Cable, tells investors he can raise broadband prices on a whim? Is this the 21st century version of the Robber Baron Era? Robust competition guarantees no executive can make such a statement. Congress must act to bolster competition, including financial and tax savings incentives for new providers willing to enter markets of all sizes;
Wireless mobile broadband spectrum auctions do not promote competition because the biggest incumbent players are sure to win the bulk of the frequencies, guaranteeing more of the same anemic competition. Some of the newly available blocks of frequencies should be reserved for bidders who do not currently serve the market where those frequencies are available. Only that guarantees new competition in wireless;
Free or deeply discounted access to basic Internet service at broadband speeds should be a part of any National Broadband Plan, to ensure access to every American who wants it.


 Subscribe
Subscribe









