When lawmakers talk about “unleashing” anything for “innovation,” it’s a safe bet we’re about to be treated to an anti-regulatory rant about how government rules are ruining everything for big business. Rep. Greg Walden (R-Ore.) does not disappoint.
Walden is chairman of the Communications and Technology Subcommittee of the House Energy and Commerce Committee, an important place to be if you want to influence telecommunications policy in the United States. Walden slammed the Federal Communications Commission this morning in an editorial piece in Politico, accusing the agency of regulating communications companies before they have a chance to engage in bad behavior:
Sometimes the FCC acts before thoroughly examining whether regulation is needed. It’s now time to stop putting the regulatory cart before the horse. That’s why this bill requires the FCC to survey the marketplace, identify a failure and conduct a cost-benefit analysis before imposing rules.
[…] When the FCC reviews a merger, it now often imposes unrelated conditions. These extraneous agreements may not correspond to any harm presented by the transaction, may not be justified industry-wide and, in some cases, are outside the commission’s jurisdiction.
Such bootstrapping is unfair to the singled-out parties. It also results in poor policy. Imposing extraneous conditions on a transaction that is not otherwise harmful is inappropriate. And if a transaction is harmful, imposing extraneous conditions cannot cure it. Merger conditions should be directly related to transaction-specific harms, and within the FCC’s general authority.
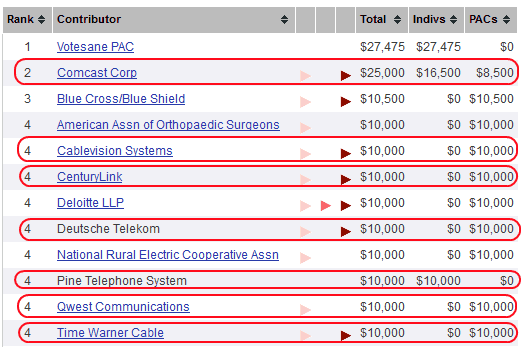
Walden’s concerns coincide with the corporate agendas of some of the nation’s largest telecommunications companies he oversees as chairman. That may not be surprising, considering seven of the top 10 corporate contributors to his campaign fund are all telecommunications companies.
Walden’s record on “innovation” is open to interpretation. He is on record opposing Net Neutrality, has sought to “streamline” the FCC by hamstringing its authority, and has favored a variety of mergers and acquisitions that have effectively reduced competition for American consumers.
The FCC’s zeal for increased competition appears occasionally in its rulemakings, although the agency under Chairman Julius Genachowski can hardly be considered aggressive and out of control when it comes to some of the most contentious telecom issues that have arisen during the Obama Administration. It only followed the Justice Department’s lead opposing the AT&T/T-Mobile USA merger. It punted on Net Neutrality enforcement, doesn’t oppose Internet Overcharging, and has granted more mergers and acquisitions than it has sought to block.

FCC Chairman Julius Genachowski has not always successfully stared down industry efforts to consolidate and deregulate.
Some examples of “unrelated conditions” the FCC has imposed on mergers include no price hikes for consumers for a limited time (Sirius-XM), a discounted Internet service for poor families (Comcast-NBC Universal), and spinoffs of acquired cellular network assets in barely competitive markets (Verizon Wireless-Alltel).
Sirius-XM mostly kept to their agreement, but promptly raised prices when it expired, Comcast followed the FCC’s agreement to the letter but found ways to limit the number of qualified families, and Verizon Wireless sold some of their acquired Alltel assets to AT&T, which at least provided improved AT&T reception in certain markets they largely ignored earlier.
Consumer advocates would argue the FCC should never have approved these transactions in the first place, and the conditions the FCC imposed were so mild, they faced little opposition from the companies involved. But apparently even that is too much for Walden, who we have a hard time seeing opposing any of these mergers. Besides, some of the largest companies donating to Walden’s campaign fund are already adept at working around the FCC, suing their way past the regulations they oppose.
Walden advocates the FCC only perform its oversight functions after the industry is proven to have imposed unfair, anti-competitive, and discriminatory policies against consumers, not to act to prevent those abuses in the first place. In short, he wants the FCC to regulate only after the damage has been done. That would be akin to calling the fire department after your house burned to the ground. Companies would be free to walk away with their ill-gotten gains with little threat the FCC would punish bad behavior and fine the bad actors.
If you are Comcast, that is innovation. If you are a consumer, it’s something else.


 Subscribe
Subscribe