 A sweeping deregulation measure sponsored by Verizon Communications would end the telephone company’s obligation to provide landline service and remove state-mandated customer quality of service standards in Massachusetts.
A sweeping deregulation measure sponsored by Verizon Communications would end the telephone company’s obligation to provide landline service and remove state-mandated customer quality of service standards in Massachusetts.
House Bill 2930, “An Act modernizing telephone regulation and encouraging economic growth,” introduced by Rep. Stephen L. DiNatale (D-Fitchburg) is succinct:
SECTION 1. Chapter 25C of the General Laws, as appearing in the 2010 Official Edition, is hereby amended by inserting after section 7 thereof the following sections.
Section 8. Notwithstanding any other general or special law to the contrary, the department shall have no jurisdiction, general supervision, regulation or control over wireless service, including mobile radio telephone service, or radio utilities.
Section 9. Notwithstanding any general or special law to the contrary, subject to the provisions of section 10 of this chapter, no provision of this chapter, Chapter 25 or Chapter 159, 8 and no regulation, order or settlement or portion thereof adopted pursuant to any such provision, shall apply to any telephone company (or a common carrier offering telephone service) in any municipality for which the company or carrier certifies to the Office of Consumer Affairs and Business Regulation that there are at least two providers offering voice telephone service to retail residential customers in that municipality using any technology, including but not limited to wireless voice service and VoIP service.
Section 10. Nothing in sections 8 or 9 of this chapter shall be construed to affect or modify:
a. the authority of the attorney general to apply and enforce chapter 93A or other consumer protection laws of general applicability;
b. the department’s authority under sections 18B and 18H of Chapter 159, concerning enhanced 911 service, and under section 15E of Chapter 166, concerning telephone relay service;
c. the rights or obligations of any carrier under 47 U.S.C. § 251 or 47 U.S.C. § 252; or
d. the department’s authority to administer the federal Lifeline and Link-up programs or the Connect America Fund.
SECTION 2. Sections 11, 12, 12A, 13, 14 and 15 of Chapter 166 are hereby repealed.
The measure was discussed at a hearing this week before the Legislature’s Energy & Telecommunications Committee. Verizon argued its company is still regulated as if it was a monopoly, with reporting requirements and customer service mandates that do not apply to its competitors in the cable or wireless industry.

DiNatale
“We have to answer a customer’s call within x number of seconds,” said Verizon spokesman Phil Santoro. “If we don’t, we get penalized. No other company that provides phone service has to do that. They’re all regulations that were formed when we were a monopoly, and they haven’t been changed.”
Verizon lobbyist Joe Zukowski told the Boston Business Journal Verizon is required to respond to repair calls within a 24-hour window, something not required of its biggest competitor Comcast. Verizon has to report its annual finances and various customer metrics governing response times and outages to state regulators. Verizon also has to offer landline service anywhere in its service area across most of the state, while cable companies can pick the places they wish to serve.
DiNatale regularly supports Verizon’s legislative initiatives. In 2012, he proposed a bill to amend state law to remove the authority of the Department of Telecommunications and Cable to regulate the wireless industry, deferring instead to federal regulations that industry representatives said would level the playing field.
DiNatale suggested Massachusetts could be left behind if the legislature didn’t adopt the measure. Rep. Randy Hunt, a Sandwich Republican, asked if Massachusetts had missed out on any innovations in technology because of overregulation. Zukowski suggested a Massachusetts legislature hostile to business interests would make the company think twice about expanding its 4G LTE network in the state. By November, the bill was effectively buried in a legislative maneuver and by June 2013, Verizon announced it largely completed its 4G LTE upgrade, regardless of the bill.
DiNatale’s latest bill includes last year’s wireless oversight ban as well as forbidding the Department of Telecommunications and Cable from regulating Verizon in any part of the state where at least one provider of any kind offers competitive service.
Despite DiNatale’s attempt to ban state regulation of wireless service, Sen. Karen Spilka (D-Ashland), argued at Tuesday’s hearing for (S 1617), “The Cellphone User’s Bill of Rights,” that would require clearly published prices and service policies, monitors the quality of cell service in the state, and limits all cell contracts to 12 months.
“Many people don’t have landline phones anymore. However, as wireless subscribership increases, so do complaints about the contracts and services,” Spilka told the committee.
Zukowski suggested that rural areas will still be covered by regulation where Verizon maintains a monopoly. But the legislation eliminates regulation from any part of the state where even one competitor promises to provide service. AT&T Mobility alone would give Verizon an effective way out of regulatory oversight, because AT&T claims it already provides solid service to the majority of the state.
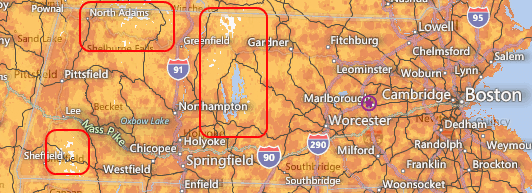
AT&T Mobility claims its competing cell service is available across almost the entire state of Massachusetts. The areas boxed in red are the only significant parts of the state without claimed coverage by AT&T.
There are only about three dozen or so towns in the state with no cable voice service, and even fewer with significant sections that have no cell phone service, all in the sparsely populated rural central and western parts of the state.
Other key components of this and another bill Verizon is supporting this term:
- Verizon would end its commitment to provide universal service in the state. Under the terms of the bill, Verizon could also justify ceasing rural landline service and offer an alternative such as Voice Link, a wireless landline replacement not subject to state oversight;
- Verizon would not have to report finances and customer service metrics and would no longer have to meet mandated customer service standards;
- State authority to compel reliable E911 service without any charge to the calling party and mandates regarding service for the disabled are weakened or eliminated;
- Elimination of a requirement providing Verizon customers with 10 free directory assistance calls per month, unless the customer is certified as elderly or disabled;
- Impose clear terms that wireless service is off-limits to state regulators.
The bill is co-sponsored by: Rep. Stephen Kulik (D-Worthington), Sen. Anthony Petruccelli (D-East Boston), Rep. Kathi-Anne Reinstein (D-Revere), and Sen. Sal DiDomenico (D-Everett).
 A joint venture between Verizon, Comcast, and Time Warner Cable to explore the development of innovative new services delivered across cable and wireless networks has been terminated, according to Fran Shammo, Verizon’s chief financial officer.
A joint venture between Verizon, Comcast, and Time Warner Cable to explore the development of innovative new services delivered across cable and wireless networks has been terminated, according to Fran Shammo, Verizon’s chief financial officer.

 Subscribe
Subscribe A new research report issued by Time Warner Cable concludes cell phone companies like AT&T and Verizon Wireless cannot meet the future data demands of customers over their 4G LTE wireless networks without punitive usage caps and high fees to deter usage, even with new spectrum becoming available for the wireless industry’s use.
A new research report issued by Time Warner Cable concludes cell phone companies like AT&T and Verizon Wireless cannot meet the future data demands of customers over their 4G LTE wireless networks without punitive usage caps and high fees to deter usage, even with new spectrum becoming available for the wireless industry’s use. “Given a choice, more than 80 percent of tablet, laptop, and eReader owners would either prefer Wi-Fi to mobile access, or have no preference,” Cisco concluded. “And, just over half of smartphone owners would prefer to use Wi-Fi, or are ambivalent about the two access networks.”
“Given a choice, more than 80 percent of tablet, laptop, and eReader owners would either prefer Wi-Fi to mobile access, or have no preference,” Cisco concluded. “And, just over half of smartphone owners would prefer to use Wi-Fi, or are ambivalent about the two access networks.”
 A sweeping deregulation measure sponsored by Verizon Communications would end the telephone company’s obligation to provide landline service and remove state-mandated customer quality of service standards in Massachusetts.
A sweeping deregulation measure sponsored by Verizon Communications would end the telephone company’s obligation to provide landline service and remove state-mandated customer quality of service standards in Massachusetts.

 Comcast
Comcast 
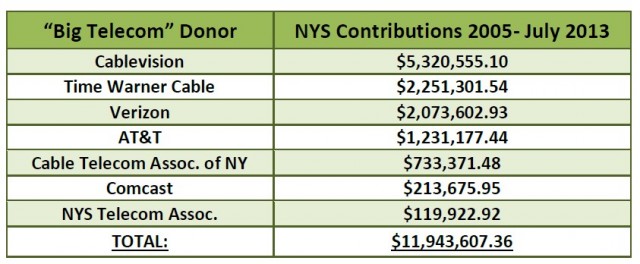 Since 2005, five cable and telephone companies and their respective lobbying trade associations have donated nearly $12 million to New York politicians, making Big Telecom companies among the biggest political donors in the state. Now a government reform group wants an investigation by the state’s anti-corruption commission.
Since 2005, five cable and telephone companies and their respective lobbying trade associations have donated nearly $12 million to New York politicians, making Big Telecom companies among the biggest political donors in the state. Now a government reform group wants an investigation by the state’s anti-corruption commission.
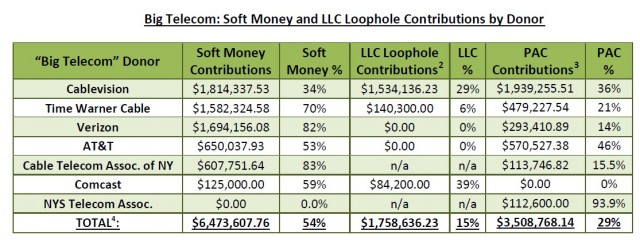
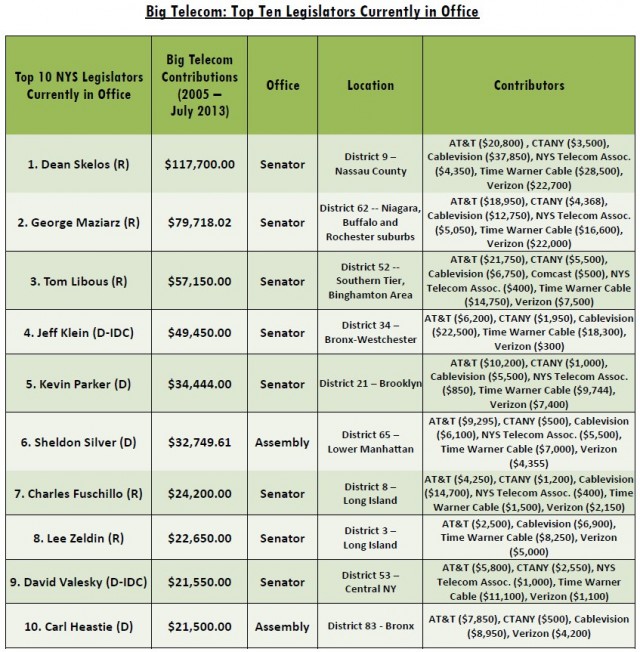
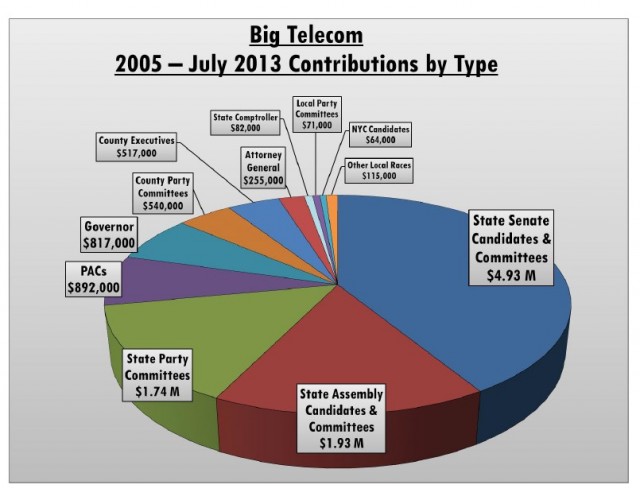 Where does all the money go?
Where does all the money go?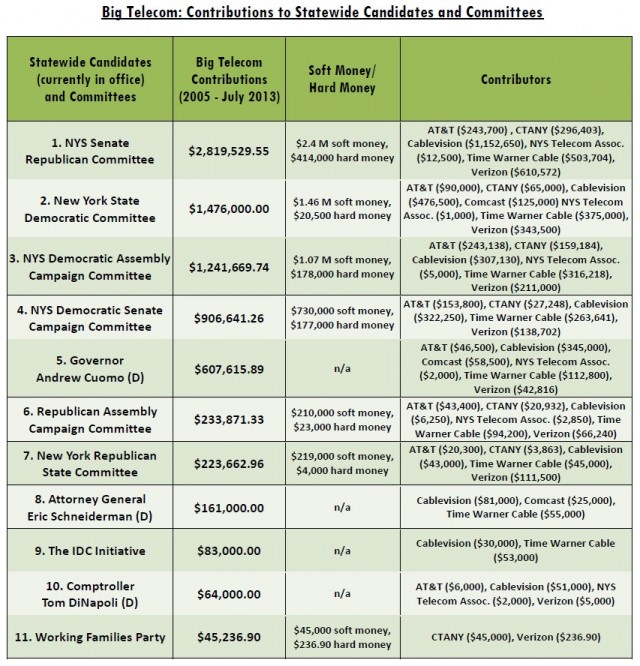
 A 7635-A / S5630-A: Establishes a moratorium on telephone corporations on the replacement of landline telephone service with a wireless system.
A 7635-A / S5630-A: Establishes a moratorium on telephone corporations on the replacement of landline telephone service with a wireless system.
 A6003/S5577 — Directs the Department of Public Service to study and report on the current status of cable television systems providing services over fiber optic cables.
A6003/S5577 — Directs the Department of Public Service to study and report on the current status of cable television systems providing services over fiber optic cables.
