
AT&T is a frequent backer of anti-community broadband initiatives, as are some of the nation’s biggest cable companies.
The Kansas Senate’s Commerce Committee has introduced a bill that would make it next to impossible to build publicly owned community broadband networks that could potentially compete against the state’s largest cable and phone companies.
Senate Bill 304 is the latest in a series of measures introduced in state legislatures across the country to limit or prohibit local communities from building better broadband networks that large commercial providers refuse to offer.
SB 304 is among the most protectionist around, going well beyond the model bill produced by the corporate-backed American Legislative Exchange Council (ALEC). At its heart, the bill bans just about any would-be competitor that works with, is run by, or backed by a local municipality:
Sec. 4. Except with regard to unserved areas, a municipality may not, directly or indirectly offer or provide to one or more subscribers, video, telecommunications or broadband service; or purchase, lease, construct, maintain or operate any facility for the purpose of enabling a private business or entity to offer, provide, carry, or deliver video, telecommunications or broadband service to one or more subscribers.
For purposes of this act, a municipality offers or provides video, telecommunications or broadband service if the municipality offers or provides the service:
- Directly or indirectly, including through an authority or instrumentality:
- Acting on behalf of the municipality; or for the benefit of the municipality;
- by itself;
- through a partnership, joint venture or other entity in which the municipality participates; or
- by contract, resale or otherwise.
Tribune, Kansas is the county seat of Greeley County.
This language effectively prohibits just about everything from municipally owned broadband networks, public-private partnerships, buying an existing cable or phone company to improve service, allowing municipal utilities to establish broadband through an independent authority, or even contracting with a private company to offer service where none exists.
The proposed legislation falls far short of its intended goals to:
- Ensure that video, telecommunications and broadband services are provided through fair competition;
- Provide the widest possible diversity of sources of information, news and entertainment to the general public;
- Encourage the development and widespread use of technological advances in providing video, telecommunications and broadband services at competitive rates and,
- Ensure that video, telecommunications and broadband services are each provided within a consistent, comprehensive and nondiscriminatory federal, state and local government framework.
Proponents claim the bill is open to allowing municipalities to build broadband services in “unserved areas.” But upon closer inspection, the bill’s definition of “unserved” is practically impossible to meet anywhere in Kansas:
“Unserved area” means one or more contiguous census blocks within the legal boundaries of a municipality seeking to provide the unserved area with video, telecommunications or broadband service, where at least nine out of 10 households lack access to facilities-based, terrestrial broadband service, either fixed or mobile, or satellite broadband service, at the minimum broadband transmission speed as defined by the FCC.
Even the FCC does not consider satellite broadband service when it draws maps where broadband is unavailable. But this Big Telecom-backed bill does. Even worse, it requires would-be providers to prove that 90 percent of customers within a “census block” don’t have access to either mobile or satellite broadband. Since satellite Internet access is available to anyone with a view of the southern sky, and the most likely unserved customers would be in rural areas, it would be next to impossible for any part of the notoriously flat and wide open state to qualify as “unserved.”
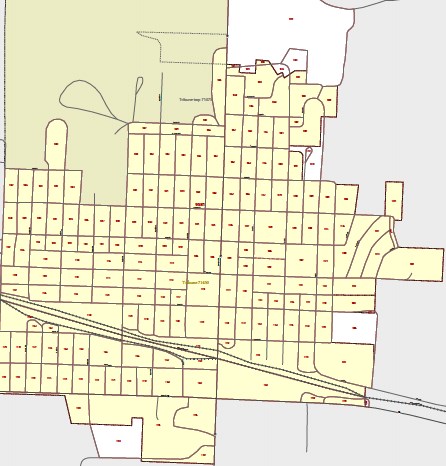
Each rectangle represents one “census block” within a larger “census tract” that partially covers Greeley County. Under the proposed legislation, a community provider would have to visit each census block to verify whether a private company is capable of providing broadband service, including satellite Internet access.
To illustrate, Stop the Cap! looked at Greeley County in western Kansas. The county’s total population? 1,247 — the smallest in the state. Assume Greeley County Broadband, a fictional municipal provider, wanted to launch fiber broadband service in the area. Under the proposed bill, the largest potential customer base is 1,247 — too small for most private providers. Still, if a private company decided to wire up the county, it could with few impediments, assuming investors were willing to wait for a return on their investment in the rural county. If SB 304 became law, a publicly owned broadband network would have to do much more before a single cable could be installed on a utility pole.
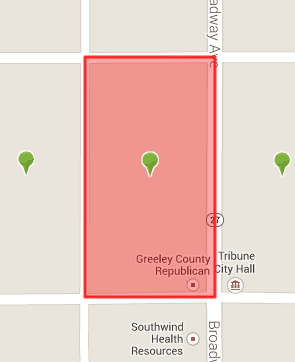
Census Block 958100-1-075, in downtown Tribune, has a population of 10.
To open for business, Greeley County Broadband would have to spend tens of thousands of dollars to independently verify its intended service area — the county — is unserved by any existing broadband technology, including satellite and mobile broadband. The authors of the bill intentionally make that difficult. Just one census tract in Greeley County (#9561), encompassing the county seat town of Tribune (pop. 741) has dozens of census blocks. Some are populated, others are not.
Greeley County Broadband now has several big problems. Under the language in the bill, a municipal provider must first define its service area entirely within its borders — in this case Greeley County — and base it on contiguous census blocks. That means if pockets of qualifying potential customers exist in a census block surrounded by non-qualifying census blocks, Greeley County Broadband cannot include them in its service area.
Census Block 958100-1-075 — essentially at the intersection of Broadway Ave. and West Harper St., right next to City Hall — has a population of 10. AT&T Mobility’s coverage maps show Tribune is covered by its 3G wireless data network (but not 4G). That census block, along with every other in the area, would be disqualified from getting municipal broadband the moment AT&T upgrades to 4G service, whether reception is great or not. It doesn’t matter that customers will have to pay around $60 for a handful of gigabytes a month.
But wait, Verizon Wireless declares it already provides 4G LTE service across Greeley County (and almost all Kansas). So Greeley County Broadband, among other would-be providers, are out of business before even launching. Assuming there was no 4G service, if just two of those ten residents had a clear view to any satellite broadband provider, Greeley County Broadband would not be permitted to provide anyone in the census block with service under the proposed law. Under these restrictions, no municipal provider could write a tenable business plan, starved of potential customers.
Kansans need to consider whether that is “fair competition” or corporate protectionism. Is it a level playing field to restrict one provider without restricting others? If competition promotes investment in technologically challenged rural Kansas, would not more competition from municipal providers force private companies to finally upgrade their networks to compete?
In fact, the bill introduced this week protects incumbent cable and phone companies from competition and upgrades by keeping out the only likely competition most Kansans will ever see beyond AT&T, Comcast, or CenturyLink’s comfortable duopoly – a municipal or community-owned broadband alternative. Providing the widest possible diversity is impossible in a bill that features the widest possible definition of conditions that will keep new entrants out of the market. Community-owned networks usually offer superior technology (often fiber optics) in communities that are usually trapped with the most basic, outdated services. While the Kansas legislature coddles AT&T, that same company wants to mothball its rural landline network pushing broadband-starved customers to prohibitively expensive, usage capped wireless broadband service indefinitely.

Seeing Big Red? The areas colored dark red represent the claimed coverage of Verizon Wireless’ 4G LTE network in Kansas. Under SB 304, these areas would be prohibited from having a community-owned broadband alternative.


 Subscribe
Subscribe Comcast Corporation and Charter Communications are actively working on a deal to let Comcast acquire Time Warner Cable subscribers in New York, New England, and North Carolina, according to sources
Comcast Corporation and Charter Communications are actively working on a deal to let Comcast acquire Time Warner Cable subscribers in New York, New England, and North Carolina, according to sources  Comcast’s involvement in the deal could inject much-needed cash into a takeover bid financed largely by debt. It might also prompt Charter to sweeten its offer for TWC.
Comcast’s involvement in the deal could inject much-needed cash into a takeover bid financed largely by debt. It might also prompt Charter to sweeten its offer for TWC. Comcast is likely getting into the electricity business in Pennsylvania, offering customers a “quad play” bundle of Internet, telephone, television, and electricity service with discounts for one or more services.
Comcast is likely getting into the electricity business in Pennsylvania, offering customers a “quad play” bundle of Internet, telephone, television, and electricity service with discounts for one or more services.
 The state of Texas is the largest deregulated power market in the country, where hundreds of suppliers compete in the retail energy market. Pennsylvania
The state of Texas is the largest deregulated power market in the country, where hundreds of suppliers compete in the retail energy market. Pennsylvania  Verizon FiOS expansion is still dead while cash cow Verizon Wireless will continue to get the bulk of Verizon’s attention this year, according to a top executive.
Verizon FiOS expansion is still dead while cash cow Verizon Wireless will continue to get the bulk of Verizon’s attention this year, according to a top executive. Again this year, Verizon Wireless will get the bulk of Verizon’s attention and financial resources. Verizon Wireless finished 2013 with $81 billion in wireless revenue — up $5.2 billion from 2012 — which represents two-thirds of Verizon’s total earnings. The wireless business has delivered a profit margin of 49% or higher for five of the last seven quarters.
Again this year, Verizon Wireless will get the bulk of Verizon’s attention and financial resources. Verizon Wireless finished 2013 with $81 billion in wireless revenue — up $5.2 billion from 2012 — which represents two-thirds of Verizon’s total earnings. The wireless business has delivered a profit margin of 49% or higher for five of the last seven quarters.


