Despite assurances from FCC Chairman Ajit Pai that the repeal of net neutrality would inspire cable operators to increase investment in broadband, a year-long virtual spending freeze by the nation’s top cable operators has resulted in a major vendor pulling out of the next generation cable broadband standard until there are signs cable companies are prepared to spend money on upgrades again.
Despite assurances from FCC Chairman Ajit Pai that the repeal of net neutrality would inspire cable operators to increase investment in broadband, a year-long virtual spending freeze by the nation’s top cable operators has resulted in a major vendor pulling out of the next generation cable broadband standard until there are signs cable companies are prepared to spend money on upgrades again.
Cisco Systems has confirmed to Light Reading it has ceased investment in Full Duplex DOCSIS technology that would allow cable customers to get the same upload speed as download speed.
“Cisco has internally communicated that we are suspending further investment in Full Duplex DOCSIS (FDX) until the market timing, ecosystem development and size of the opportunity can be quantified,” a Cisco spokesperson said in a statement to Light Reading.
The news is a significant blow to the cable industry’s plans to upgrade to 10 Gbps capacity and a growing desire by customers to get much faster upload speeds than are currently available.
Cisco blamed its pullback on the cable industry’s lack of investment in broadband upgrades and an uncertain timetable when major cable companies including Comcast, Charter, Cox, and others will announce specific plans for future upgrades.
 FDX has already been the victim of delays. Originally planned as an incremental upgrade for DOCSIS 3.1, FDX is now scheduled to be included in CableLabs’ DOCSIS 4.0 specification, which is not expected to be released for a few years. FDX will be one of several new features incorporated into the next cable broadband standard, which will allow for low latency connections and an expanded amount of coaxial cable spectrum that can be devoted to broadband services.
FDX has already been the victim of delays. Originally planned as an incremental upgrade for DOCSIS 3.1, FDX is now scheduled to be included in CableLabs’ DOCSIS 4.0 specification, which is not expected to be released for a few years. FDX will be one of several new features incorporated into the next cable broadband standard, which will allow for low latency connections and an expanded amount of coaxial cable spectrum that can be devoted to broadband services.
The cable industry has been taking a sober look at the costs associated with adopting FDX, which includes scrapping a significant amount of coaxial cable and pushing fiber optic technology much closer to customers. Cable systems that want to move towards FDX will have to remove amplifiers that maintain signal strength between the fiber optic connection and the coaxial cable entering customers’ homes. In some cases, this will mean removing multiple amps from the cable system and stringing new fiber optic cables deep into neighborhoods. This is known as node+0 architecture. Moving towards node+0 is expected to be both costly and labor intensive, and some large cable systems and investors are balking.
“There are a lot of operators who have no intention of getting to a node+0 environment in next 10 years,” Tom Cloonan, chief technical officer of Arris’ Networks Solutions unit, told Multichannel News last fall. “It’s going to take a while to run fiber deep enough to get to node+0.”
To date, the only major cable operator that has definitively backed moving to node+0 is Comcast. Other cable companies, notably Cox Communications, are seeking a much cheaper solution to manage upgrades.
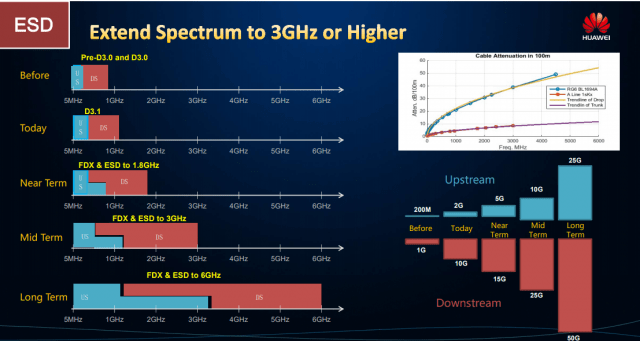
Extended Spectrum DOCSIS (ESD)
Image courtesy of: Huawei
An emerging alternative concept has emerged that can be implemented at a lower cost. Extended Spectrum DOCSIS (ESD) would essentially repurpose much of the bandwidth available over a coaxial cable solely to broadband service. DOCSIS 3.1 currently dedicates 1.2 GHz of spectrum for broadband. FDX would increase that to more than 1.8 GHz. ESD would devote as much as 3 (or possibly 6) GHz of spectrum for data transmissions. The cable system would devote as much as half of that spectrum for downstream traffic, the other half for upstream. Theoretical speeds in the future could be as high as 60 Gbps, and ESD will not require cable systems to ditch existing amplifiers. It will, however, force some cable systems to evaluate and replace at least part of their older coaxial cable network. ESD will be less forgiving of deteriorating cable than DOCSIS 3.1 is.
Unfortunately for Cisco, and other cable broadband equipment suppliers, ESD is still more theory than fact, and with cable operators demonstrating they are in no rush to move to either FDX or ESD, it will likely be several years before either technology becomes available to customers. Cloonan predicts ESD will not be implemented by cable systems until the mid-2020s.
The muddy waters over where the cable industry will ultimately plant the flag on next generation broadband upgrades means a lot of uncertainty for companies like Cisco, which has resulted in the company pulling out of developing FDX until there are assurances the cable industry has a timetable to implement it. The decision has also cost several Cisco employees their jobs. Multiple industry sources told Light Reading job cuts included 5-7 engineers dedicated to FDX, and some sources also report at least 40 employees in the cable access division of Cisco have also been let go.
If certainty does not return to the cable broadband market soon, Cisco could ultimately jettison much of its cable broadband technology division to focus on other technology growth areas.
The cable industry’s investment freeze is ironic because the Trump Administration’s FCC trumpeted its decision to repeal net neutrality, claiming it would inspire cable operators to accelerate investment in network upgrades. It appears the exact opposite has occurred.


 Subscribe
Subscribe
 A
A