Charter Communications has introduced internet-delivered cable television packages that its cable TV subscribers have requested for years, including one offering a true a-la-carte lineup of network TV channels and the customer’s choice of 10 cable channels for $25 a month.
Spectrum Choice was soft-launched this week and is a companion to a larger internet-delivered package of TV services targeting cord-cutters called Spectrum Stream, which is also available in many areas.
 Although Spectrum customers can visit the order page to sign up for Spectrum Choice immediately, when we tested it this afternoon we found the website was not able to complete an order. It turns out Spectrum is initially “hand-selecting” about 100,000 customers in selected areas for Spectrum Choice, but won’t disclose exactly where those areas are. We know from some reviews, it is available in parts of Ohio.
Although Spectrum customers can visit the order page to sign up for Spectrum Choice immediately, when we tested it this afternoon we found the website was not able to complete an order. It turns out Spectrum is initially “hand-selecting” about 100,000 customers in selected areas for Spectrum Choice, but won’t disclose exactly where those areas are. We know from some reviews, it is available in parts of Ohio.
For now, would-be customers can try building their own package from at least 65 cable networks, including several networks Spectrum usually bundles into higher cost Silver and Gold packages. For example, Turner Classic Movies, Hallmark Movies and Mysteries, and FX Movie Channel are all available to choose. Spectrum Choice also offers all three major cable news networks as well as Spectrum News (where available). ESPN, ESPN II, FOX Sports, NBC Sports Network, and NFL Network are also available for sports fans. Even Music Choice is included.
Spectrum Choice customers are not tied down with a bloated package of channels, except for the included large bundle of local stations, which includes ABC, CBS, NBC, FOX, CW, MyNetworkTV, PBS, and independent/foreign language over the air stations. The availability of public television is a rarity among online cable TV alternatives. In most areas, digital subchannels like Grit and MeTV are also included, depending on what networks are provided by stations in your area. You will also get several shopping channels, C-SPAN I, II, and III, and local Public, Educational, and Government Access channels as seen on your local cable system.
If you visit their website can complete an order online, you are qualified to receive their service. If there is no option to move forward to complete an order, you are not qualified to sign up at this time, but check back later or call Spectrum and ask.
The service relies on the Spectrum TV app (available on iOS, Android, Roku, and Xbox One) and the Spectrum website to stream video programming to customers, and no set-top box is required. DVR service is not worth the effort or cost. It requires a traditional DVR set top box and you can only watch recorded shows on the television connected to the DVR. Be aware there are also restrictions viewing some channels outside of the home, just as Spectrum’s cable TV customers already understand:
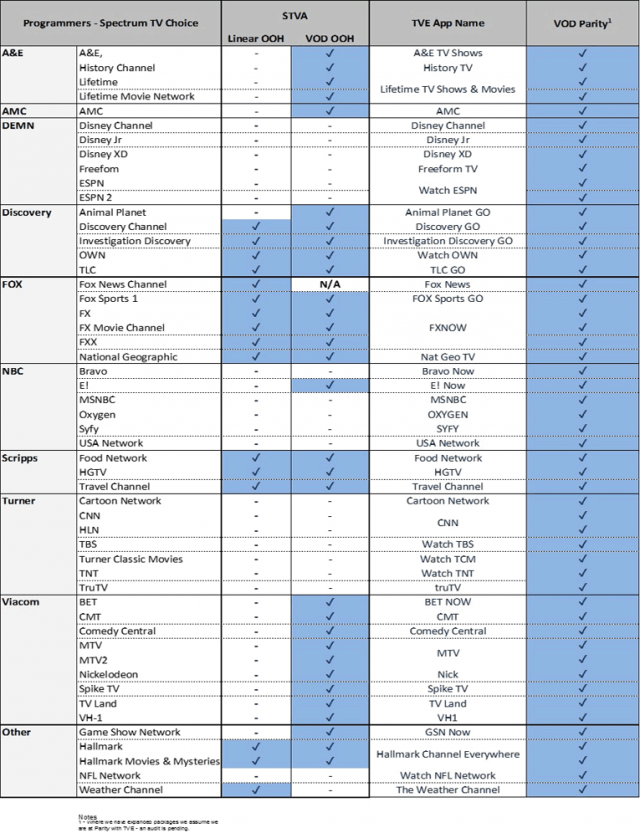
Linear OOH: Watching a live channel while away from home
VOD OOH: Watching on-demand content while away from home
TVE App Name: TV Everywhere App Name – Independent apps used by programmers or viewing on their websites
VOD Parity: Cable TV and Spectrum Choice customers get access to the same on-demand programming options.
Details (click the name of the package for more information):
- 7-day money back guarantee/trial, then $15 for the first month
- To get the service, you must have an internet-only plan or an internet + voice plan from Spectrum. You cannot be a current traditional cable TV subscriber
- After the first month, the service costs $25 per month for the first two years, including the Broadcast TV Surcharge, but excluding tax
- After 24 months, price increases to $30 a month
- Your assigned Spectrum TV username and password will also work on websites that authenticate you as a qualified cable TV customer
- Premium channels are $7.50 each for HBO, Showtime, The Movie Channel, Starz, and Starz Encore or bundle all-five for $15 a month for two years. Epix is also available a-la-carte.

If you don’t mind Charter/Spectrum choosing your channel lineup, a second option offers more channels for about the same price.
- $21.99 a month (not including $3 Broadcast TV Surcharge) for 25+ pre-selected channels including local stations and major basic cable networks
- All features included with Choice TV work similarly except the lineup is not a-la-carte. But you may get more channels at a comparable price.
- After two years, the price increases to $26.99. Starting in year three, the price rises again to $34.99.
- The same $15 promotion for five premium movie networks noted above applies, if interested.
Spectrum’s promotion of Stream TV. (1:00)


 Subscribe
Subscribe Charter Communications will have to face a courtroom to answer accusations the cable company intentionally sold internet service at speeds it knew it could not provide to its customers in New York.
Charter Communications will have to face a courtroom to answer accusations the cable company intentionally sold internet service at speeds it knew it could not provide to its customers in New York.
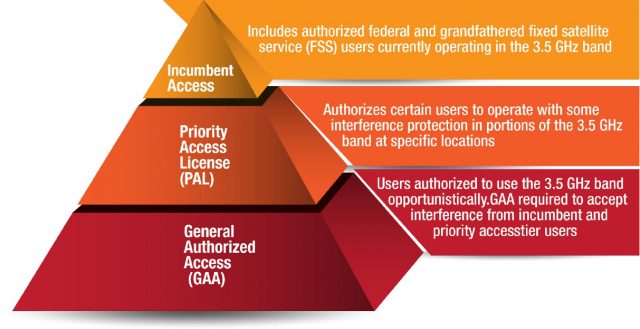
 Charter is proposing to license PALs based on county lines, not PEAs, which will likely reduce the costs of licensing and, in Charter’s view, will “attract interest and investment from new entrants to small and large providers.” If Charter’s proposal is adopted, its costs deploying small cell technology used with CBRS will be much lower, because it will not have to serve larger geographic areas.
Charter is proposing to license PALs based on county lines, not PEAs, which will likely reduce the costs of licensing and, in Charter’s view, will “attract interest and investment from new entrants to small and large providers.” If Charter’s proposal is adopted, its costs deploying small cell technology used with CBRS will be much lower, because it will not have to serve larger geographic areas.
 So Mrs. Peartree and Spectrum are at an impasse. She took her plight to a local talk radio show and
So Mrs. Peartree and Spectrum are at an impasse. She took her plight to a local talk radio show and 
 Charter did not restart its digital television conversion program until June of 2017, and 30% of Time Warner Cable and 50% of Bright House Networks customers are still watching analog cable television as a result. Company officials promise digital conversion will be completed nationwide by the end of this year, the first step the company will take to make dramatic broadband speed increases possible.
Charter did not restart its digital television conversion program until June of 2017, and 30% of Time Warner Cable and 50% of Bright House Networks customers are still watching analog cable television as a result. Company officials promise digital conversion will be completed nationwide by the end of this year, the first step the company will take to make dramatic broadband speed increases possible.