One of the rural groups fighting to keep funding for rural broadband networks.
The Republican platform on telecommunications and its criticism of the Obama Administration’s handling of broadband inspired a blogger at the Washington Post to ponder the question, “Whatever happened to Obama’s goal of universal broadband access?”
Brad Plumer sees the Republican criticism as valid, at least on the surface:
Does anyone remember when the Obama administration promised to bring “true broadband [to] every community in America”? The Republican Party definitely does, and its 2012 platform criticizes the president for not making any progress on this pledge:
“The current Administration has been frozen in the past…. It inherited from the previous Republican Administration 95 percent coverage of the nation with broadband. It will leave office with no progress toward the goal of universal coverage—after spending $7.2 billion more. That hurts rural America, where farmers, ranchers, and small business manufacturers need connectivity to expand their customer base and operate in real time with the world’s producers.
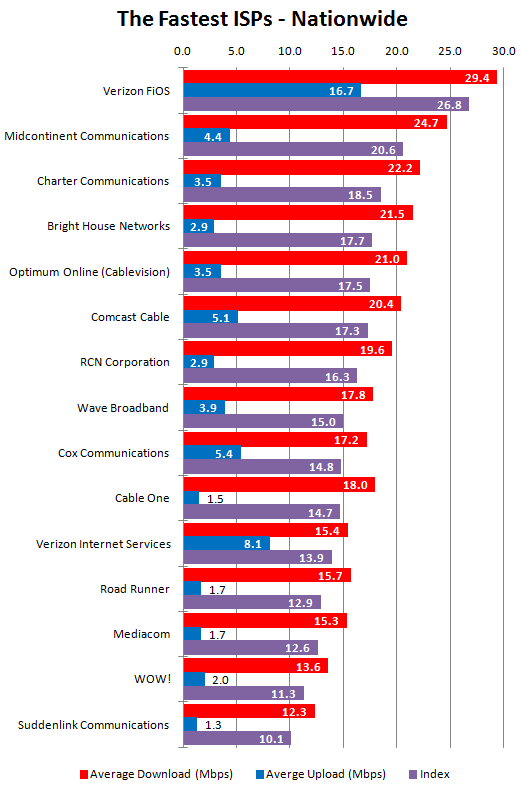
So whatever happened to the Obama administration’s plan to expand broadband access, anyway? In one sense, the Republican critics are right. Universal broadband is still far from a reality. According to the Federal Communications Commission’s annual broadband report, released in August, there are still 19 million Americans who lack access to wired broadband. Only about 94 percent of households have broadband access. Obama hasn’t achieved his goal.
Stop the Cap! has been watching the rural broadband debate since the summer of 2008, and believes the failure to do better isn’t primarily the fault of Republicans or Democrats — it lies with the nation’s phone companies — particularly AT&T and Verizon. But both political parties, to different degrees, have helped and hindered along the way.
Plumer slightly misstates the commitment of the Obama Administration at the outset. The Obama-Biden Plan never promised to successfully complete universal broadband access in the United States. Here is their actual pledge (emphasis ours):
Deploy Next-Generation Broadband: Work towards true broadband in every community in America through a combination of reform of the Universal Service Fund, better use of the nation’s wireless spectrum, promotion of next-generation facilities, technologies and applications, and new tax and loan incentives. America should lead the world in broadband penetration and Internet access.
Big Phone Companies Struggle to Abandon Landlines in Rural America

The Obama-Biden Plan for broadband never promised you a rose garden. It simply promised the administration would get to work planting one.
By far, AT&T and Verizon Communications are the most culpable for leaving rural Americans without broadband service. Over the last four years, both companies have diverted investment away from their landline networks into wireless. AT&T has also spent millions lobbying state governments to free itself from the requirement of serving as “the carrier of last resort,” a critical matter for rural landline customers, particularly because rural wireless coverage remains lacking.
In most states, the dominant phone company is still mandated to provide basic telephone service to every customer who wants it. Universal electric and telephone service goes all the way back to the Roosevelt Administration, who saw both as essential to the rural economy.
The Communications Act of 1934 that the Republicans today dismiss as outdated established the concept of universal telephone service: “making available, so far as possible, to all the people of the United States a rapid, efficient, nationwide and worldwide wire and radio communication service with adequate facilities at reasonable charges.”
The concept of universal service was reaffirmed, with the blessing of the telephone companies, under the sweeping deregulation of the landmark Telecommunications Act of 1996. Republicans call that law outdated as well.
Rural America Can’t Win Better Broadband If Their Providers Don’t Play

Decided not to participate in rural broadband funding programs.
The American Recovery and Reinvestment Act provided the Department of Commerce’s National Telecommunications and Information Administration (NTIA) and the U.S. Department of Agriculture’s Rural Utilities Service (RUS) with $7.2 billion to expand access to broadband services in the United States. Of those funds, the Act provided $4.7 billion to NTIA to support the deployment of broadband infrastructure, enhance and expand public computer centers, encourage sustainable adoption of broadband service, and develop and maintain a nationwide public map of broadband service capability and availability.
This first round of serious broadband stimulus was designed to help defray the costs of bringing broadband to rural areas where “return on investment” formulas used by large phone companies deemed them insufficiently profitable to service.
Remarkably, America’s largest phone companies declined to participate. In March 2009, AT&T and Verizon delivered their response to the Obama Administration through Bloomberg News:
Verizon Communications Inc. and AT&T Inc. may have this response to the U.S. government’s offer of $7.2 billion for high-speed Internet projects: Keep it.
Unlike the businesses that welcomed the $787 billion stimulus package approved by Congress last month, the two biggest U.S. phone companies have reservations. They’re urging the government not to help other companies compete with them through broadband grants or to set new conditions on how Internet access should be provided.
The companies have remained noncommittal as they lobby to shape rules for the grants.
“We do not have our hand out seeking government funds,” James Cicconi, AT&T’s senior executive vice president, told reporters March 11. While the company is “open to considering things that might help the economy and might help our customers at the same time,” he said AT&T’s primary focus for broadband is its own investment program.

Also declined to participate.
AT&T’s own financial reports illustrate its “investment program” was largely focused on its wireless services division, not rural broadband. Many other phone companies filed objections to projects they deemed invasive to their service areas, whether they actually provided broadband in those places or not.
When the final NTIA grant recipients were announced, the overwhelming majority were middle-mile or institutional broadband networks that would not provide broadband to any home or business.
The U.S. Department of Agriculture’s Rural Utilities Service managed the rest of the broadband grants and loans, and the majority went to exceptionally rural telephone companies, co-ops, and tribal telecommunications. AT&T did participate in one aspect of broadband stimulus — its legal team and lobbyists appealed to grant administrators to change the rules to be more flexible about how and where grant money was spent.
In the past year, both AT&T and Verizon have signaled their true intentions for rural landline service:

Verizon’s McAdam: Ready to pull the plug on rural landlines.
Verizon CEO Lowell McAdam: “In […] areas that are more rural and more sparsely populated, we have got [a wireless 4G] LTE built that will handle all of those services and so we are going to cut the copper off there,” McAdam said. “We are going to do it over wireless. So I am going to be really shrinking the amount of copper we have out there and then I can focus the investment on that to improve the performance of it.”
AT&T CEO Randall Stephenson: “We have been apprehensive on moving, doing anything on rural access lines because the issue here is, do you have a broadband product for rural America?,” Stephenson told investors earlier this year. “And we’ve all been trying to find a broadband solution that was economically viable to get out to rural America and we’re not finding one to be quite candid.”
More recently, Verizon has nearly disinherited its DSL service, making it more difficult to purchase (impossible in FiOS fiber to the home service areas). In states like West Virginia, it effectively slashed expansion and infrastructure investment as it prepared to exit the state, selling its network to Frontier Communications. AT&T has shown almost no interest expanding the coverage of its DSL service either. If you don’t have access to it today, you likely won’t tomorrow.
A good portion of the broadband stimulus funding provided by the government is actually in the form of low-interest, repayable loans. Despite rhetoric in the Republican platform about supporting public-private partnerships to expand rural broadband, the Republicans in Congress launched coordinated attacks on the Broadband Access Loan Program offered by the USDA’s Rural Utilities Service in the spring of 2011. Various right-wing pundits and pressure groups joined forces with several Republican members of Congress attempting to permanently de-fund the program, starting with $700 million in federally-backed loans in April, 2011. The loans were targeted to public and private rural telecommunications companies attempting to expand or introduce broadband service.
Attacks on the effectiveness of President Obama’s broadband campaign pledges in the Republican platform ring a little hollow when Republican lawmakers actively blocked the administration’s efforts to keep those promises.
Killing Community Broadband: Priority #1 for Providers With the Help of Corporate-Backed ALEC and State Politicians

AT&T’s Stephenson: Doesn’t have a solution for the rural broadband problem, so why try?
Stop the Cap! has repeatedly reported on the challenges of community broadband in the United States. Launched by towns and villages to provide quality broadband service in areas where larger companies have either underserved or delivered no service at all, publicly-owned broadband is often the only chance a community has to stay competitive in the digital age.
That goal is shared by the GOP’s platform, which states how important it is to connect “rural areas so that every American can fully participate in the global economy.”
Unfortunately, unless your local phone or cable company is providing the service, all too often they would prefer communities continue to receive no service at all.
AT&T is among the most aggressive phone companies lobbying state officials, often through the American Legislative Exchange Council (ALEC), to pass state laws hindering or banning community broadband development. ALEC supporters, overwhelmingly Republican, accept company-drafted legislation as their own and introduce it in state legislatures, hoping it will become law. Generous campaign contributions often follow.
In the past few years, AT&T and Time Warner Cable have been especially active in broadband backwater states like North and South Carolina and Georgia, where rural counties often receive nothing more than DSL service at speeds that no longer qualify as “broadband” under the Obama Administration’s National Broadband Plan. In North Carolina, Democratic state politicians well funded by Time Warner Cable helped push bills forward, but it took a Republican takeover of the North Carolina legislature to finally get those laws enacted. South Carolina presented fewer challenges for state lawmakers, despite protests from communities across the state bypassed by AT&T and other phone companies.
The efforts to de-fund broadband stimulus and tie the hands of communities seeking their own broadband solutions have done considerable damage to the rural broadband expansion effort.
Universal Service Fund Reform: Not Much Help If America’s Largest Phone Companies Remain Uninterested
The Obama Administration has also kept its pledge to reform the Universal Service Fund, recreating it as the Connect America Fund (CAF) to help wire rural America.

Hopes for rural broadband drowned in the cement pond.
In its first phase of broadband funding, $300 million dollars became available to help subsidize the cost of rural broadband construction. Deemed a “mild stimulus” effort that would test the CAF’s grant mechanisms, only $115 million of the available funding was accepted by the nation’s phone companies — all independent providers like Frontier, FairPoint, CenturyLink, Windstream, and smaller players. Once again, both AT&T and Verizon refused to participate. There is no word yet on whether the two largest phone companies in the country will also effectively boycott the second round of funding, estimated to allocate over $1.8 billion to expand rural broadband.
“Getting to 100 percent is going to be a very difficult long-term goal, given the size of the U.S. landmass and the huge expense to reach those final couple of percentage points,” John Horrigan of the Joint Center Media and Technology Institute told Brad Plumer.
Politics and provider intransigence seem to be getting in the way just as much as America’s vast expanse. Many conservative and provider-backed groups have called America’s claimed 94% broadband availability rate a success story, and don’t see a need to fuss over the remaining six percent that cannot buy the service (and pointing to a larger number that don’t want the service at today’s prices).
Beyond the partisan obstructionism and middle mile/institutional network “successes” that ordinary consumers cannot access, the real issue remains the providers themselves. You can lead a horse to water but you cannot make him drink.
It seems as long as AT&T and Verizon treat their rural landline customers as hayseed relatives they (and Wall Street) could do without, the rural broadband picture for customers of AT&T and Verizon will remain bleak at current stimulus levels regardless of which party promises what in their respective platforms.
 Colorado-based TW Telecom is up for sale and CenturyLink is now seen as a potential buyer, according to reports in mergers and acquisitions trade publication DealReporter, citing unnamed sources.
Colorado-based TW Telecom is up for sale and CenturyLink is now seen as a potential buyer, according to reports in mergers and acquisitions trade publication DealReporter, citing unnamed sources.

 Subscribe
Subscribe