
Coming soon nationwide? Comcast, Time Warner, AT&T and CenturyLink sure hope not.
Verizon is talking to major cable programmers about launching a nationwide version of FiOS TV as an over-the-top video service that works with your existing broadband provider.
The NY Post reports Verizon is looking at launching an online pay television service for customers without installing additional fiber optic lines to deliver it.
The service would likely be an extension of the “TV Everywhere” online video platforms that many national cable and telco-TV providers already offer existing cable TV subscribers. What would make Verizon’s offer radically different is selling the virtual cable TV service in areas where it does not offer FiOS service.
Verizon must carefully negotiate with programmers to distribute networks over an online video service that would likely compete directly with those programmers’ best customers: cable operators and telco IPTV services like U-verse and Prism TV.
The concept was rejected out of hand Wednesday by Time Warner Cable chief operating officer Rob Marcus, who agreed with Comcast executive vice president Steve Burke’s contention that “over the top” video services that offer virtual cable television outside of their respective service areas lacked a compelling business model and would be difficult to monetize.
“At this point we don’t really aspire to delivering an over-the-top service,” Marcus said. “Our value proposition is delivering video via our facilities as opposed to being a retailer of somebody else’s video, which is a somewhat commoditized product.”
Neither cable executive mentioned the fact cable operators have also maintained an informal “wink and nod” agreement to steer clear of head-on competition with each other for decades.

Verizon: The next big supporter of Net Neutrality?
Verizon apparently wants to shake things up and sell online video without incurring the cost of expanding its fiber optic network FiOS to deliver it.
“They’ve had exploratory talks about how to become a virtual [multiple-system operator],” one person close to the conversations told the Post. “It’s a question of how to get there.”
Interestingly, Verizon CEO Lowell McAdam is worried about developing the service without Net Neutrality protection or some other form of government oversight of broadband. Verizon could spend millions to negotiate programming contracts only to find competitors with their own TV packages to protect outmaneuvering the venture. Without Net Neutrality, Verizon could find its service blocked by competitors or made untenable with the implementation of broadband usage caps or consumption billing that would make a subscription too costly to consider.
The company is now trying to figure out exactly which branch of government (or agency) controls broadband policy in the nation.
The FCC’s current Net Neutrality policy depends on a shaky regulatory framework now being challenged in federal court.
Verizon declined to comment.


 Subscribe
Subscribe Nine of the ten lowest ranked firms in America are cable and telephone companies, according to a
Nine of the ten lowest ranked firms in America are cable and telephone companies, according to a 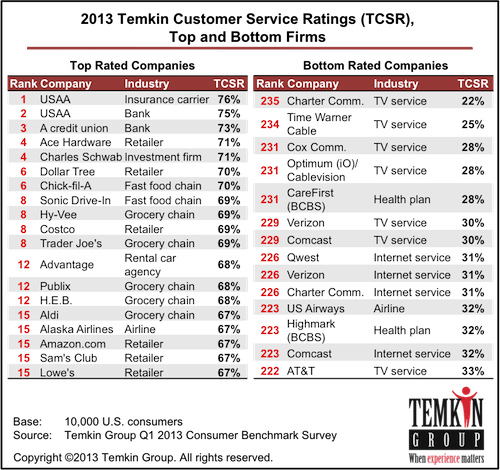


 Frontier Communications Northwest, Inc., has won an end to rate regulation, arguing sufficient competition exists between telecom companies in Washington State to make the oversight unnecessary.
Frontier Communications Northwest, Inc., has won an end to rate regulation, arguing sufficient competition exists between telecom companies in Washington State to make the oversight unnecessary.