The National Association of Broadcasters (NAB), a trade association and lobbying group representing many of the nation’s television stations, says claims by wireless carriers of a nationwide spectrum crisis are troubling and counterfactual. That conclusion comes in a new report issued by the NAB this morning that wants the FCC to keep its hands off UHF broadcast channel spectrum the agency wants to sell off to improve mobile broadband.
The paper, “Solving the Capacity Crunch: Options for Enhancing Data Capacity on Wireless Networks,” written by a former FCC employee, suggests claims by wireless carriers that they will “run out” of frequencies to serve America’s growing interest in wireless services are simply overblown.
Many wireless companies own spectrum they are not using, the report argues, and other licensed users are holding onto spectrum without using it either, hoping to make a killing selling it off at enormous profits in the future. Besides, the federal government holds the largest amount of underutilized spectrum around — frequencies that could easily be allocated to wireless use without further reducing the size of the UHF broadcast TV band.
Many of the ideas in the NAB report emphasize the need for carriers to deploy innovative technology solutions to increase the efficiency of the spectrum they are already using. Those ideas include additional cell towers to split traffic loads into smaller regional areas, and improving on network channel-bonding, caching, and intelligent network protocols.
But the NAB report has some obvious weak spots the wireless industry will likely exploit — notably their recommendations that seek a reduction in wireless traffic — ideas that would suggest there is not enough spectrum to handle every user. Among those recommendations:
- Implementing Internet Overcharging schemes like “fair use” policies and consumption-based pricing to discourage use;
- Migrating voice traffic to Internet Protocol;
- Migrating data traffic to a prolific network of “femtocells” — mini antennas that provide 3G service inside buildings, but deliver that traffic over home or business wired broadband connections;
- Offering wider access to Wi-Fi networks in public areas;
- Encouraging the development of bandwidth sensitive devices and applications.
 The National Broadband Plan’s conclusion of a spectrum shortage is based on little more than a wish list by wireless carriers, says the paper. Its author, Uzoma Onyeije, cites contradictory statements by high-ranking corporate officials to show the Plan’s calls for making 500MHz of spectrum available for broadband in ten years is a gross overestimate of the actual need.
The National Broadband Plan’s conclusion of a spectrum shortage is based on little more than a wish list by wireless carriers, says the paper. Its author, Uzoma Onyeije, cites contradictory statements by high-ranking corporate officials to show the Plan’s calls for making 500MHz of spectrum available for broadband in ten years is a gross overestimate of the actual need.
“There is no denying that the corporate imperative of mobile wireless carriers is to obtain as much spectrum as they can,” Onyeije wrote. “However, the fact that wireless carriers cannot find a unified voice on the amount and timing of their spectrum needs suggests that this advocacy is more strategic gamesmanship than factual reality.”
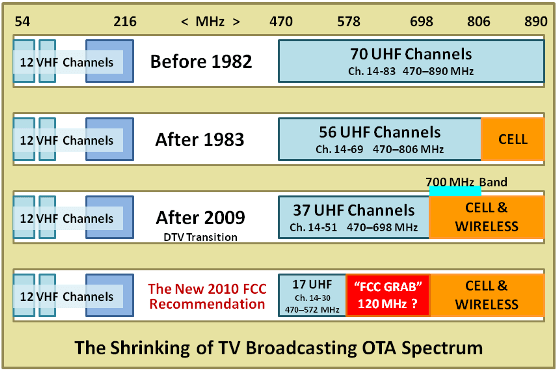
The NAB has heavily lobbied Washington officials on the issue of spectrum because their members — broadcast television stations — are facing the loss of up to 120MHz of what’s left of the UHF dial, already shrinking because of earlier reallocations. The FCC proposal would resize the UHF dial to channels 14-30 — 16 channels. In crowded television markets like Los Angeles, up to 16 stations would be forced to sign-off the public airwaves for good, because there would be insufficient space to allow them to continue a broadcast signal. Instead, the FCC proposes they deliver their signal over pay television providers like cable or telco-provided IPTV. Or they could always stream over the Internet. But that would mean the decline of free, over the air television in this country.
Considering the millions of dollars many stations are worth, it’s no surprise broadcasters are howling over the proposal.
Onyeije’s report suggests AT&T and Verizon, among others, are grabbing whatever valuable spectrum they can get their hands on. What they don’t use, they’ll “warehouse” for claimed future use. By locking up unused spectrum, potential competitors can’t use it. The proof, Onyeije writes, is found when comparing claims by the wireless industry with the FCC’s own independent research:
AT&T predicts 8-10 times of data growth between 2010 and 2015 and T-Mobile forecasts that data will have 10 times of growth in 5 years. Yet, the Commission’s assessment that 275MHz of spectrum is needed to meet mobile data demand is premised on data growth of 35 times between 2009 and 2014.
The Data Tsunami Debunked
The NAB also takes to task the “evidence” many providers use to claim the zettabyte era is at hand, where a veritable exaflood of data will force America into a widespread data brownout if more capacity isn’t immediately made available.
[…] The [industry claims rely] on suspect data. In arriving at its conclusion, OBI Technical Paper No. 6 relies heavily on forecast data from Cisco that is both wildly optimistic about data growth and unscientific. In a blog entry entitled, Should a Sales Brochure Underlie US Spectrum Policy?, Steven Crowley states that “[t]here is overlap between the people who prepare the forecast and the people responsible for marketing Cisco’s line of core-network hardware to service providers. The forecast is used to help sell that hardware. Put simply, it’s a sales brochure.”
Onyeije takes apart the oft-repeated claim that a data explosion will be unyielding, unrelenting, and will be the wireless industry’s biggest challenge for years to come. It also speaks to issues about broadband use in general:
In particular, the paper appears to be premised on the highly suspect assumption that the high demand curve for mobile data will not slow. While smartphone growth is significantly increasing now, it will no doubt plateau and slow. It has been widely accepted for decades that the process of technological adoption over time is typically illustrated as a classic normal distribution or “bell curve” where a phase of rapid adoption ends in slowed adoption as the product matures or new technologies emerge.
As recently reported, Cisco now projects that U.S. mobile growth will drop by more than half by 2015. As Dave Burstein, Editor of DSL Prime, explains: “The growth is clearly not exponential.” Mr. Burstein went on to say “Every CFO and engineer has to plan carefully for the network upgrades needed, but the numbers certainly don’t suggest a ‘crisis.’” Jon Healey of the Los Angeles Times Editorial Board similarly explains that “Much of the growth in the demand for bandwidth has come from two parallel forces: a new type of smartphone (epitomized by the iPhone) encourages people to make more use of the mobile Web, and more people are switching from conventional mobile phones to these new smartphones. Once everyone has an iPhone, an Android phone or the equivalent, much of the growth goes away.” AP Technology writer Peter Svensson echoes this concern and explains “AT&T’s own figures indicate that growth is slowing down now that smartphones are already in many hands.” Thus, the assumption that data demand will continue to grow unabated is deeply flawed.
Internet Overcharging is About Rationing and Reducing Use
Although the NAB favors Internet Overcharging to drive down demand for use, Onyeije’s report inadvertently provides additional evidence to the forces that oppose data caps, meters, and speed throttles: they are designed to monetize usage while driving it down at the same time:
While unlimited data plans on mobile phones were once the standard, there is now more focus on using pricing as a network management tool. As AT&T Operations President John Stankey put it, “I don’t think you can have an unlimited model forever with a scarce resource. More people get drunk at an open bar than a cash bar.” In the past year, AT&T and Virgin Mobile abandoned unlimited data plans. In 2010, T-Mobile announced that it would employ data throttling and slow the download speeds of customers that use more than five GB of data each month. And Bloomberg reported on March 1, 2011 that “Verizon Communications Inc. will stop offering unlimited data plans for Apple Inc.’s iPhone as soon as this summer and switch to a tiered pricing offering that can generate more revenue and hold the heaviest users in check.” Usage-based smartphone data plans substantially reduce per-user data traffic. As a result, data growth is likely to slow over time. And companies, including Cisco, are marketing products to carriers to help make tiered data plans easier to implement and help carriers “increase the monetization of their networks.”


 Subscribe
Subscribe