The arrival of the LTE/4G wireless standard in the United States, and its adoption by the country’s two largest super-carriers AT&T and Verizon was supposed to open the door for true equipment interoperability, allowing customers to take devices purchased from one carrier to another. In the past, incompatible network standards (GSM – AT&T and CDMA – Verizon Wireless) made device portability a practical impossibility. The arrival of LTE could have changed everything, with device manufacturers using chipsets that would allow an iPad owner to switch from Verizon to AT&T without having to purchase a brand new tablet.
The arrival of the LTE/4G wireless standard in the United States, and its adoption by the country’s two largest super-carriers AT&T and Verizon was supposed to open the door for true equipment interoperability, allowing customers to take devices purchased from one carrier to another. In the past, incompatible network standards (GSM – AT&T and CDMA – Verizon Wireless) made device portability a practical impossibility. The arrival of LTE could have changed everything, with device manufacturers using chipsets that would allow an iPad owner to switch from Verizon to AT&T without having to purchase a brand new tablet.
A new lawsuit filed by a small regional cell phone company alleges AT&T conspired to create their own wireless fiefdom that would not only discourage their own customers from considering a switch to a new carrier, but also locked out smaller competitors from getting roaming access.
C-Spire, formerly Cellular South, filed suit in U.S. federal court accusing AT&T and two of their biggest equipment vendors — Qualcomm and Motorola, of conspiring to keep the southern U.S. carrier from selling the newest and hottest devices and hampering their planned upgrade to LTE. The company also accuses AT&T of blocking access to roaming service for the benefit of C-Spire customers traveling outside of the company’s limited coverage area.
According to the lawsuit, the interoperability benefits of LTE have been artificially blocked by some of America’s largest carriers that force consumers to only use devices specifically approved for a single company’s network.
Divide Your Frequencies to Conquer and Hold Market Share
The Federal Communications Commission licenses wireless phone companies to use specific frequencies for phone calls and data communications. An industry standard group, the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP), is largely responsible for defining the standards of operation for wireless technology networks like LTE. In the United States, the group is dominated by the two largest cell phone companies and the technology vendors that make their living selling chipsets and phones to those major carriers.
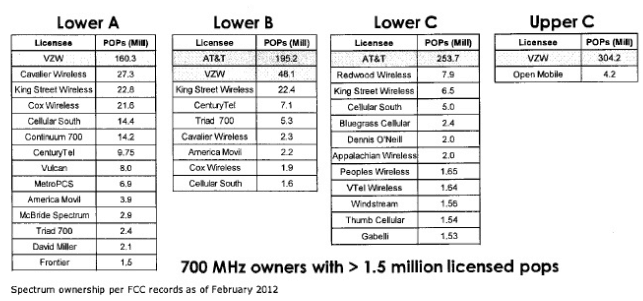
Smaller carriers specifically bought spectrum near frequencies used by larger companies AT&T and Verizon with the plan to sign roaming agreements with them. But now Verizon is selling off its "Lower A, B and C" spectrum and intends to focus its LTE network on Upper C "Band 13," which it occupies almost exclusively. Meanwhile, AT&T has carved out its own exclusive "Band 17" for its Lower B and C frequencies where it will be able to effectively lock out other carriers. (Cellular South is now known as C-Spire).
 It is 3GPP that elected to organize wireless spectrum into a series of frequency “blocks” and “bands” that different companies utilize to reach customers. Verizon Wireless, for example, has its 4G LTE network on a large chunk of the 700MHz band known as the “Upper C-block” or “Band 13.” Verizon earlier won control of some frequencies on the lower “A and B blocks,” which gave smaller companies the confidence to invest in adjacent frequencies, believing they would be able to negotiate roaming deals with Verizon.
It is 3GPP that elected to organize wireless spectrum into a series of frequency “blocks” and “bands” that different companies utilize to reach customers. Verizon Wireless, for example, has its 4G LTE network on a large chunk of the 700MHz band known as the “Upper C-block” or “Band 13.” Verizon earlier won control of some frequencies on the lower “A and B blocks,” which gave smaller companies the confidence to invest in adjacent frequencies, believing they would be able to negotiate roaming deals with Verizon.
Verizon has since elected to mass its 4G LTE operations on its “Upper C block,” and is selling off its lower “A and B block” frequencies. That leaves Verizon with overwhelming control of “Band 13.” The companies manufacturing equipment sold by Verizon are manufacturing phones that only work on Verizon’s frequencies, not those used by Verizon’s competitors. This effectively stops a Verizon customer from taking their device (and their business) to a competitor’s network.
This limitation comes not from the LTE network technology standard, but from the wireless companies themselves and equipment manufacturers who design phones to their specifications.
It would be like buying a television set from your local NBC station and discovering that was the only station the set could receive.
 Verizon effectively created its own wireless “gated community” comprised of itself and a single tiny competitor still sharing a small portion of “Band 13.” AT&T was stuck in a considerably more crowded neighborhood, sharing space with more than a dozen smaller players, some who have a clear interest in being there to coordinate roaming agreements with AT&T to extend their coverage.
Verizon effectively created its own wireless “gated community” comprised of itself and a single tiny competitor still sharing a small portion of “Band 13.” AT&T was stuck in a considerably more crowded neighborhood, sharing space with more than a dozen smaller players, some who have a clear interest in being there to coordinate roaming agreements with AT&T to extend their coverage.
Regional cell phone companies could not exist without a roaming agreement that lets customers maintain coverage outside of their home service area. Without it, customers would gravitate to larger companies who do provide that coverage.
But large companies like AT&T and Verizon also have a vested interest not selling access to the crown jewels of their network, giving up a competitive advantage.
AT&T noticed its larger competitor Verizon Wireless had effectively segregated its operations onto its own band, and if that worked for them, why can’t AT&T have its own band, too?
 Using a controversial argument that AT&T needed protection from potential interference coming from television signals operating on UHF Channel 51, located near the “A Block,” AT&T managed to convince 3GPP to carve out brand new “Band 17” from pieces of “Band 12.” Coincidentally, “Band 17” happens to comprise frequencies controlled by AT&T.
Using a controversial argument that AT&T needed protection from potential interference coming from television signals operating on UHF Channel 51, located near the “A Block,” AT&T managed to convince 3GPP to carve out brand new “Band 17” from pieces of “Band 12.” Coincidentally, “Band 17” happens to comprise frequencies controlled by AT&T.
C-Spire alleges AT&T has since asked manufacturers to create devices that only support “Band 17,” not the much larger “Band 12,” effectively locking out small regional phone companies from LTE roaming agreements and the latest phones and devices.
Not surprisingly, Qualcomm and Motorola, who depend on AT&T for a considerable amount of revenue, fully supported the wireless company’s plan to create a new band just for itself. C-Spire’s lawsuit claims the resulting anti-competitive conspiracy has now graduated to foot-dragging by those manufacturers, reluctant to release new phones and devices that support the greater “Band 12” on which C-Spire and other smaller carriers’ 4G LTE networks reside. That is particularly suspicious to C-Spire, which notes companies manufacturing devices supporting all of “Band 12” would have automatically worked with AT&T’s new “Band 17.” Instead, manufacturers chose to create equipment that only worked on AT&T’s frequencies.
C-Spire says both AT&T and Verizon have once again managed to lock customers to their individual networks, have created artificial barriers to block roaming agreements, and have pressured manufacturers to “go slow” on new phones and devices for smaller competitors.
Driving the Competition Out of Business

LTE: Required for future competition.
Smaller carriers have always been disadvantaged by manufacturers’ exclusive marketing agreements with AT&T and Verizon that bring the hottest new devices to one or the other, leaving smaller players with older technology or smartphones with fewer features. Even worse, both AT&T and Verizon have forced manufacturers to enforce proprietary standards that make it difficult for consumers to leave one company for another and take their phones with them. C-Spire and other regional companies have primarily managed to compete because they often sell service at lower prices. They have also survived because roaming agreements allow companies to sell functionally equivalent service to customers who do not always remain within the local coverage area.
But recent developments may soon make smaller competitors less viable than ever:
- AT&T’s spectrum plans make it difficult for smaller companies to use their valuable 700MHz spectrum, the most robust available, for LTE 4G service. Instead, companies like C-Spire will have to use less advantageous higher frequencies at an added cost to remain competitive in their own local markets.
- Equipment manufacturers, who answer to the billion-dollar contracts they have with both Verizon and AT&T, remain slow to release devices that work on smaller networks, leaving companies like C-Spire without attractive technology to sell to customers.
- The ultimate refusal by AT&T and Verizon to allow LTE roaming or make it prohibitively expensive or technologically difficult to access could be the final blow. Why sign up for C-Spire if you can’t get 4G service outside of your home service area? C-Spire admits in its lawsuit it cannot survive if it cannot sign reasonable roaming agreements with AT&T or Verizon.
Cspire complaint filed against AT&T, Qualcomm and Motorola
 The AARP was surprised to learn Idaho was considering loosening the rules imposed on the state’s phone companies to complete repairs on out of service landlines within 24 hours. The organization, which represents the elderly, says the new rules are a serious threat to older Idahoans who are the least likely to have a cell phone and require landlines in case of an emergency.
The AARP was surprised to learn Idaho was considering loosening the rules imposed on the state’s phone companies to complete repairs on out of service landlines within 24 hours. The organization, which represents the elderly, says the new rules are a serious threat to older Idahoans who are the least likely to have a cell phone and require landlines in case of an emergency. Other claims made by CenturyLink – such as the assertion that its ability to deploy broadband suffers because its personnel are unreasonably diverted to repair work – are unproven and largely irrelevant to its obligation to maintain reliable telephone services, says AARP.
Other claims made by CenturyLink – such as the assertion that its ability to deploy broadband suffers because its personnel are unreasonably diverted to repair work – are unproven and largely irrelevant to its obligation to maintain reliable telephone services, says AARP.

 Subscribe
Subscribe