![]() The company best known for the 10 daily newspapers it publishes, including the Chicago Tribune, the Orlando Sentinel, the Baltimore Sun, and the Los Angeles Times, can’t wait to get out of the newspaper business.
The company best known for the 10 daily newspapers it publishes, including the Chicago Tribune, the Orlando Sentinel, the Baltimore Sun, and the Los Angeles Times, can’t wait to get out of the newspaper business.
Last December, the Tribune Company, the second largest newspaper publisher in the country, emerged from bankruptcy without its $13 billion debt and old owners. Now in charge: the same Wall Street banks that lent the company billions to go private. Two months after assuming control, Tribune’s new owners hired Evercore Partners and J.P. Morgan to oversee the dumping of Tribune’s newspaper portfolio.
Founded in 1847 with the launch of the Chicago Tribune, 166 years later the Tribune Company was finished with print news, probably for good.
Investment bank and now owner
Today’s Tribune, controlled by Oaktree Capital Management, best known for investing in “distressed” companies, JPMorgan Chase, a Wall Street investment firm, and Angelo, Gordon & Co., a hedge fund sponsor best known for helping the U.S. government deal with the toxic assets accumulated by banks that helped trigger The Great Recession, want into the television business instead.
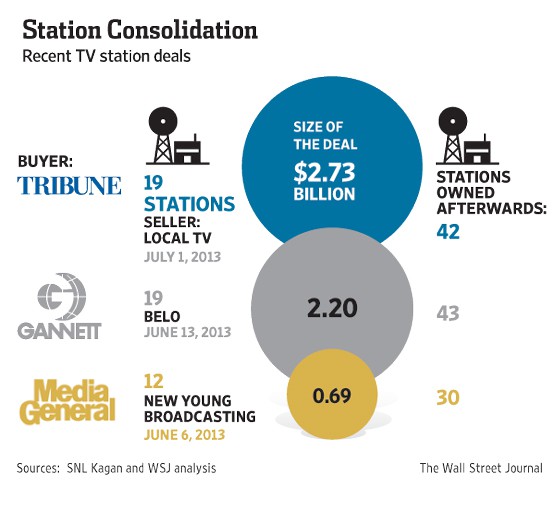
Tribune, which already owned 23 local television stations including flagship WGN in Chicago, bought another 19 Monday in a deal estimated to be worth at least $2.7 billion.
The stations were acquired from Local TV Holdings, itself owned and controlled by Wall Street investment firm Oak Hill Capital Partners, founded by Texas oil billionaire Robert Bass. Oak Hill acquired the television outlets from The New York Times and News Corp., in two prior deals. Tribune won’t pay for the stations outright. It is financing the deal with a $4.1 billion credit line granted by banks including JPMorgan Chase and Citigroup.
The stations involved:
| City of License/Market | Station | Channel TV (DT) |
Network |
|---|---|---|---|
| Huntsville, Ala. | WHNT-TV | 19 (19) | CBS |
| Fort Smith – Fayetteville, Ark. | KFSM-TV | 5 (18) | CBS |
| KXNW | 34 (34) | MyNetworkTV | |
| Denver, Col. | KDVR | 31 (32) | Fox |
| Fort Collins, Col. | KFCT* (*- satellite of KDVR) |
22 (21) | Fox |
| Des Moines, Iowa | WHO-TV | 13 (13) | NBC |
| Moline, Ill. (Quad Cities) | WQAD-TV | 8 (38) | ABC |
| Kansas City, Mo. | WDAF-TV | 4 (34) | Fox |
| St. Louis, Mo. | KTVI | 2 (43) | Fox |
| High Point – Greensboro – Winston-Salem, N.C. |
WGHP | 8 (35) | Fox |
| Cleveland – Akron, Ohio | WJW-TV | 8 (8) | Fox |
| Oklahoma City, Okla. | KFOR-TV | 4 (27) | NBC |
| KAUT-TV | 43 (40) | Independent | |
| Scranton – Wilkes Barre, Penn. | WNEP-TV | 16 (50) | ABC |
| Memphis, Tenn. | WREG-TV | 3 (28) | CBS |
| Salt Lake City, Utah | KSTU | 13 (28) | Fox |
| Norfolk – Portsmouth – Newport News, Va. |
WTKR | 3 (40) | CBS |
| WGNT | 27 (50) | The CW | |
| Richmond, Va. | WTVR-TV | 6 (25) | CBS |
| Milwaukee, Wisc. | WITI | 6 (33) | Fox |
Assuming the deal meets the approval of the Federal Communications Commission, Tribune will control 42 stations in 16 markets, including New York, Los Angeles, and Miami.
 It expects to pay off the loans and generate returns from the “significant free cash flow” generated by the stations.
It expects to pay off the loans and generate returns from the “significant free cash flow” generated by the stations.
Where will that cash flow originate? From pay television subscribers asked to pay a growing amount each year for the formerly “free TV” stations.
“Smaller players feel like they’re losing their way with pay-TV providers and broadcast networks,” Craig Huber, analyst at Huber Research Partners, told USA Today. “They feel like they’re at a disadvantage here unless they size up.”
As cable programming rates continue to increase and subscribers threaten to cut the cord, pay television providers have been more willing to play hardball and kick stations off the cable or satellite dial when they cannot reach a retransmission consent agreement.
With up to 90 percent of a station’s viewership coming from pay television platforms, a lengthy standoff can destroy a station’s primary source of income: advertising revenue.
To protect themselves, television station owners are retaliating by threatening providers with the loss of all of their stations across the country, not just one or two. The resulting subscriber uproar could prove politically difficult and threaten customer relationships with providers. The more stations a company controls, the bigger the threat it can pose to Comcast, DirecTV, AT&T and other national providers.
 Tribune is not alone bulking up the number of stations they own and control. Last month Gannett nearly doubled its portfolio from 23 to 43 stations with the acquisition of Belo’s TV stations for $1.5 billion in cash and agreeing to cover $715 million in accumulated debt.
Tribune is not alone bulking up the number of stations they own and control. Last month Gannett nearly doubled its portfolio from 23 to 43 stations with the acquisition of Belo’s TV stations for $1.5 billion in cash and agreeing to cover $715 million in accumulated debt.
Sinclair Broadcast Group, already the largest local TV station owner in the country, has gotten even larger with the purchase of four TV stations owned by Titan TV Broadcast Group. If the deal is approved, Sinclair will own 140 stations in 72 markets. In some cities, Sinclair will nominally own or control up to five local stations.
Sinclair management is well-known for injecting conservative political viewpoints into local newscasts and programming decisions. In 2004, two weeks before the presidential election, Sinclair ordered all of its television stations to air propaganda critical of Democratic candidate John Kerry. Later that year, Sinclair ordered its ABC affiliated stations not to broadcast a “Nightline” episode about soldiers killed in the Iraq war, fearing it would turn the public against the war.
But for most owners, politics has nothing to do with the desire to supersize. It’s a matter of money.
Even smaller station groups are now consolidating. Media General and New Young Broadcasting Holding, are merging their combined 30 stations.
(Image: The Wall Street Journal)
Critics worry the changing landscape of local television will threaten the concept of “local service” stations are required to provide as a condition of their broadcast license. A station owner that lives and works in the community served is becoming an increasing rarity, and the Federal Communications Commission has allowed stations that used to fiercely compete for local news viewers to now “share resources.” Many stations, especially those owned by out of area investment banks, have discontinued local news altogether in cost-savings maneuvers.
“This deal adds to a blizzard of broadcast industry consolidation that is poised to leave America’s media system less local, less diverse and less accountable to the people in these communities,” said Free Press’ Craig Aaron in a statement on the deal. “By the time all these deals are done, a handful of companies could control almost all of the network affiliates in major markets and swing states. Local broadcasts are becoming simulcasts, with the same cookie-cutter content piped in from distant corporate headquarters, once-competitive stations combined into single newsrooms and fewer journalists forced to fill more hours of airtime.”
“The FCC needs to wake up to what’s happening on local TV,” said Aaron. “Wall Street may be overjoyed at this merger mania, but the rest of us should be very worried about having fewer viewpoints on the air and fewer reporters on the beat.”
[flv width=”640″ height=”500″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/Former FCC commissioner Michael Copps shares his concerns about media consolidation 2013.mp4[/flv]
Former FCC commissioner Michael Copps shares his concerns about increasing media consolidation and its impact on an informed electorate. (Aired on Carolina Journal Radio May 23, 2013) (1 minute)


 Subscribe
Subscribe
 Malone also thinks it is time to discard reliance on cable television to bring home the revenue and profits Wall Street expects. The industry should instead turn its earning attention to broadband, a product few Americans can live without. Malone believes the cable industry is not only positioned to control content distributed on its TV Everywhere online video platform for authenticated cable subscribers, but also have a say in competing content from Netflix, among others, which are totally reliant on the broadband pipes provided by ISPs.
Malone also thinks it is time to discard reliance on cable television to bring home the revenue and profits Wall Street expects. The industry should instead turn its earning attention to broadband, a product few Americans can live without. Malone believes the cable industry is not only positioned to control content distributed on its TV Everywhere online video platform for authenticated cable subscribers, but also have a say in competing content from Netflix, among others, which are totally reliant on the broadband pipes provided by ISPs. Among the top recipients: Comcast, which collects $25-30 million a year and Time Warner Cable, which nets “tens of millions of dollars” from Google, Microsoft, and Facebook.
Among the top recipients: Comcast, which collects $25-30 million a year and Time Warner Cable, which nets “tens of millions of dollars” from Google, Microsoft, and Facebook. Time Warner Cable is extending an online promotion to Extreme (30/5Mbps) customers to upgrade to Ultimate (50/5Mbps) service for an extra $10 a month above your current pricing.
Time Warner Cable is extending an online promotion to Extreme (30/5Mbps) customers to upgrade to Ultimate (50/5Mbps) service for an extra $10 a month above your current pricing.
 William J. Morand, communications director for Charter’s Northeast Region, admitted Morin previously worked for M. Kable, a Charter contractor, and that there was no legitimate way the former contractor could have obtained current customer information.
William J. Morand, communications director for Charter’s Northeast Region, admitted Morin previously worked for M. Kable, a Charter contractor, and that there was no legitimate way the former contractor could have obtained current customer information. Time Warner Cable’s decision to spend $11 billion to broadcast Los Angeles Lakers and Dodgers games at an estimated cost of $50-60 a year per subscriber is the subject of a
Time Warner Cable’s decision to spend $11 billion to broadcast Los Angeles Lakers and Dodgers games at an estimated cost of $50-60 a year per subscriber is the subject of a 