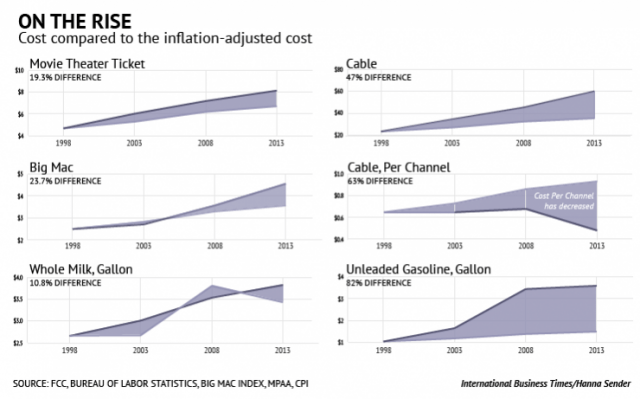
 Think you are already paying too much for cable television? If you thought Comcast charges too much, consider what CBS thinks is fair to charge for an on-demand library of CBS shows and a single live stream of your local CBS station – $5.99 a month.
Think you are already paying too much for cable television? If you thought Comcast charges too much, consider what CBS thinks is fair to charge for an on-demand library of CBS shows and a single live stream of your local CBS station – $5.99 a month.
Retransmission consent disputes are all about the money. As your local provider fights with a local station or cable network over their latest demand for more money, channels get dropped, providers get blamed and the content owners get richer when networks are restored.
One of the richest of all is CBS, which has told investors it plans to empty $2 billion from the pockets of American cable customers by the year 2020, up from $500 million in 2013. Not only will CBS demand new programming fees from its affiliates, it is also cajoling stations to demand not less than $1.75 a month from every cable subscriber for access to the local CBS over the air station.
Each time a retransmission consent contract comes up for renewal, cable operators know as certain as the sun will rise from the east that programmers will demand a healthy rate increase for the next contract period. That is why many cable companies now look to broadband for much of their future profits, because the TV business is getting very expensive when everyone has their hand out looking for more.
Some cable companies want an end to being stuck in the middle of these disputes and are supporting a plan to compel programmers like CBS, ESPN, TNT, HBO, and all the rest to publish a retail rate for their channel or network and let consumers decide whether it is worth the asking price.
A proposal introduced last year called “Local Choice” would start the process with local television stations, which have demanded ever-higher carriage fees over the last 10 years, especially for network-affiliated stations.
Under the concept, customers would be given a choice of local stations by their provider. Theoretically, a customer could subscribe to CBS and ABC and tell NBC (and its local affiliate) to take a hike if they demanded too much. Another might be happy just paying for FOX and grab the rabbit ears for anything else they wanted to watch over the air for free.

Rockefeller
No local station or network would voluntarily say goodbye to the golden goose that lays compulsory retransmission consent fees programmers currently collect from every cable subscriber, so last summer Congress proposed to mandate the concept in a clause of the Satellite Television Access and Viewer Rights Act (STAVRA).
Then Senate Commerce Committee Chairman Jay Rockefeller (D-W.V.) and Ranking Member John Thune (R-S.D.) beat the bipartisan drum loudly for change. But lobbyists also had drums. Rockefeller and Thune began wavering almost immediately.
“During the last month, Chairman Rockefeller and Ranking Member Thune have successfully begun a discussion on Local Choice, which would empower TV viewers, maintain our policy of broadcast localism, and ensure TV stations get fairly compensated for the retransmission of their signals,” read a joint statement issued last September. “Because it is a big and bold idea, Local Choice deserves more discussion and a full consideration by policymakers, and the committee may not have time to include it as part of STAVRA. Rockefeller and Thune are focused on passing STAVRA next week, and continuing to work with their colleagues on Local Choice.”
After the sudden insertion of Local Choice into a satellite television bill, an orange glow filled the night sky at 1771 N Street in Washington. It was Gordon Brown’s hair on fire. Brown is president and CEO of the National Association of Broadcasters (NAB), the very powerful lobby representing television stations and networks. But that night, he sounded exactly like a cable guy.
“NAB opposes this proposal because it eliminates the basic [cable] tier upon which millions rely for access to lifeline information,” Brown responded in a statement. “It proposes a broadcast a-la-carte scheme that will lead to higher prices and less program diversity. Furthermore, STAVRA appears to confer unfettered and unprecedented authority for government intervention into private marketplace negotiations.”
 The cable industry has fought its own battle against a-la-carte on exactly the same ground Brown was now occupying.
The cable industry has fought its own battle against a-la-carte on exactly the same ground Brown was now occupying.
Rockefeller later claimed he was only poking the Broadcast TV Bear to provoke a response, and he got one. The idea of Local Choice was stripped out of the bill by the fall. Rockefeller was reduced to saving face.
“What we wanted to do was introduce those ideas,” Rockefeller later told The Hill. “We made it sound like it was the focus of the bill, and K Street just went crazy, which is always good. But we knew that we’d have to take it out.”
Yes they did, after the NAB and their allies launched a major PR campaign against Local Choice, attracting over 130,000 comments against the plan.

Polka
But Rockefeller knew the idea was not going away.
“As people get a taste of being able to say ‘I only watch 10 channels so I should only pay for 10 channels,’ they’re going to love that. It’s going to spread like wildfire,” Rockefeller said.
Fast forward to this spring and it was back to business as usual. Retransmission consent disputes yanked several networks and stations off cable systems, providers mailed their annual rate increase notices, and the cable industry’s popularity and reputation with customers now rivaled ISIS.
Much of the collateral damage (apart from the collective emptying of your wallet) continues to be felt by America’s smallest cable operators that cannot negotiate for what passes as fair and reasonable programming rates from networks like ESPN and CBS. They cannot qualify for volume discounts that are so compelling, it drove AT&T (U-verse TV) into the arms of DirecTV just to get enough subscribers to knock a few more cents off the monthly price of regional sports channels. Only the biggest players in the game have the power and get the savings.
Matthew Polka, president of the American Cable Association (ACA), the other cable trade association representing the interests of small, often family owned cable systems, may not have the most power but he could have the strongest argument against the status quo. While the National Association of Broadcasters spent tens of thousands of dollars arguing today’s retransmission consent system works just fine, some of America’s smaller TV stations apparently didn’t read the NAB’s talking points.
 The “TV Station Group,” an informal collective of small market TV stations seeking a renewal of their carriage contract with DirecTV has been stonewalled by DirecTV for months. Last week, the station owners filed a complaint with the FCC asking them to stop or block AT&T’s merger with DirecTV until the satellite provider agreed to negotiate in good faith. It was clear from their filing DirecTV’s idea of negotiation is to send ‘take it or leave it’ nastygrams to the TV stations, serving markets like Spokane, Wash., and Yuma, Ariz. The only thing clear from the back and forth is that DirecTV has no doubt it can squash the stations like little bugs:
The “TV Station Group,” an informal collective of small market TV stations seeking a renewal of their carriage contract with DirecTV has been stonewalled by DirecTV for months. Last week, the station owners filed a complaint with the FCC asking them to stop or block AT&T’s merger with DirecTV until the satellite provider agreed to negotiate in good faith. It was clear from their filing DirecTV’s idea of negotiation is to send ‘take it or leave it’ nastygrams to the TV stations, serving markets like Spokane, Wash., and Yuma, Ariz. The only thing clear from the back and forth is that DirecTV has no doubt it can squash the stations like little bugs:
[W]e will not fall victim to your silly and obvious tactics to try to audit our retrans deals so you can see them all. We did not ask you to send to us your supposed rates, and your unilateral decision to do so doesn’t give you the right to see our other deals. But trust [us], no other station group – especially small groups such as Northwest – are paid by DIRECTV nearly what you have proposed, let alone what your sheet says.
A few weeks later, in response to another request from the broadcasters, DirecTV scolded them like a misbehaving teenager:
To repeat yet again, DIRECTV is not going to get pulled into your transparent trap to define what is ‘market’ by seeing our other deals. That is a precedent we will not set, including for NW. Please do not ask again.
“Judging from the TV stations’ complaint, it is evident that the retransmission consent market is broken and not working for these broadcasters any better than for cable operators,” Polka wrote in a press release issued today. “The time has come for these TV stations and others that have also filed good faith complaints to step out from NAB’s long shadow and join ACA in supporting efforts to update the rules and equip them with a strong referee that can help protect consumers and competition when negotiations break down.”
Polka continues to advocate letting customers decide whether they want to pay for local stations and cable networks. He argues CBS is already doing that today with its All Access program for broadband customers. In 94 markets, serving 64% of U.S. households, consumers can voluntarily subscribe to a live stream of their local CBS station and access a large 6,500 title on-demand library of CBS content for $5.99 a month.
 Nobody besides CBS knows how many have agreed to pay for All Access, but executives have told investors they are pleased with how the program is working. Still, Marc DeBevoise, executive vice president and general manager of CBS Digital Media at CBS Interactive knows he walks a very fine line promoting a product that could eventually undermine CBS’s current commitment to today’s retransmission consent system. DeBevoise told The Drum it does not market or intend to offer All Access as an alternative to the current cable model.
Nobody besides CBS knows how many have agreed to pay for All Access, but executives have told investors they are pleased with how the program is working. Still, Marc DeBevoise, executive vice president and general manager of CBS Digital Media at CBS Interactive knows he walks a very fine line promoting a product that could eventually undermine CBS’s current commitment to today’s retransmission consent system. DeBevoise told The Drum it does not market or intend to offer All Access as an alternative to the current cable model.
“At a high level, our strategy in launching CBS All Access was two-fold. First, to delivery our best fans access to the most CBS content we could on any device at any time – really delivering a service for our ‘superfans,'” DeBevoise said. “Additionally this service enables us to reach ‘cord-nevers’ that want to watch CBS content but don’t have a traditional cable package –a significant audience, with industry estimates ranging from 6.5 to 16 million households.”
But at $5.99 a month, that price may prove too steep for many casual viewers looking only for a show or two. Many viewers now rely on ad-supported Hulu, a project of the major American broadcast networks except CBS. Most Hulu customers watch their favorite network shows for free. The future possibility of paying $6 for each of four major American broadcast networks will likely be seen as out of line, especially by more casual viewers.
But for Polka and ACA member cable systems, the idea that customers will direct their All Access price shock wrath out on CBS, not the cable company, may be worth it.


 Subscribe
Subscribe A Prattsburgh, N.Y. family-owned company has picked up where Verizon left off and is busily wiring up small communities across western New York and the Southern Tier with fiber to the home service, giving both Verizon and Time Warner Cable some competitive headaches.
A Prattsburgh, N.Y. family-owned company has picked up where Verizon left off and is busily wiring up small communities across western New York and the Southern Tier with fiber to the home service, giving both Verizon and Time Warner Cable some competitive headaches.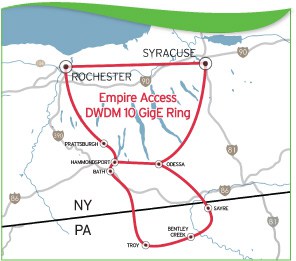 With the help of public and non-profit broadband infrastructure, residents in small communities across a region extending from Sayre, Pa., north to Batavia, N.Y., will have another choice besides Verizon or Frontier DSL, Comcast or Time Warner Cable.
With the help of public and non-profit broadband infrastructure, residents in small communities across a region extending from Sayre, Pa., north to Batavia, N.Y., will have another choice besides Verizon or Frontier DSL, Comcast or Time Warner Cable. The arrival of Empire reminds some of the days when the first cable company arrived to wire their village. Word of mouth is often enough to attract new customers, but a handful of local sales agents are also on hand to handle customer signups. From there, one of the company’s 80+ employees in New York handle everything else.
The arrival of Empire reminds some of the days when the first cable company arrived to wire their village. Word of mouth is often enough to attract new customers, but a handful of local sales agents are also on hand to handle customer signups. From there, one of the company’s 80+ employees in New York handle everything else. John Malone’s Liberty Global has bought out Puerto Rico’s second biggest cable television operator — Choice Cable TV — and will convert its customers to Liberty Cablevision of Puerto Rico.
John Malone’s Liberty Global has bought out Puerto Rico’s second biggest cable television operator — Choice Cable TV — and will convert its customers to Liberty Cablevision of Puerto Rico.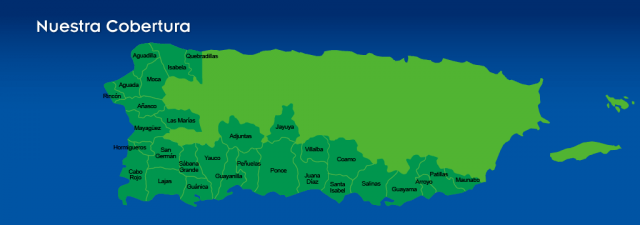

 On May 15, the last day of this year’s session of the Missouri Legislature,
On May 15, the last day of this year’s session of the Missouri Legislature, 
 Indeed, when Comcast tried to acquire Time Warner last year, the dominance (nearly 60 percent of the market) that the combined company would have had over broadband service caused federal regulators to look askance. Comcast
Indeed, when Comcast tried to acquire Time Warner last year, the dominance (nearly 60 percent of the market) that the combined company would have had over broadband service caused federal regulators to look askance. Comcast 