 Just when you thought the cable television lineup could not possibly get any larger, insiders at Comcast are anticipating one of the possible conditions that could be imposed by the Federal Communications Commission in return for approval of its merger with Time Warner Cable is an agreement to carry more independently owned cable television channels.
Just when you thought the cable television lineup could not possibly get any larger, insiders at Comcast are anticipating one of the possible conditions that could be imposed by the Federal Communications Commission in return for approval of its merger with Time Warner Cable is an agreement to carry more independently owned cable television channels.
One of the most vocal groups of consumers opposed to the merger deal have been viewers of independent Omaha, Neb.-based RFD-TV, which has landed carriage deals with Time Warner Cable but has been largely ignored by Comcast. For most of the summer, RFD-TV encouraged viewers to pelt the FCC with complaints about the merger deal, insisting that more networks not owned or operated by the top five media conglomerates get equal treatment on the Comcast cable dial. Thousands of viewers responded.
Comcast vice president David Cohen told Congress Comcast already carries more than 170 small or independent networks, although Comcast counts international networks distributed to customers at premium rates.
“It sounds wonderful. But when you peel back the onion . . . it’s really nothing at all,” Pat Gottsch, founder of RFD-TV told the Philadelphia Inquirer. “Very few [independent] channels have full distribution, other than BBC World News and Al Jazeera.”
Independent networks have little leverage with major cable operators because they cannot tie carriage agreements to more popular mainstream cable networks. That is why little-known networks like Crime & Investigation Channel or the spinoffs of fX – fXX and fXM – have glided onto cable lineups while networks like RFD, The Tennis Channel, and BlueHighways TV have a much tougher time.
Time Warner Cable now widely carries RFD-TV, but often only on an added-cost mini-pay tier. In many Time Warner markets, RFD and Smithsonian TV replaced HDNet, also an added-cost network.
 The independent networks fear they will never become viable if they cannot reach the nearly one-third of the country’s cable television subscribers a combined Comcast and Time Warner Cable would serve. Others question whether they will be given fair consideration if their networks compete with an existing Comcast or Time Warner Cable-owned channel.
The independent networks fear they will never become viable if they cannot reach the nearly one-third of the country’s cable television subscribers a combined Comcast and Time Warner Cable would serve. Others question whether they will be given fair consideration if their networks compete with an existing Comcast or Time Warner Cable-owned channel.
The Tennis Channel and Bloomberg have both tussled repeatedly with Comcast over carriage agreements and channel placement. The Tennis Channel took Comcast all the way to a federal appeals court, but lost their case. Cable companies have won recognition of their First Amendment rights to choose the channels on their systems.
In years past, cable operators cited limited channel capacity as the most frequent reason a network could not be added to the lineup. Comcast continues to claim they have limited channel space for television channels, but that has not stopped the cable company from launching dozens of little-watched networks they receive compensation to carry (home shopping, TBN and certain other religious networks) or are contractually obligated to carry (add-on sports and entertainment networks owned by Disney, Viacom, Time Warner (Entertainment), Fox, and even Comcast itself, through its Universal division).
 Comcast’s claim it already carries nearly 180 independent networks drew scrutiny when the company released the list of networks. At least half were added-cost international or pornography networks — all sold at a higher cost. More than a dozen others were independent sports channels packed into a higher-cost sports tier. Most of the rest were regional networks given very limited exposure. BlueHighways TV, which features bluegrass music, is seen in only 210,000 Comcast homes, mostly in Tennessee. That is less than 1% of Comcast’s total subscriber base.
Comcast’s claim it already carries nearly 180 independent networks drew scrutiny when the company released the list of networks. At least half were added-cost international or pornography networks — all sold at a higher cost. More than a dozen others were independent sports channels packed into a higher-cost sports tier. Most of the rest were regional networks given very limited exposure. BlueHighways TV, which features bluegrass music, is seen in only 210,000 Comcast homes, mostly in Tennessee. That is less than 1% of Comcast’s total subscriber base.
The only prominent and truly independent networks given wide carriage on Comcast include Home Shopping Network and QVC, which pay a commission to Comcast for every sale made to a Comcast customer, BBC World News, and the Catholic EWTN network.
Mitigating the problem of independent network carriage may push the FCC to the path of least resistance – making carriage of some of these networks a requirement in return for merger approval.
It wouldn’t be the first time. Comcast agreed to launch 10 independent networks as a condition for FCC approval of its buyout of NBCUniversal. That deal is what brought BBC World News to the Comcast lineup, along with a range of little-known networks on high channel numbers: ASPiRE, BabyFirst Americas, Revolt, and El Rey. BabyFirst is targeted to babies and toddlers from 0-3 years old, but is also enjoyed by recreational drug users who find the network’s use of bright colors in their short-form videos entertaining. ASPiRE’s programming has been described by its critics as “crap.”


 Subscribe
Subscribe
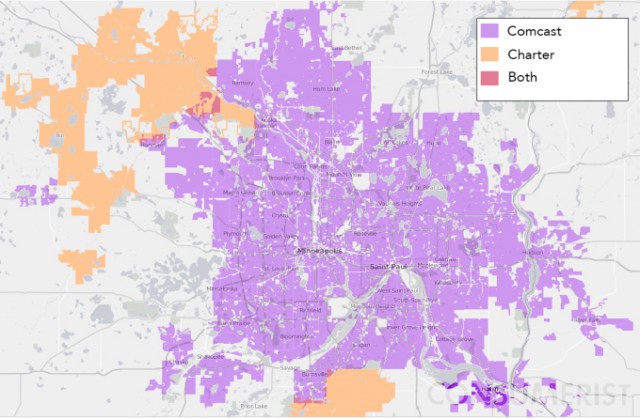
 The federal government is likely to count Bright House’s 2.2 million customers as part of the Time Warner Cable family, at least as far as control of cable programming pricing is concerned. Despite Comcast’s voluntary commitment to keep its national share of the cable TV business under 30 percent with the merger of Time Warner, Comcast hasn’t taken seriously counting the customers of the uninvited cousin – Bright House.
The federal government is likely to count Bright House’s 2.2 million customers as part of the Time Warner Cable family, at least as far as control of cable programming pricing is concerned. Despite Comcast’s voluntary commitment to keep its national share of the cable TV business under 30 percent with the merger of Time Warner, Comcast hasn’t taken seriously counting the customers of the uninvited cousin – Bright House.

 Making a direct comparison between the prices charged by Comcast and those of Time Warner Cable require unnecessary perseverance made even more difficult by the fact Comcast only serves a tiny portion of New York State.
Making a direct comparison between the prices charged by Comcast and those of Time Warner Cable require unnecessary perseverance made even more difficult by the fact Comcast only serves a tiny portion of New York State.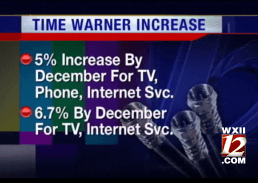 In 2011, Time Warner Cable raised some of its “rack rates” by up to 51.1 percent.[4]
In 2011, Time Warner Cable raised some of its “rack rates” by up to 51.1 percent.[4]