
Struck Out
For most of the current baseball season, Los Angeles Dodgers fans who don’t subscribe to Time Warner Cable have been shut out, unable to watch the games shown exclusively on the extremely expensive SportsNet LA cable network, jointly owned by the Dodgers and Time Warner Cable.
Most of Time Warner’s southern California competitors balked at the asking price: about $4 a month per subscriber. Had they agreed to carry the network, subscribers would ultimately pay for it during the next round of rate hikes, whether they watched sports or not.
Time Warner Cable has a 25-year, $8.35 billion dollar contract to manage the network, and observers believe they have struck out.
“They rolled the dice and lost big time,” said Jimmy Schaeffler, head of consulting firm the Carmel Group.
With networks like ESPN commanding whatever they set as an asking price, sports team owners have rushed to get a piece of the lucrative sports network pie. Even individual teams are now demanding their own exclusive networks, hoping to charge top dollar to companies agreeing to carry them.
Angry cable customers watching their bills skyrocket can primarily blame sports programming for much of the endless increases. Around 20 regional and national sports channels now comprise 20% of the wholesale cost of cable television — a high percentage considering the average cable system now carries over 200 channels. While some basic cable networks are lucky to get 10 cents a month per subscriber, regional Fox Sports North demands $4.67 a month from each subscriber, whether they watch the network or not. Smaller independent cable systems usually pay even more.
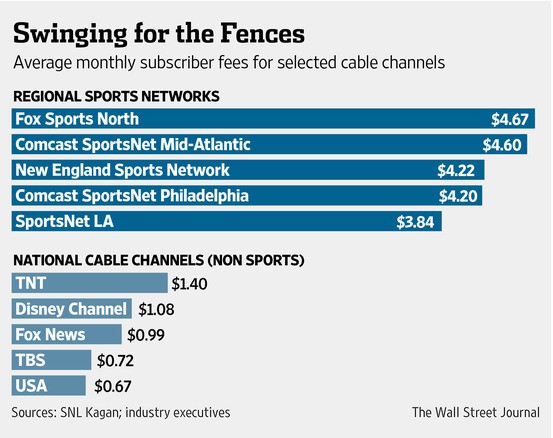
In southern California, the average cable subscriber pays $20 a month for seven sports channels. There was little interest raising that to more than $24 a month to carry what Dodgers team president Stan Kasten called, “a Dodger-only channel with Dodger-only content 24/7.”
“We’ve been approaching a tipping point in sports programming costs for years and the Los Angeles market has sent a strong message that we’ve reached it,” Andy Albert, senior vice president of content acquisition at Cox Communications, one of the distributors that declined to carry SportsNet LA, told the Wall Street Journal.
 The embargo has cost both the Dodgers and Time Warner Cable plenty of advertising and subscription revenue. Ratings are dramatically down from an average of 228,000 viewers when the baseball games were shown on widely carried Prime Ticket, to just 55,000 today on SportsNet LA. Advertising rates have been slashed to compensate for the lack of an audience.
The embargo has cost both the Dodgers and Time Warner Cable plenty of advertising and subscription revenue. Ratings are dramatically down from an average of 228,000 viewers when the baseball games were shown on widely carried Prime Ticket, to just 55,000 today on SportsNet LA. Advertising rates have been slashed to compensate for the lack of an audience.
The cost of the dispute between Time Warner Cable and its competitors also included bad public relations, which attracted the attention of regulators at the FCC and area elected officials, who have loudly complained that viewers are increasingly caught in the middle of these disputes.
The pressure worked, and Time Warner Cable announced in mid-September it would broadcast the six final Dodgers games of the season locally for free on KDOC-TV, an independent channel based in Orange County mostly known for airing endless reality shows and reruns of off-network series. On a good day, KDOC attracts at most 18,000 viewers. But the station is doing better today — grabbing an average of 259,000 viewers last week during one Dodgers game — essentially the same audience the Dodgers used to have before SportsNet LA came along. Even better for the station, Time Warner Cable is paying KDOC to carry the games.
KDOC management is now desperately trying to figure out how to keep its new audience after baseball season ends, running promotions for its various shows as often as possible. The station is easy enough to find over-the-air and on every significant cable, satellite, and telco-TV operator. But with more than three dozen high power, low power, and digital sub-channels to choose from across Los Angeles, the Inland Empire, and Orange County, airing stale series and courtroom drama shows may not be enough.
[flv]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/KDOC Los Angeles New Years Show Eve Show of FAIL 12-31-12[/flv]
Many Los Angeles residents became familiar with KDOC after the station attracted national media coverage for its infamous 2013 New Year’s special hosted by actor and comedian Jamie Kennedy. As viewers watched the slow motion train wreck unfold with D-listers like Shannon Elizabeth, they were treated to endless technical issues, dead air, sudden commercials in the middle of interviews, open mics, unbleeped profanity, a stand-up routine not suitable for children or broadcast television, and special musical guests like rappers Bone Thugs-n-Harmony who dropped F-bombs on live television. Nobody at KDOC thought of pulling the plug, despite violating just about every FCC content regulation. It finally ended with an inebriated Macy Gray hoping to hurry along the festivities and, as the credits rolled, a sudden on-stage fight. Kennedy thanked fast-food chain Carl’s, Jr. for sponsoring the event, which undoubtedly caused extreme discomfort until they could disavow their involvement. An exasperated KDOC engineer assembled this montage of the disaster, which is definitely not suitable to watch at work. (6:23)


 Subscribe
Subscribe
 The federal government is likely to count Bright House’s 2.2 million customers as part of the Time Warner Cable family, at least as far as control of cable programming pricing is concerned. Despite Comcast’s voluntary commitment to keep its national share of the cable TV business under 30 percent with the merger of Time Warner, Comcast hasn’t taken seriously counting the customers of the uninvited cousin – Bright House.
The federal government is likely to count Bright House’s 2.2 million customers as part of the Time Warner Cable family, at least as far as control of cable programming pricing is concerned. Despite Comcast’s voluntary commitment to keep its national share of the cable TV business under 30 percent with the merger of Time Warner, Comcast hasn’t taken seriously counting the customers of the uninvited cousin – Bright House.
 While Comcast is excited about the proposition of transitioning Time Warner Cable customers away from the current mixed analog-digital platform to an all-digital lineup, Time Warner Cable customers have paid less and avoided costly, unwanted extra equipment as a result of the choices consciously made by Time Warner Cable.
While Comcast is excited about the proposition of transitioning Time Warner Cable customers away from the current mixed analog-digital platform to an all-digital lineup, Time Warner Cable customers have paid less and avoided costly, unwanted extra equipment as a result of the choices consciously made by Time Warner Cable. On January 1, 2013 Comcast began informing subscribers a new $1.99/month “additional outlet service charge,” now applied for each DTA installed. [7]
On January 1, 2013 Comcast began informing subscribers a new $1.99/month “additional outlet service charge,” now applied for each DTA installed. [7] Since Thomas Rutledge was hired on as CEO at Charter Communications, a steady stream of his former colleagues from Cablevision’s executive suites have followed him to his new employer.
Since Thomas Rutledge was hired on as CEO at Charter Communications, a steady stream of his former colleagues from Cablevision’s executive suites have followed him to his new employer. Nuzzo has been with Cablevision since 1986, so his sudden choice to leave, along with other long-time Cablevision executives, continues to fuel speculation Cablevision won’t be around much longer, especially if Comcast successfully wins approval to acquire Time Warner Cable. Of course, Wall Street analysts have made similar predictions for years without anything to show for it.
Nuzzo has been with Cablevision since 1986, so his sudden choice to leave, along with other long-time Cablevision executives, continues to fuel speculation Cablevision won’t be around much longer, especially if Comcast successfully wins approval to acquire Time Warner Cable. Of course, Wall Street analysts have made similar predictions for years without anything to show for it.