Suddenlink, one of America’s smaller cable operators, has been undergoing a transformation as it tries to meet expectations of today’s cable subscribers and match whatever phone company competition comes their way. While some of the upgrades are customer-friendly, others pose ominous signs for the future — particularly with respect to Internet Overcharging broadband customers.
Suddenlink, one of America’s smaller cable operators, has been undergoing a transformation as it tries to meet expectations of today’s cable subscribers and match whatever phone company competition comes their way. While some of the upgrades are customer-friendly, others pose ominous signs for the future — particularly with respect to Internet Overcharging broadband customers.
Let’s explore:
The Good — New Broadband Speeds, New DVR, New Investments
In parts of Suddenlink’s service area, particularly in Texas, the company is moving most of its cable service to a digital platform. This transition is designed to open up additional space for more HD channels, keep up with broadband demands, and open the door for additional on-demand programming.
In Nacogdoches, Suddenlink announced it was adopting an all-digital TV lineup. Starting this week, the company is offering subscribers free digital adapters — also known as “DigitaLinks,” to enable continued viewing on analog television sets that do not have a set top box or digital tuning capability. Every subscriber purchasing more than the broadcast basic package (that only includes local stations and a handful of cable networks) will either need a digital tuner-ready television, a set top box, or a DigitaLink device to continue watching.
What is good about this transition is that Suddenlink is not charging customers a monthly fee for the adapters, either now or in the future. That contrasts with other cable companies like Comcast and Time Warner Cable that have handed customers a set top box or a digital adapter they will begin charging for after a year or two.
Suddenlink expects to invest nearly $120 million this year in Texas, and by the end of the year will have invested nearly a half-billion dollars in the state since 2006.
Texas is extremely important to Suddenlink. The third largest cable company in Texas serves about 450,000 households and approximately 27,000 business customers in Amarillo, Lubbock, Abilene, Bryan-College Station, Midland, San Angelo, Georgetown, Tyler, Victoria, Conroe, Kingwood and Nacogdoches.
The company has also lit new fiber connections to handle data communications, primarily for business customers, and is upgrading its broadband service to fully support DOCSIS 3, which will deliver faster speeds and less congested service.
Customers in the state are also among the first to get access to a new and improved DVR box built on a TiVo software platform. Suddenlink’s “Premiere DVR” service ($17/mo) is now available in Midland, Floydada, Plainview, Amarillo, Canyon, and Tulia.
The Bad — “Suddenlink Residential Internet Service is for Entertainment” Purposes Only

The Humboldt County, Calif. Journal's "Seven-o-heaven" comic strip commented on Suddenlink's problems. (Click the image to see the entire strip.)
Do you take your broadband service seriously, or is it simply another entertainment option in your home? If you answered the latter, this story may not be so surprising.
In Humboldt County, Calif., broadband users started noticing their favorite web pages stopped updating on a regular basis. At one point, a blogger in McKinleyville noticed he couldn’t manage to post comments on his own website. But things got much worse when several web pages started reaching customers with other users’ names (and occasionally e-mail addresses) already filled in on login screens and comment forms.
It seems Suddenlink started to cache web content in the far northern coastal county of California, meaning the first customer to visit a particular website triggered Suddenlink’s local servers to store a copy of the page, so that future customers headed to the same website received the locally-stored copy, not the actual live page.
But the caching software went haywire.
Web visitors began to receive mobile versions of web sites even though they were using home computers at the time. Some were asked if they wanted to download a copy of a web page instead of viewing it. And many others discovered websites were customized for earlier visitors.
While the caching problem was irritating, the privacy breaches Suddenlink enabled were disturbing, as was the initial total lack of response from Suddenlink officials when the problem first started in late January.
The Journal finally reached a representative who provided this explanation:
Suddenlink Senior Vice President of Corporate Communications Pete Abel knew that a cache system had recently been installed in Humboldt County, but was unaware of the particular problems reported by users. After speaking with the Journal and other Suddenlink employees, though, he released a statement explaining what appeared to have happened.
According to the release, the cache system was installed in Humboldt County on Thursday, Jan. 27 — the very day that users began experiencing problems — and was intended as an interim solution to relatively low Internet speeds in Humboldt County. The system, it said, was able to cache only unsecure websites — those which, unlike almost all reputable banking or commerce systems — do not encrypt communications. But the company eventually discovered the problems that its customers had been reporting and, having fruitlessly worked with its vendor to find a solution, turned the system off on Monday.
“The good news is that secure Web site pages will not have been cached,” Abel said in a follow-up call to the Journal. “And I have been assured 100 ways from Sunday that never would have happened.”
Andrew Jones, who runs a blog with his Suddenlink broadband account, tried to opt out of the web caching and received an interesting response, in writing, from a Suddenlink representative. He was told he could not opt out of cached web pages with a residential account because, “the residential service is for entertainment only.”
Jones was told he would have to upgrade to a business account to escape the cache.
“If a small local radio station intermittently went off air for multiple days, the radio host would be apologizing and explaining the situation,” Jones wrote the Journal. “If a large utility company experienced sporadic power outages, people could hear a recording on a toll-free number to learn the cause and about ongoing repairs. What does an Internet provider do when web access becomes spotty and begins serving customers old copies of web pages? The company gets back to you in a couple days and suggests you pay more if you don’t like its recently degraded services.”
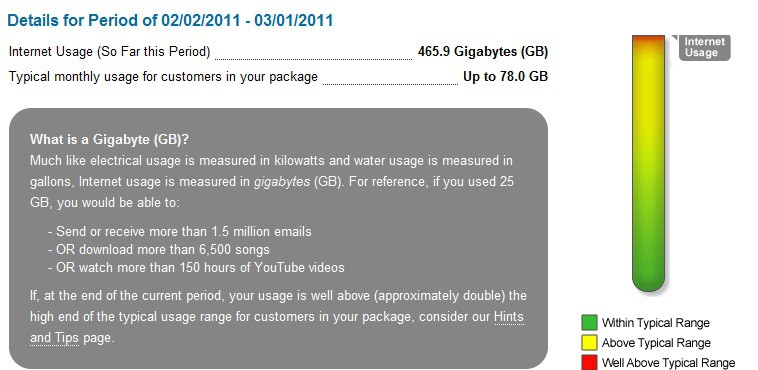
The Ugly — Suddenlink’s New Usage Meter Suggests 43GB is An Appropriate Amount of Usage for Standard Internet, 87GB is Plenty for Their $60 Premium Package
Although Suddenlink has not formally adopted an Internet Overcharging scheme of usage caps or metered billing, the company is sending automated e-mail messages to customers who exceed what they call “typical monthly usage for customers in your package.” The e-mail tells customers they may be infected with a virus or someone else could be using your connection without your permission. Boo! For the uninitiated, this kind of message can bring fear that their computer has been invaded, either with malicious malware or the neighbor next door.
Customers have also received letters in the mail from the company telling them to check out their new “usage meter.” Several have been sharing how much they’ve racked up in usage during the month on Broadband Reports. One customer managed 243GB while another looking at the company’s super premium 107/5Mbps package managed a whopping 786GB.
Although the wording of the message has strenuously avoided telling customers they are wrong for this amount of usage, the implication is clear to many: they are counting your gigabytes and identifying the outliers. One customer called it Suddenlink’s “You’re actually using your connection, and we really wish you wouldn’t”-message.
“No one with an ounce of sense would pay for a 20/3Mbps connection and only use 78 GB in a month. Let’s hope they’re just making cute suggestions, not easing us into a cap, because that just won’t fly,” wrote one West Virginia customer.
Another in Georgetown, Texas did the math and made it clear 43GB better not turn out to be a cap because it means customers can barely use the service they are paying for.
“It’s way too low. I got 10Mbps [service] because of price/value and not because I use less than 43GB,” he writes. “[Even] if I downloaded at 1.25MB/s for 30 days straight (1.25 * 2592000 seconds) I could [still] grab 3.164TB.”
Meanwhile, some controversy over the quality of Suddenlink’s service during the upgrade process had some residents in Cushing, Okla., up in arms at a recent city meeting. Lorene Clyde complained Suddenlink’s “new and improved” service is worse than ever.
“I’m tired of paying for a service I’m not getting,” Clyde said. “And the Suddenlink commercials – they are like rubbing salt in a wound.”
KUSH-AM reporters were on hand to cover the event, noting Clyde was not the only one complaining. The radio station noted that “the buzz around town echoes her sentiments – from the ‘mildly irritated’ to the ‘downright mad’ – citizens have been complaining. Not only have they been complaining to Suddenlink – as difficult as that may be (the call center is in Tyler, Texas) – but to city leaders.”
What Clyde and others may not have realized is that Suddenlink officials were in attendance and were able to apologize for the problems, but a growing consensus among consumers and city leaders is that a broad-based refund for the poor service was warranted.
Commissioner Joe Manning said while he appreciated the promise to figure out the problem, it wasn’t good enough to just apologize and promise – that subscribers’ bills should be adjusted to reflect the poor service.
Commissioners Carey Seigle and Tommy Johnson agreed with Manning. Seigle pointed out it would be “good P.R.” to give some sort of rebate across the board to subscribers while Johnson complained that the original “upgrade” was only going to take a few weeks and now 8 months later – things are not better, but worse, noted the radio station.
Suddenlink officials on hand said they did not have that kind of authority, but continued to promise things are going to get better. “I pledge to you,” one said, “We will find it [the problem] and fix it.”
[flv]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/KJTV Lubbock Borrowing Wi-Fi 2-7-11.flv[/flv]
KJTV-TV in Lubbock, Texas talked with Suddenlink about the growing trend of neighbors “borrowing” neighbors’ unsecured Wi-Fi networks. Other than the accidental recommendation that consumers should “invest in Internet spyware” to keep your computer safe, the report does a fair job of shining a light on a practice that could have financial consequences if the provider implements an Internet Overcharging scheme. (2 minutes)


 Subscribe
Subscribe