Comcast is being sued for deceptively advertising cable packages at a low price, but actually charging much more because of compulsory “junk fees” that customers cannot avoid.
Comcast is being sued for deceptively advertising cable packages at a low price, but actually charging much more because of compulsory “junk fees” that customers cannot avoid.
Plaintiffs’ lawyers Dan M. Hattis of Bellevue, Wash., and Jason Skaggs of Palo Alto, Calif., jointly brought the class action case against the cable company, asking a judge to force Comcast to stop charging the fees and return all of its “unjust profits” to impacted subscribers.
“Comcast promises to charge customers a fixed monthly price for the service plans, but in fact Comcast charges a much higher rate for those plans via concealed and deceptive ‘fees’ which Comcast intentionally disguises in both its advertising and in its customer bills,” the attorneys complain. “These illegal and deceptive fees, which Comcast calls the Broadcast TV Fee and the Regional Sports Fee, earn Comcast over $1 billion each year, accounting for approximately 15% of Comcast’s annual profits.”
But in fact Comcast’s bill padding goes well beyond its TV and sports programming surcharges. No other cable company has mastered the art of the surcharge and fee better than America’s largest cable operator. Consumer advocates in California complain those fees can now cost an average subscriber in that state more than $40 a month.
 “Although Charter Communications and Cox — California’s other major cable operators — also charge many of these fees, Comcast pioneered most of them and charges more than any other cable operator,” claimed Geoff Nawasaki, a San Mateo resident that has filed complaints against Comcast for several years. “A class action lawsuit is long overdue.”
“Although Charter Communications and Cox — California’s other major cable operators — also charge many of these fees, Comcast pioneered most of them and charges more than any other cable operator,” claimed Geoff Nawasaki, a San Mateo resident that has filed complaints against Comcast for several years. “A class action lawsuit is long overdue.”
Once Comcast establishes a new fee or surcharge, the company often boosts those fees dramatically over a very short time. Vaughn Aubuchon has been tracking Comcast’s rates in the Monterey Bay area of central California since 2010 and has documented Comcast routinely increasing its junk fees by as much as 1,000%. But most regulators and members of Congress may not realize how much customer bills are increasing, because the rate card Comcast shares with Washington and the general public doesn’t typically include the extra fees.
Aubuchon has documented significant spikes in Comcast’s prices, even though the company is still promoting packages costing $79-89 a month for new customers. But once those customers open their first bill, the advertised price no longer matters.
Hattis and Skaggs’ 2016 lawsuit documents Comcast’s online order system making no mention of its mandatory surcharges and fees. In fact, even Comcast’s fine print fails to mention the exact amount customers will pay in surcharges. According to Comcast, you have to already be a Comcast customer to review your local rates.
Aubuchon’s rate tracking shows just how lucrative Comcast’s billing tactics have become to the cable operator, especially since 2014:
- XFINITY TV cost $80.94 in 2010. As of August, the rate is now $102.98 — more than $20 a month more.
- XFINITY INTERNET cost $47.95 including the $5 modem rental fee in 2010. Today, that price is $68.95 a month, and the modem rental fee has doubled. That’s another $20 more a month.
- Comcast now charges Aubuchon $6 a month for its Broadcast TV Surcharge and $5 a month for sports programming — an extra $11 month that wasn’t there in 2010.
- After adding up all the fees and surcharges, Aubuchon’s bill went from $135.58 in 2010 to $196.65 today — $62.23 more a month.

Aubuchon
Some of the biggest recent hidden rate hikes have come from Comcast’s Broadcast TV Fee and Regional Sports Fee.
“In the Sacramento area in July 2016, Comcast increased the Broadcast TV Fee by 54% from $3.25 to $5.00, and tripled the Regional Sports Fee from $1.00 to $3.00,” the lawsuit notes. “Then, just three months later in October 2016 Comcast increased the fees yet again to $6.50 for the Broadcast TV Fee and $4.50 for the Regional Sports Fee.”
“Comcast has admitted these invented fees are actually just price increases for broadcast channels and sports channels in its cable television packages,” the lawsuit claims. “But Comcast intentionally does not include the cost of these fees in its advertised or quoted rates for those channel packages, in order to mislead customers into thinking that they will pay less than Comcast will actually charge them.”
The plaintiffs also argue Comcast is intentionally deceptive to customers questioning the ballooning fees on their cable bills.
“Comcast staff and agents explicitly lie by stating that the Broadcast TV Fee and the Regional Sports Fee are government-related fees or taxes over which Comcast has no control.”
A Guide to Comcast’s Junk Bill-Padding Fees
- Broadcast TV Fee (up to $7.50): Ostensibly the cost of retransmission consent fees required to carry free, over the air stations on Comcast’s lineup. The amount varies depending on the fees paid in each local market, with a significant likelihood Comcast rounds those amounts up in ‘friendlier’ $0.25 increments. Introduced in 2014.
- Digital Adapter ($3.99): Originally $1.99/mo when introduced in 2014, the fee covers the rental of a basic set-top box to continue receiving Comcast’s encrypted digital cable TV service on older “cable-ready” analog televisions that did not require a cable box in the past.
- Gateway Rental ($10): This is the monthly rental fee for your cable modem, “gateway,” or Wi-Fi enabled router. You can buy your own equipment and avoid this fee. Recently, Comcast has offered customers a waiver of equipment charges if they upgrade to an X1 set-top box. But in practice the rental fees are stopped for your existing equipment only because Comcast has started charging rental fees for the new equipment it bundles with the upgrade.
- HD/DVR Rental Fees (up to $10 a month for equipment you cannot buy outright yourself).
- HD Technology Fee ($9.95): for viewing HD content on a set-top box you already pay up to $10 a month to use.
- Service Protection Plan ($5.99): Was $1.45 (or less) per month for years until Comcast started hiking the price five years ago. Went from $1.99 in early 2012 to $5.99 in August 2017. Many customers sign up out of fear they will be charged between $36.50-$70 for a home visit from a Comcast technician dealing with a service problem. In reality, all the Service Protection Plan covers for certain is inside wiring that does not travel within a wall and protection from in-home service call fees.
- Regional Sports Fee (up to $5): A way to pass on sports programming costs to every subscriber without boosting the published rate for cable television.
Comcast’s Service Protection Plan = “Service Call Extortion Insurance”
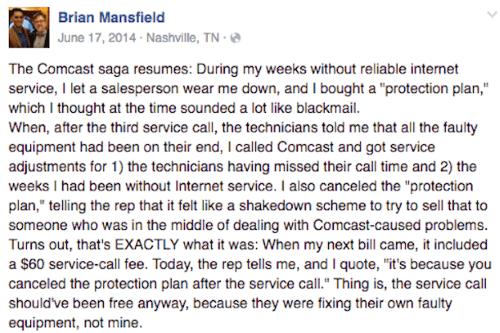 Comcast’s $5.99/month Service Protection Plan has been called “extortion insurance” by some customers who buy the plan to avoid Comcast’s notorious service charges for in-home service calls. Unlike many other cable companies, Comcast charges customers to visit their homes for any reason other than a true, company-caused service outage. A 2016 lawsuit in Washington alleged Comcast’s process for determining whether a service call is charged or free is subjective and frequently at the whim of the technician, who enters “fix codes” at the end of a service call. Some “fix codes” are free, others trigger service call visit fees. The lawsuit claims, “Comcast does not formally train the technicians on what each fix code means.”
Comcast’s $5.99/month Service Protection Plan has been called “extortion insurance” by some customers who buy the plan to avoid Comcast’s notorious service charges for in-home service calls. Unlike many other cable companies, Comcast charges customers to visit their homes for any reason other than a true, company-caused service outage. A 2016 lawsuit in Washington alleged Comcast’s process for determining whether a service call is charged or free is subjective and frequently at the whim of the technician, who enters “fix codes” at the end of a service call. Some “fix codes” are free, others trigger service call visit fees. The lawsuit claims, “Comcast does not formally train the technicians on what each fix code means.”
Comcast customers that have faced the sting of an unwarranted service call charge often readily agree to Comcast’s sales push for its Service Protection Plan, which normally waives those fees. It doesn’t take much to trigger those fees. The Washington lawsuit noted that if a Comcast technician talks to the customer about how to use their DVR, program a remote control, reset their cable modem, or use Wi-Fi, it is considered “customer education,” which results in a service call charge.
“Thus, if a technician fixes a broken Comcast cable box but also provides ‘customer education’ during the service call, the customer will be charged for the service call if the technician applies the customer education code because customer education fix codes are chargeable,” the lawsuit said. “This occurred 2,078 times between 17 June 2014 and June 2016 [in Washington State].”
Customer education fees are waived for those who pay for Comcast’s Service Protection Plan.
 Cable One, the Phoenix-based mid-sized cable operator serving some of the poorest communities in the country is charging some of the nation’s highest prices for broadband service, raking in an unprecedented 47% margin in the fourth quarter of 2017, the highest in the cable industry.
Cable One, the Phoenix-based mid-sized cable operator serving some of the poorest communities in the country is charging some of the nation’s highest prices for broadband service, raking in an unprecedented 47% margin in the fourth quarter of 2017, the highest in the cable industry.


 Subscribe
Subscribe [
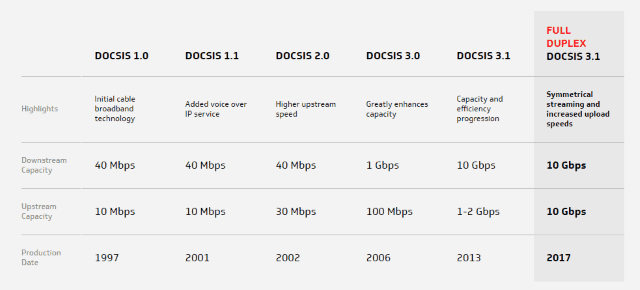
[ CableLabs has resolved the cable industry’s long-standing competitive disadvantage with fiber optic broadband with the introduction of a Full Duplex (FDX) DOCSIS 3.1 specification.
CableLabs has resolved the cable industry’s long-standing competitive disadvantage with fiber optic broadband with the introduction of a Full Duplex (FDX) DOCSIS 3.1 specification.