Time Warner Cable’s approval of its request to offer regulated “digital phone” service in New York has been quickly followed by an appeal for deregulation to loosen rules covering disconnection for non-payment and reduced service quality standards.
Time Warner Cable’s approval of its request to offer regulated “digital phone” service in New York has been quickly followed by an appeal for deregulation to loosen rules covering disconnection for non-payment and reduced service quality standards.
The cable operator now qualifies — as a designated Eligible Telecommunications Carrier (ETC) — for significant federal and state subsidies in return for providing discounted Lifeline telephone service for the state’s poorest residents.
The cable industry has traditionally escaped regulation and oversight with claims “digital phone” Voice over IP (VoIP) products are “unregulated information services.”
In March, the New York Public Service Commission approved a petition filed by subsidiary Time Warner Cable Information Services (NY) LLP (TWCIS-NY), to begin offering regulated telephone service to the company’s 1,235,710 phone customers in New York.
As a result, Time Warner agreed to a range of oversight and service standard requirements. But on May 1 — less than two months later — Time Warner filed a new petition with the PSC requesting deregulation and exemption from several provisions the company initially agreed to follow.
 “Now that it is concededly a regulated telephone service provider, Time Warner is acting like other regulated phone companies, in that it immediately is seeking to relax the rules designed to protect customers,” writes Gerry Norlander from the Public Utility Law Project of New York (PULP), a consumer protection group.
“Now that it is concededly a regulated telephone service provider, Time Warner is acting like other regulated phone companies, in that it immediately is seeking to relax the rules designed to protect customers,” writes Gerry Norlander from the Public Utility Law Project of New York (PULP), a consumer protection group.
Not so, says the cable company.
“In order to offer the best telecommunications service to its customers and expand this customer base, TWCIS-NY respectfully requests that the Commission grant the waivers discussed in this Petition,” the company writes.
The changes Time Warner requests would make it easier for the cable company to disconnect service for late or non-payment, allow Time Warner to avoid distributing unwanted paper telephone directories, and escape oversight of its phone service for all but the most critical “core” customers with special needs.
Your Partial Payment Will Not Necessarily Prevent Us From Cutting Off Your Phone Line
 The Telephone Fair Practices Act (TFPA), prohibits regulated phone companies from shutting off phone service for late/non-payment outside of normal business hours, Fridays after 1pm, weekends, and holidays:
The Telephone Fair Practices Act (TFPA), prohibits regulated phone companies from shutting off phone service for late/non-payment outside of normal business hours, Fridays after 1pm, weekends, and holidays:
(d) Suspension or termination of service–time. A telephone corporation complying with the conditions set forth in this section may suspend or terminate service to a residential customer for nonpayment of bills only between the hours of 8 a.m. and 7:30 p.m., Monday through Thursday, and between 8:00 a.m. and 3:00 p.m. on Friday, provided such day or the following day is not:
(1) a public holiday, as defined in the General Construction Law;
(2) a day on which the main business office of the telephone corporation is closed for business; or
(3) during the periods of December 23rd through December 26th and December 30th through January 2nd.
Time Warner Cable claims those limitations are too much, and “for its customers’ convenience, TWCIS-NY respectfully requests […] to extend these hours.”
If approved, Time Warner claims it will make your life easier if they can cut you off at their convenience — between the hours of 8:00am and 9:00pm, Monday through Friday, and between 8:00am and 5:00pm on Saturday.
Those times coincidentally match the hours technicians are now dispatched to collect equipment and shut off service for deadbeat customers.
Time Warner says people are often busy or not at home during the day and it would make more sense to coordinate the surrender of service when people are available to hand over equipment. Unfortunately, Time Warner’s preferred hours often fall outside of the calling hours at the Public Service Commission, which maintains a ‘last resort hotline’ for customers about to have their service disconnected.
‘Time Warner Cable Punishes Late Payers With Telephone Service Suspensions and Terminations on a “Massive” Scale’
Unlike cable television and broadband, New York designates telephone service as an essential utility, and regulators take every step to maintain service wherever possible.
Under rules originally adopted when consumers chose both a local and long distance phone company that put all of your charges on a single monthly invoice, regulators sought to protect landline service when customers did not pay the full amount due. Under those rules, partial payments are allocated first to past due charges from the local phone company, then past due charges for regional long distance or local calling, then charges billed by your long distance carrier, and then everything else.
Since your local phone company has the power to cut off your dial tone for late payment, making sure they were first in line to get paid usually kept your phone line working.
“It Appears that Time Warner Has Increased its Reliance Upon Telephone Service Suspensions and Terminations as a Tool to Enforce Customer Payment Obligations.”
 According to data provided by Time Warner Cable in response to PULP information requests, during the month of March, 2012 Time Warner Cable sent 68,134 shutoff notices to Time Warner phone customers in New York. The threats worked for the majority of those customers. Only 17,218 were eventually disconnected after the shutoff deadline passed.
According to data provided by Time Warner Cable in response to PULP information requests, during the month of March, 2012 Time Warner Cable sent 68,134 shutoff notices to Time Warner phone customers in New York. The threats worked for the majority of those customers. Only 17,218 were eventually disconnected after the shutoff deadline passed.
Since then, shutoffs and suspensions have soared. By July 2013, Time Warner mailed 146,026 shutoff notices and followed through with 42,777 disconnects, increases of 114% and 148%, respectively.
“As a consequence, interruption of phone service for bill collection purposes has reached massive proportion,” says PULP. “It appears that Time Warner has increased its reliance upon telephone service suspensions and terminations as a tool to enforce customer payment obligations. In the 12 months ending July 2013, Time Warner terminated or suspended telephone service on 592,250 occasions for bill collection purposes. Of that number, telephone service was reinstated after an interruption for collection purposes on 461,268 occasions. Thus, 130,982 or 22% of the customers terminated were not promptly reinstated.”
Those figures concern PULP because it suggests many disconnected customers are now without phone service, swelling the “unacceptably large number of New York households lacking telephone service.”
New York now ranks fourth from the bottom of all states in the most recent FCC Universal Services Monitoring Report of telephone subscribers.
Verizon’s Request to “Streamline” the Payment Process Gives Time Warner Cable the Same Idea
In 2010, Verizon New York successfully petitioned the PSC to streamline that payment allocation system. Few people bother with choosing a long distance carrier these days because most phone companies now offer unlimited long distance as part of a bundled service package. Verizon asked to simplify things so that Verizon New York got paid first and everything else came second.
Time Warner is seeking a variation on that same theme, requesting the PSC allow it to allocate partial payments first to telephone service, with the rest distributed to cover charges for broadband and cable television service.
While that is good news for your Time Warner phone line, it is bad news for your broadband and television service which can still be interrupted for non-payment because your partial payment was applied to phone service above all else.
 Customers are unlikely to be aware of this, however. Time Warner Cable bills include a regular notice that if a customer is in arrears for any Time Warner Cable service, telephone service may be shut off.
Customers are unlikely to be aware of this, however. Time Warner Cable bills include a regular notice that if a customer is in arrears for any Time Warner Cable service, telephone service may be shut off.
PULP argues the cable company should let customers decide which services are most important to keep up and running during an emergency.
“For example, a customer might want to jettison cable TV and keep the Internet on to hunt for jobs during a spell of unemployment or other household financial crisis,” writes Norlander. “While the bills include separate items for cable TV, broadband, and telephone services, there is no information given in the bills on how customers can, if they are in arrears, keep the service they pay for with a partial payment.”
Indeed, there is no provision on Time Warner’s website or on its paper bill payment coupon to allocate which services a customer wishes their partial payment to be applied to first.
Time Warner Cable argues it gives late paying customers every opportunity to either make up past due payments or negotiate a payment plan before any service is interrupted.
 “Customers have the opportunity to walk into the local [cable] office and make a payment during these extended hours,” Time Warner argues. “They also have the opportunity to pay online and over the phone 24 hours a day, as well as paying cable representatives directly when they arrive at the customer’s premises to disconnect service. TWCIS-NY believes that streamlining of the rules for disconnection of phone and cable services will make the Commission’s rules more consistent across the board and less confusing for customers.”
“Customers have the opportunity to walk into the local [cable] office and make a payment during these extended hours,” Time Warner argues. “They also have the opportunity to pay online and over the phone 24 hours a day, as well as paying cable representatives directly when they arrive at the customer’s premises to disconnect service. TWCIS-NY believes that streamlining of the rules for disconnection of phone and cable services will make the Commission’s rules more consistent across the board and less confusing for customers.”
We Shouldn’t Have to Provide Printed Residential Phone Books We Didn’t Offer Anyway
Time Warner Cable wants to opt out from distributing printed copies of residential telephone directories it doesn’t publish.
When the company provided unregulated telephone service, it never had to offer customers a phone book. But in its new life as a regulated provider, New York requires phone companies to offer, upon request, a printed telephone directory:
Each service provider shall distribute at no charge to its customers within a local exchange area, a copy of the local exchange directory for that area, and one additional copy shall be provided for each working telephone number upon request. A copy shall be filed with the Commission.
Nobody has formally opposed Time Warner Cable’s proposed alternative: distributing residential listings only to customers who specifically request them in print or on CD-ROM.
Most customers don’t realize Time Warner Cable used to outsource most of its telephone service operation to Sprint. In addition to providing VoIP service, Sprint relied on dominant local telephone companies to provide phone books to Time Warner phone customers. In return, Sprint passed along customers’ names, addresses and phone numbers to phone companies like AT&T, Verizon, Frontier, CenturyLink and Windstream to be incorporated into those directories.
In 2010, Time Warner announced a four-year transition project to take its telephone service “in-house.”
Will All of This Competition, Oversight Rules Should Be Relaxed; If Customers Don’t Like Us, They Can Go Somewhere Else
Virtually every telephone company in New York agrees with the assessment Verizon has made for years — if a phone company does not provide excellent service, subscribers will simply switch to a competitor, negating the need for oversight of service quality standards.

Verizon paved the road Time Warner Cable is driving down to offer NY’ers less-regulated phone service.
The PSC agreed, reducing requirements for service outage reporting and other documented service issues. Today, Verizon only reports incidents involving “core” customers — low-income Lifeline subscribers, “special needs” customers including the elderly, those with serious medical conditions, the disabled and the visually impaired. Core customers also include those with no competitive service providers available to them.
Time Warner Cable wants a modified version of the Verizon “core customer” standard applied to its cable phone service — one that defines core customers as those with Lifeline service or special needs.
Time Warner does not want to include those without competitive alternatives and seeks an exemption from any reporting requirements until it signs up at least 5,000 accounts designated as “core customers.” That could take a while. PULP obtained records from Time Warner Cable showing as of Aug. 7 the company has only signed up 149 telephone customers it defines as “core customers.”
The cable company may be thinking of the future. Verizon Communications has made its intentions clear it wants to abandon rural landline service in favor of questionably regulated wireless Voice Link service. The idea that a cable company provides landline service in an area the local phone company no longer does is unprecedented in New York, but perhaps for not much longer.
If Time Warner Cable successfully argues “core customers” need not include those without competing alternatives, the PSC may unintentionally hand the cable operator a rural telephone monopoly without quality of service oversight in some communities.


 Subscribe
Subscribe
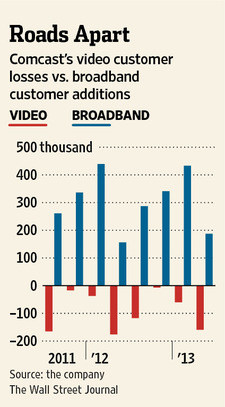
 Cablevision has tried to avoid being picked off by the likes of neighboring Comcast or Time Warner Cable by trying (and failing) to go private in 2005 and 2007. Cablevision’s service area formerly extended well into western New York — especially in small communities and rural towns, before selling out to Time Warner Cable and retreating to its home base of Long Island, a few New York City boroughs, and parts of Connecticut and New Jersey.
Cablevision has tried to avoid being picked off by the likes of neighboring Comcast or Time Warner Cable by trying (and failing) to go private in 2005 and 2007. Cablevision’s service area formerly extended well into western New York — especially in small communities and rural towns, before selling out to Time Warner Cable and retreating to its home base of Long Island, a few New York City boroughs, and parts of Connecticut and New Jersey. Cablevision has recently taken steps that only make a sale more likely, shutting down ancillary businesses like Newsday Westchester, OMGFAST! — a start-up wireless broadband provider in Florida, and selling off Clearview Cinemas, AMC Networks, and reducing holdings in sports programming.
Cablevision has recently taken steps that only make a sale more likely, shutting down ancillary businesses like Newsday Westchester, OMGFAST! — a start-up wireless broadband provider in Florida, and selling off Clearview Cinemas, AMC Networks, and reducing holdings in sports programming. If Time Warner Cable is concerned about the rising cost of cable television, it sure didn’t show it after sources revealed the cable company quickly accepted CBS’ demands for more compensation but is refusing to budge until it wins rights to show CBS programming on mobile platforms.
If Time Warner Cable is concerned about the rising cost of cable television, it sure didn’t show it after sources revealed the cable company quickly accepted CBS’ demands for more compensation but is refusing to budge until it wins rights to show CBS programming on mobile platforms.

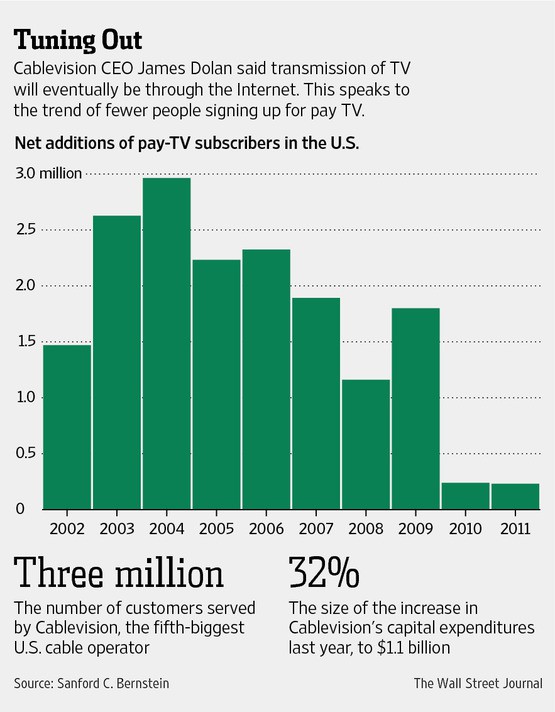 Existing customers like the changes, but don’t appreciate the price hikes that have accompanied them. Wall Street has the exact opposite point of view, welcoming increased revenue from rate hikes, but concerned about the company’s spending. Investors complain Cablevision’s returns are well below those of other cable operators which don’t face the Verizon FiOS juggernaut.
Existing customers like the changes, but don’t appreciate the price hikes that have accompanied them. Wall Street has the exact opposite point of view, welcoming increased revenue from rate hikes, but concerned about the company’s spending. Investors complain Cablevision’s returns are well below those of other cable operators which don’t face the Verizon FiOS juggernaut.