 With billions of dollars in new revenue and royalties to be made, Qualcomm and some members of the wireless industry are pushing regulators to quickly approve a new version of LTE wireless technology that will share many of the same frequencies used by home and business Wi-Fi networks, creating the potential for speed-killing interference.
With billions of dollars in new revenue and royalties to be made, Qualcomm and some members of the wireless industry are pushing regulators to quickly approve a new version of LTE wireless technology that will share many of the same frequencies used by home and business Wi-Fi networks, creating the potential for speed-killing interference.
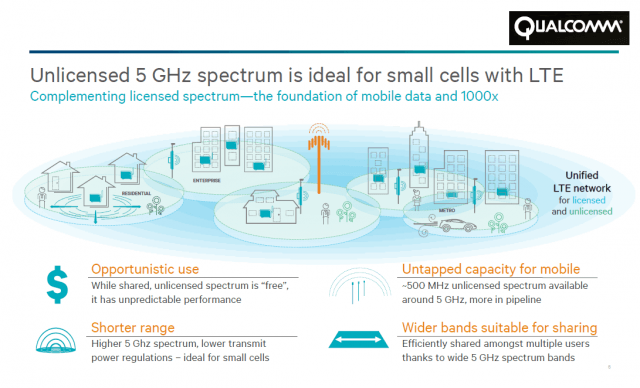
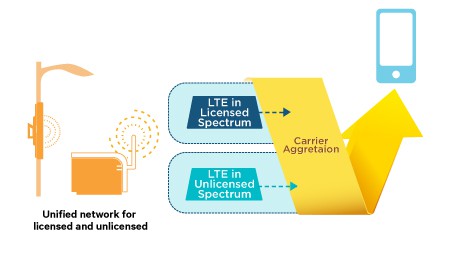
Wireless operators believe LTE-Unlicensed (LTE-U) could be used to offload much of the growing wireless data traffic off traditional 4G LTE wireless data networks. With the cost of securing more wireless spectrum from regulators growing, LTE-U technology would allow operators like AT&T, Verizon, Sprint and T-Mobile to use the U-NII-1 (5150-5250MHz) and U-NII-3 (5725-5850MHz) unlicensed bands currently used for Wi-Fi to deliver high-speed wireless broadband traffic to their customers.
Qualcomm and Ericsson, behind the newest iteration of LTE, have a vested interest promoting it as the ideal choice for metrocell, indoor enterprise, and residential small cell applications. Every manufacturer incorporating LTE-U technology into everything from carrier-owned microcells to smartphones will owe royalty payments to both companies. With billions at stake, Qualcomm is doing everything possible to tamp down fears LTE-U signals will create harmful interference to Wi-Fi signals.
[flv]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/CES2015 Qualcomm Demonstrates LTE-U 1-2015.mp4[/flv]
At the Consumer Electronics Show in Las Vegas held in January, a Qualcomm representative went as far as suggesting LTE-U will improve home Wi-Fi service. (5:42)
RCRWireless News:
[Qualcomm] set up a screened room with eight pairs of access points occupying the same channel and added Wi-Fi access-point terminals in one room and LTE-U terminals in another. The results show the average throughput of 3.3Mbps with Wi-Fi alone more than doubled to 6.7Mbps when the LTE-U access point was introduced.
In another test to show that LTE-U is a better neighbor to Wi-Fi than Wi-Fi itself, they took eight Wi-Fi nodes and replaced four of them with LTE-U nodes, the result of which showed a 1.9Mbps increase in average Wi-Fi throughput. In almost every test, the LTE-U enhanced network outperformed traditional Wi-Fi.

Burstein
Industry observer Dave Burstein is concerned advocates of LTE-U are trying to rush approval of the technology without verifying Qualcomm’s non-interference claims.
“The telcos are considering 40 and 80MHz channels that could easily swallow half of more of the Wi-Fi spectrum,” Burstein writes in response to an EE Times article about the technology. “If Wi-Fi is important, that’s a mistake to allow. Advocates are trying to rush it through even though there is not a single independent test or field trial.”
Qualcomm dismisses the interference complaints pointing to its own research showing the two standards can co-exist adequately. But multi-billion dollar wireless companies with nationwide Wi-Fi networks at stake are far less confident. In fact, LTE-U has already divided the two largest wireless carriers in the United States. Verizon Wireless is an original proponent of LTE-U while AT&T has expressed “concern,” a polite way of saying it isn’t happy. What separates AT&T and Verizon Wireless? AT&T has invested in a nationwide network of more than 34,000 Wi-Fi hotspots. Verizon offers just over 5,000, most for FiOS customers or those in especially high traffic venues.
A Stanford University professor with no ties to Qualcomm or the wireless industry privately shared his belief allowing 5GHz Wi-Fi signals to commingle with LTE-U is going to cause problems.
 The development of “Wild West” Wi-Fi has always tracked differently than the licensed cellular/wireless business. Over more than a decade, evolving Wi-Fi standards have come to expect interference from other nearby Wi-Fi signals. In a densely packed city, more than two dozen Wi-Fi signals can easily be found all competing for their own space across the old 2.4GHz and newer 5GHz unlicensed bands.
The development of “Wild West” Wi-Fi has always tracked differently than the licensed cellular/wireless business. Over more than a decade, evolving Wi-Fi standards have come to expect interference from other nearby Wi-Fi signals. In a densely packed city, more than two dozen Wi-Fi signals can easily be found all competing for their own space across the old 2.4GHz and newer 5GHz unlicensed bands.
Wi-Fi proponents credit its robustness to its “politeness protocol.” Before a wireless router or home hotspot fires up its Wi-Fi signal, it performs several tests to check for other users and constantly adjusts performance by backing off when it discovers interference from other signals. That is why a user can receive strong Wi-Fi signals but still endure reduced performance, as the hotspot accommodates nearby hotspots and other traffic.
It works reasonably well, according to Rupert Baines, a consultant at Real Wireless.
“But [Wi-Fi signals] are delicate, and they rely on implicit assumptions that there aren’t other things there (or aren’t too many),” Baines told EE Times. “In effect, they behave as though the unlicensed band were not technology neutral but were Wi-Fi only.”
The intrusion of LTE-U changes everything.
[flv]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/Wireless Week Tuesdays with Roger LTE-Us Gain is Wi-Fis Loss 3-24-15.flv[/flv]
On the March 24, 2015 episode of Tuesdays with Roger, Recon Analytics’ founder Roger Entner talks with Wireless Week about the questions raised as major carriers, including T-Mobile and Verizon Wireless, plan to launch LTE into unlicensed territory. Concerns abound, particularly for consumers and companies who rely on Wi-Fi and don’t want licensed use in unlicensed bands to interrupt that service. (7:31)
Change in and of itself is not necessarily a bad thing, especially if LTE-U is superior to Wi-Fi, and some proponents suggest it is. Jag Bolaria, an analyst at The Linley Group, argues LTE better manages data/call handoff better than Wi-Fi access points can. LTE is also a more efficient spectrum user than Wi-Fi.
Last week, South Korea’s LG U+ demonstrated LTE-U was capable of 600Mbps speed, eight times faster than traditional LTE. But to accomplish that level of speed, LG U+ had to occupy 60MHz of bandwidth in the 5.8GHz band and allocate an extra 20MHz from its traditional LTE service. The company plans to further expand its use of South Korea’s 5.8GHz unlicensed band by occupying 80MHz of it to further boost speeds to 750Mbps. But the company did not say how the tests affected others sharing the same frequencies.
If LTE-U is superior, then why not gradually move every user towards the technology and away from Wi-Fi?
Aptilo Networks AB CEO Torbjorn Ward answers LTE-U is a solution in search of a problem.
“I think LTE on unlicensed sounds like a good idea if it wasn’t for the fact that there are four billion devices on Wi-Fi out there,” he told Light Reading, noting that 802.11ac can already run at 100Mbps, so there’s little need for the LTE boost. “I think when it comes to unlicensed, you can do a longer range with LTE, but I don’t see the full benefit.”
That does not seem to matter to LTE-U’s developers or cell phone companies that lack robust Wi-Fi networks of their own.

In the original Qualcomm/Ericsson proposal, both companies promote the fact they could launch LTE-U in the unlicensed Wi-Fi bands “as-is.” That is a big problem for AT&T and other Wi-Fi users because LTE-U evidently employs few, if any protection protocols in its initial specifications for other traffic. Verizon Wireless is reportedly lobbying against the development of interference protection protocols and has publicly asserted its interest in deploying LTE-U regardless of other users.
“In [the] USA, there are no requirements for unlicensed deployment that require changes to LTE air interface,” Verizon stated in its proposal: “New Band for LTE deployment as Supplemental Downlink in unlicensed 5.8GHz in USA.”
LTE-Unlicensed has been characterized as “rude” for not avoiding interference to other users.
Clint W. Brown, business development director of mobility wireless connectivity at Broadcom, and a vice-chairman of the Wi-Fi Alliance counters it is premature to approve LTE-U in the unlicensed Wi-Fi band without more testing and information about its interference protocols.
“We’ve heard about the tests they’ve done, but it’s not factual,” Brown told EE Times. We haven’t seen the data and we don’t know how the tests were set up. First, I’d like to see if [LTE-U] can detect low-level signals. Second, I want to make sure it features a ‘Listen before Talk’ decision process so that LTE-U will wait for an opening rather than barging into the conversation already taking place in the unlicensed spectrum. Third, there should be a back-off mechanism, when it sees a collision. “We aren’t aware of any publicly available documents explicitly stating those attributes.”
The Federal Communications Commission has also now taken an interest and issued a public notice asking stakeholders and consumers to share their thoughts on LTE-U and a companion technology known as Licensed Assisted Access (LAA) that would hand off data sessions between a wireless carrier’s traditional 4G LTE network and LTE-U.
The makes the discussion political as well as technical. The FCC traditionally permits industry groups to define standards, but Republican Commissioner Mike O’Rielly now worries the FCC might butt into that process.
“The decision to jump into this space rather casually causes me great concern,” O’Rielly said. “In particular, any step that could insert the commission into the standards work for LTE-U comes with great risk. I will be vigilant in ensuring that the commission’s involvement does not result in taking sides with various stakeholders, hindering technological innovation, or having any say about what technologies should or should not be deployed.”
 For the moment, O’Rielly’s concerns about the FCC are premature as long as a division exists over LTE-U among many of the industry players:
For the moment, O’Rielly’s concerns about the FCC are premature as long as a division exists over LTE-U among many of the industry players:
- Companies FOR LTE-U: Verizon, China Mobile, Qualcomm, Ericsson, NTT DoCoMo, T-Mobile USA, Deutsche Telekom, TeliaSonera, and China Unicom. Equipment manufacturers also in support: Nokia, NSN, Alcatel-Lucent, LG, Huawei, ZTE, Hitachi, Panasonic, and others;
- Companies AGAINST LTE-U (as now defined): Orange, Telefónica, Vodafone, AT&T, Sprint, SouthernLINC, US Cellular, DISH and a handful of vendors.
Burstein also uncovered evidence the wireless industry may be stacking the deck against increased competition and consumers. He found 11 of the world’s largest wireless companies (including AT&T, T-Mobile, and Sprint) quietly colluding on a proposal that would block anyone other than currently licensed LTE users from being able to use LTE-U on a standalone basis. The opaquely-titled proposal, “Precluding standalone access of LTE on unlicensed carriers,” is at least frank about its reasoning: “Standalone deployment in unlicensed spectrum implies drastically different business models from nowadays and might impact the value chain.”
In other words, if consumers are able to get savings from LTE-U using a new generation of non-traditional providers like Republic Wireless or Cablevision’s Freewheel that do not depend primarily on cellular networks, it could cost those 11 traditional wireless companies billions in lost revenue. To stop that, the companies propose requiring a special LAA “guard signal” to stop standalone access of LTE-U. Since only licensed cell phone companies have access to those frequencies, it automatically locks out new upstarts that lack mobile spectrum of their own.
Sneaky insertions like that may be exactly why the Obama Administration’s FCC is being more activist about monitoring the wireless industry, potentially cutting off anti-competitive proposals before they can become adopted as part of a formal technical standard.
[flv]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/Fairness to Wi-Fi and LTE unlicensed 5-8-2015.mp4[/flv]
RCRWireless News gets deep into the development of LTE-Unlicensed and how it will impact cellular infrastructure, Wi-Fi and small cells. (25:39)
 Despite a firm commitment with the Justice Department not to be involved in the day-to-day management of Hulu as a condition of approving Comcast’s merger with NBC/Universal, new revelations suggest Comcast not only promoted the online video service to its partners as a nationwide streaming platform for the cable industry, it also convinced them not to sell the service to a Comcast competitor.
Despite a firm commitment with the Justice Department not to be involved in the day-to-day management of Hulu as a condition of approving Comcast’s merger with NBC/Universal, new revelations suggest Comcast not only promoted the online video service to its partners as a nationwide streaming platform for the cable industry, it also convinced them not to sell the service to a Comcast competitor.


 Subscribe
Subscribe With billions of dollars in new revenue and royalties to be made, Qualcomm and some members of the wireless industry are pushing regulators to quickly approve a new version of LTE wireless technology that will share many of the same frequencies used by home and business Wi-Fi networks, creating the potential for speed-killing interference.
With billions of dollars in new revenue and royalties to be made, Qualcomm and some members of the wireless industry are pushing regulators to quickly approve a new version of LTE wireless technology that will share many of the same frequencies used by home and business Wi-Fi networks, creating the potential for speed-killing interference.

 The development of “Wild West” Wi-Fi has always tracked differently than the licensed cellular/wireless business. Over more than a decade, evolving Wi-Fi standards have come to expect interference from other nearby Wi-Fi signals. In a densely packed city, more than two dozen Wi-Fi signals can easily be found all competing for their own space across the old 2.4GHz and newer 5GHz unlicensed bands.
The development of “Wild West” Wi-Fi has always tracked differently than the licensed cellular/wireless business. Over more than a decade, evolving Wi-Fi standards have come to expect interference from other nearby Wi-Fi signals. In a densely packed city, more than two dozen Wi-Fi signals can easily be found all competing for their own space across the old 2.4GHz and newer 5GHz unlicensed bands.

 For the moment, O’Rielly’s concerns about the FCC are premature as long as a division exists over LTE-U among many of the industry players:
For the moment, O’Rielly’s concerns about the FCC are premature as long as a division exists over LTE-U among many of the industry players:
 Cable’s bad reputation has come home to roost, allowing everyone to assume the worst and see a need to erect protective fences like Net Neutrality to keep cable companies from capitalizing on new fees for Internet usage.
Cable’s bad reputation has come home to roost, allowing everyone to assume the worst and see a need to erect protective fences like Net Neutrality to keep cable companies from capitalizing on new fees for Internet usage. The Cable Show (now known as INTX) is often used by the cable industry to announce and preview new products and services, and at this year’s convention in Chicago, Comcast CEO Brian Roberts used the occasion to introduce the company’s new DOCSIS 3.1 multi-purpose Home Gateway capable of delivering gigabit speeds over its existing hybrid fiber-coax network.
The Cable Show (now known as INTX) is often used by the cable industry to announce and preview new products and services, and at this year’s convention in Chicago, Comcast CEO Brian Roberts used the occasion to introduce the company’s new DOCSIS 3.1 multi-purpose Home Gateway capable of delivering gigabit speeds over its existing hybrid fiber-coax network.
 Comcast customer service horror stories reached a level unparalleled by other cable companies when a Comcast
Comcast customer service horror stories reached a level unparalleled by other cable companies when a Comcast  N.Y. State Assembly Leader Joe Morelle: “The combination of Comcast and Time Warner Cable will create a world-class communications, media and technology company to help meet the increasing consumer demand for advanced digital services on multiple devices in homes, workplaces and on-the-go.”
N.Y. State Assembly Leader Joe Morelle: “The combination of Comcast and Time Warner Cable will create a world-class communications, media and technology company to help meet the increasing consumer demand for advanced digital services on multiple devices in homes, workplaces and on-the-go.” David Cohen, executive vice-president, Comcast: “The combination of Comcast and TWC will create a world-class communications, media, and technology company to help meet the insatiable consumer demand for advanced digital services on multiple devices in homes, workplaces, and on-the-go.”
David Cohen, executive vice-president, Comcast: “The combination of Comcast and TWC will create a world-class communications, media, and technology company to help meet the insatiable consumer demand for advanced digital services on multiple devices in homes, workplaces, and on-the-go.”
