Charter Communications will have to face a courtroom to answer accusations the cable company intentionally sold internet service at speeds it knew it could not provide to its customers in New York.
Charter Communications will have to face a courtroom to answer accusations the cable company intentionally sold internet service at speeds it knew it could not provide to its customers in New York.
New York State Supreme Court Justice O. Peter Sherwood rejected a motion by the cable company to dismiss New York Attorney General Eric Schneiderman’s 2017 lawsuit accusing Time Warner Cable (now owned by Charter) of systematically shortchanging as many as 640,000 New York internet customers by falsely advertising internet speeds it knew it could not deliver, often with at least 900,000 outdated company-provided cable modems incapable of supporting the higher speeds the company promoted.
“Today’s decision by the New York Supreme Court marks a major victory for New York consumers — rejecting every single argument made by Charter-Spectrum in its attempts to block our lawsuit,” said Schneiderman. “This decision ensures that our office can continue to hold Charter-Spectrum to account for its failure to deliver the reliable internet speeds it promised consumers, ripping you off by promising internet speeds it simply could not deliver.”
Charter’s Defense: Spectrum’s Ad Claims for Fast Internet Service are: “Prototypical instances of non-actionable puffery.”
Charter’s lawyers attempted a variety of legal strategies to get Schneiderman’s lawsuit tossed, including undermining the cable company’s own marketing efforts. Lawyers argued the court should ignore Charter’s claims it sold a “blazing fast, super-reliable connection” that could “stream Netflix and Hulu movies and shows effortlessly” as nothing more than “prototypical instances of non-actionable puffery.”
Scheniderman’s office claimed it was much more than that.

N.Y. Attorney General Eric Schneiderman
“Spectrum-TWC failed to maintain enough network capacity in the form of interconnection ports to deliver this promised content to its subscribers without slowdowns, interruptions, and data loss,” stated Schneiderman. “It effectively ‘throttled’ access to Netflix and other content providers by allowing the ports through which its network interconnects with data coming from those providers to degrade, causing slowdowns. Spectrum-TWC then extracted payments from those content providers as a condition for upgrading the ports As a result, Spectrum-TWC’s subscribers could not reliably access the content they were promised, and instead were subjected to the buffering, slowdowns and other interruptions in service that they had been assured they would not encounter.”
Charter also claimed it was not legally responsible for meeting its own advertised speeds because the company only sold speeds “up to” a level, without guaranteeing customers would get the speeds it advertised.
Even if a judge found Charter lacking in its legal defense, lawyers for the company more broadly argued that under FCC Chairman Ajit Pai’s net neutrality order, state courts and regulators had no power to regulate or oversee broadband providers because “regulation of broadband internet access service should be governed principally by a uniform set of federal regulations, rather than by a patchwork of separate state and local requirements,” according to Charter’s attorney Christopher Clark.
Justice Sherwood uniformly rejected all of Charter’s arguments to dismiss the case:
- Improper state venue for the lawsuit: “Spectrum-TWC fails to identify any provision [of law] that preempts state anti-fraud or consumer-protection claims, or reflects any intention by Congress to make federal law the exclusive source of law protecting consumers from broadband providers’ deceptive conduct.”
- False advertising: “This court finds that, contrary to defendants’ contentions, the FCC’s goal of promoting competition through [the Internet Transparency Rule], the FCC stated that the rule was intended to ensure consumers had the “right to accurate information, so [they] can choose, monitor, and receive the broadband internet services they have been promised. New York’s Executive Law and Consumer Protection Act […] require that [providers] refrain from fraud, deception, and false advertising when communicating with New York consumers.
- Netflix/YouTube slowdowns: The issue of interconnection agreements between content providers and Spectrum-TWC are matters for the court to consider because it is not an attempt to regulate those agreements. “Rather, the complaint simply alleges that Spectrum-TWC misled subscribers by claiming that specific online content would be swiftly accessible through its network, while it was simultaneously deliberately allowing that service to degrade […] and failing to upgrade its network’s capacity to meet demand for this content.”
- “Up to” speeds: Spectrum-TWC claimed that advertising speeds “up to” a certain level was not misleading because consumers understood this to mean the maximum speed, not average speed. In Spectrum’s argument, it claimed “reasonable consumers understand this is not a promise of ‘minimum’ performance, but rather ‘maximum’ performance.” But the judge disagreed. “Defendant’s theory is contrary to New York law regarding ‘up to’ claims” when those speeds are “functionally unattainable as a result of the defendants’ knowing conduct.”
Schneiderman’s office is seeking civil fines and restitution from Spectrum-TWC for customers in New York.


 Subscribe
Subscribe
 West Plains’ fiber network has grown carefully over the last few years, both in terms of its reach and its capabilities. At the outset, the network offered 25/25 Mbps dedicated connections primarily to business customers. But where West Plains’ fiber loop passes residential homes, the city has also been willing to provide service to local homeowners as well.
West Plains’ fiber network has grown carefully over the last few years, both in terms of its reach and its capabilities. At the outset, the network offered 25/25 Mbps dedicated connections primarily to business customers. But where West Plains’ fiber loop passes residential homes, the city has also been willing to provide service to local homeowners as well.


 The Republican-pushed corporate tax rollback will bring a $14.4 billion increase in available cash flow for Comcast to use for future mergers and acquisitions or share buybacks by 2021, even as the cable company has no plans to share its tax savings bonanza with subscribers in the form of lower rates.
The Republican-pushed corporate tax rollback will bring a $14.4 billion increase in available cash flow for Comcast to use for future mergers and acquisitions or share buybacks by 2021, even as the cable company has no plans to share its tax savings bonanza with subscribers in the form of lower rates.
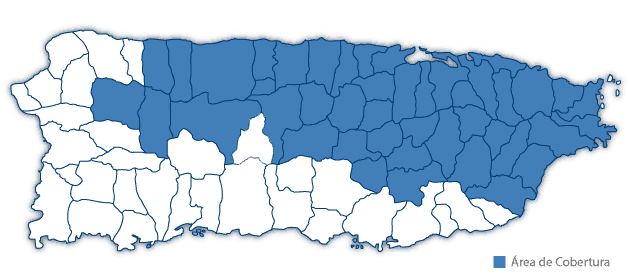
 Liberty Cablevision of Puerto Rico has estimated it will take as long as June of this year to fully restore cable and broadband service to Puerto Rico.
Liberty Cablevision of Puerto Rico has estimated it will take as long as June of this year to fully restore cable and broadband service to Puerto Rico.