
Moving on out?
New York’s Public Service Commission on Friday set the stage for ‘an orderly transition’ ending Spectrum’s brief life in New York, to be replaced with a ‘to be announced’ new cable operator to serve the needs of New York subscribers.
Or so the New York Public Service Commission hopes.
Although Friday’s 4-0 unanimous decision to revoke Charter’s merger deal in New York is a public relations and legal nightmare for the country’s second largest cable operator, we suspect top executives are getting a good night’s sleep tonight, not too concerned about the immediate consequences of today’s stunning vote.
Losing New York is what Wall Street would call “a materially adverse event” for any cable operator. New York City is the country’s largest media market. Billions of dollars worth of cable infrastructure, subscriber and advertising revenue, and prestige are at stake. Despite the ‘vote to revoke,’ Charter’s attorneys have signaled for weeks they intend to preserve and protect the cable company’s legal rights, and it is almost certain the PSC’s merger revocation order will meet a court-ordered injunction as soon as next week.
The courts are likely to make the final decision about whether Spectrum can stay or has to go. That aforementioned injunction will stop the clock on any ‘rash action’ and start what could be years of litigation, filled with discovery, endless hearings, stall tactics, blizzards of motions, appeals, more appeals, and then more lawsuits over whatever final exit plan is eventually filed, if one is required by the courts. A judge could also order the cable company and the state to work it out in a court-approved settlement, something the PSC seems loathe to do in its two orders published today which make it clear the regulator is done talking only to feel strung along by the cable company.
 For the near term, Spectrum customers won’t notice a thing. Even if the PSC was not taken to court, Charter has 60 days to file a six month transition plan, making the earliest date to waive Spectrum goodbye is sometime in early 2019.
For the near term, Spectrum customers won’t notice a thing. Even if the PSC was not taken to court, Charter has 60 days to file a six month transition plan, making the earliest date to waive Spectrum goodbye is sometime in early 2019.
To help readers out, we’ve prepared a short FAQ to address any concerns:
Q. Will I lose my cable and internet service?
A. No. Regardless of what happens, the PSC has ordered a transition plan designed to provide a seamless switch between Spectrum and a future provider. For most customers, it will resemble Charter’s own transition from Time Warner Cable to Spectrum.
Q. Who will replace Spectrum?

Not again.
A. The cable industry often resembles a cartel, whose members go to great lengths to protect each other. Historically, no large cable operator will entertain requests for proposals from cities or states requesting a replacement of a cable company already providing service. In short, if a city is fed up with Comcast and wants to shop around for another provider, it is highly unlikely Charter/Spectrum, Cox, Altice/Cablevision, Mediacom, or other providers will submit a bid to replace Comcast. If they did, Comcast could theoretically retaliate in their service areas. Should the Public Service Commission itself solicit bids to replace Spectrum, it is unlikely any operator will send a proposal unless/until Charter indicates it wants to leave the state. This kind of informal protectionism has proven highly effective limiting the power of towns and cities to play companies off each other to get a better deal for their residents.
Q. If Charter loses its court challenge and has to leave, what happens then?
A. If Charter exhausts its appeals and realizes it can no longer do business in New York, it will seek a private sale or system swap with another provider. Comcast would be the most likely contender, having shown prior interest in serving New York and having contiguous cable operations in adjoining states, especially in northern New England, Massachusetts, Pennsylvania and New Jersey. Comcast could agree to trade its cable systems in states like Texas, Florida, or California in return for its New York State’s Spectrum systems, which cover cities across the state. But that is likely years away.
Q. Isn’t Comcast worse than what we have now with Spectrum?
 A. Consumer satisfaction surveys suggest the answer is yes. Comcast is routinely rock bottom in customer satisfaction, customer service, pricing, and service options. Its 1 TB data cap on internet service has not yet reached many of its northeastern customers, but most observers expect it eventually will. In contrast, Charter has agreed not to impose data caps for up to seven years after its 2016 merger. But Comcast has delivered more frequent broadband speed upgrades and has more advanced set-top boxes and infrastructure.
A. Consumer satisfaction surveys suggest the answer is yes. Comcast is routinely rock bottom in customer satisfaction, customer service, pricing, and service options. Its 1 TB data cap on internet service has not yet reached many of its northeastern customers, but most observers expect it eventually will. In contrast, Charter has agreed not to impose data caps for up to seven years after its 2016 merger. But Comcast has delivered more frequent broadband speed upgrades and has more advanced set-top boxes and infrastructure.
Stop the Cap! would vociferously oppose Comcast’s entry in New York, however, just as we did a few years ago when we participated in the successful fight to stop Comcast’s merger attempt with Time Warner Cable.
Q, What other providers might be interested?
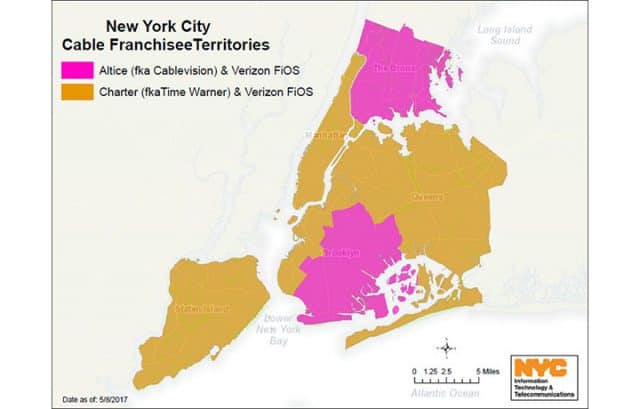
 A. Altice, which does business as Cablevision or Optimum, is New York’s other big cable operator, providing service exclusively downstate. Altice had aggressive plans to become a big player in the U.S. cable business, but its acquisition dreams were halted by shareholders, concerned about the European company’s already staggering debt, run up acquiring other companies. Altice is currently scrapping Cablevision’s existing Hybrid Fiber Coax infrastructure and replacing it with direct fiber to the home service, which offers improved service. But the company charges a lot for its advanced set-top box, has bloated modem rental fees, and is notorious for vicious cost-cutting, which stalled service improvements at its mobile and cable companies in France and raised a lot of controversy among employees.
A. Altice, which does business as Cablevision or Optimum, is New York’s other big cable operator, providing service exclusively downstate. Altice had aggressive plans to become a big player in the U.S. cable business, but its acquisition dreams were halted by shareholders, concerned about the European company’s already staggering debt, run up acquiring other companies. Altice is currently scrapping Cablevision’s existing Hybrid Fiber Coax infrastructure and replacing it with direct fiber to the home service, which offers improved service. But the company charges a lot for its advanced set-top box, has bloated modem rental fees, and is notorious for vicious cost-cutting, which stalled service improvements at its mobile and cable companies in France and raised a lot of controversy among employees.
Cox could be another contender, but would have to find a few billion to acquire Spectrum’s statewide system. Wild card players include AT&T and Verizon. Verizon would face extreme regulatory challenges, however, because it is the local phone company for most residents in the state. AT&T sold its U-verse system in Connecticut to Frontier Communications and seems increasingly focused on content, not on the systems that deliver content. A hedge fund or private equity firm could also be contenders, but perhaps not considering the high cost to acquire the systems and New York’s reputation for fierce customer protection. Remember, New York insists that a cable company ownership transfer must meet public interest tests, not simply enrich hedge fund participants.
Q. What happens to Charter’s pre-existing deal conditions on rural broadband and speed increases?
 A. Officially, the PSC has ordered Charter to continue abiding by the 2016 Merger Order and its deal commitments. The state will likely continue to fine Charter if it keeps missing rural broadband rollout targets until a court stops them or the company leaves. Charter will probably continue rural broadband expansion to show good faith. Charter has met its merger obligations related to speed increases, so it is not currently out of compliance. But a legal challenge offers the opportunity for a third-party judge to suspend or modify existing deal commitments, at least temporarily. It is unlikely Charter will want to invest large sums in its cable systems if it believes it will lose its case in court. The timetable for an upgrade to 200 Mbps Standard speed will likely now occur on a regional basis. The northeast division will still likely activate these speeds across multiple cities in the region sometime this summer, especially in places where it faces competitive pressure. The 300 Mbps upgrade in 2019 is more likely to be impacted by any forthcoming legal action.
A. Officially, the PSC has ordered Charter to continue abiding by the 2016 Merger Order and its deal commitments. The state will likely continue to fine Charter if it keeps missing rural broadband rollout targets until a court stops them or the company leaves. Charter will probably continue rural broadband expansion to show good faith. Charter has met its merger obligations related to speed increases, so it is not currently out of compliance. But a legal challenge offers the opportunity for a third-party judge to suspend or modify existing deal commitments, at least temporarily. It is unlikely Charter will want to invest large sums in its cable systems if it believes it will lose its case in court. The timetable for an upgrade to 200 Mbps Standard speed will likely now occur on a regional basis. The northeast division will still likely activate these speeds across multiple cities in the region sometime this summer, especially in places where it faces competitive pressure. The 300 Mbps upgrade in 2019 is more likely to be impacted by any forthcoming legal action.
Q. Is this political or about the union striking Charter? It is an election year.
A. All things are political to some degree in an election year in New York. That said, the New York Public Service Commission has the nation’s best track record of protecting consumers from bad actor telecom and energy companies. They take their responsibilities very seriously, and have shown consistent independence from the governor’s office, especially in recent years. The Commission was by far the most responsive of any state, including California, in taking our concerns about the Charter/Time Warner Cable merger seriously, and incorporated several of our suggestions into the final Merger Order. We warned the PSC cable companies have routinely reneged or slipped through deal conditions. We even predicted Charter would attempt to count new buildouts in non-rural areas and business office parks towards any commitment to expand their service areas. The PSC smartly conditioned its Merger Order by defining the goal of Charter’s broadband expansion — serving the unserved and underserved. That is why the company is not getting away with counting New York City buildouts towards this commitment.

Cynthia Nixon and Andrew Cuomo, both running for New York governor, neither fans of Charter Spectrum.
Few voters are likely to tie a PSC decision to the governor’s race, although Gov. Andrew Cuomo has repeatedly taken credit and praised the PSC for not tolerating bad behavior from Spectrum. If it was a purely political play, it would originate in the governor’s office. Gov. Cuomo’s Broadband for All program depends on achieving near-100% broadband penetration, something it may not manage if Charter fails its rural buildout commitments. That would be a PR mess. There is ample evidence that Charter’s own conduct was sufficient to trigger this kind of response, with or without an election looming.
New York is also a union-friendly state, and the International Brotherhood of Electrical Workers (IBEW) Local 3 has held out for over a year in the New York City area striking to preserve important job benefits Charter wants to discontinue. New revelations from the PSC outlining Charter’s increasingly bad safety record has strengthened the union’s case that Charter would rather bring in unqualified replacement workers and put safety at risk than settling with a union that essentially built the cable system serving New York City. There is no credible evidence that the union is involved in the PSC’s decision to revoke the merger agreement, although we suspect most affected members will fully support the decision.
Q. Is the PSC being too harsh? Can’t they work it out with Charter?
A. For New York to revoke a merger and effectively boot the company out of business in the state is remarkable. Utility companies that irresponsibly lack a credible disaster plan or do not comply with industry standards to maintain tree trimming and infrastructure repairs that result in plunging parts of upstate into darkness for up to two weeks after wind storms in two consecutive years were fined, but not ordered to leave. The ongoing scandal of competing private ESCO electric companies that have almost all scandalously overcharged New Yorkers with electric bills higher than their incumbent utility have been threatened with de-certification and fines, but are still conducting business, even though much of their marketing material was misleading.

Is it too late to work it out?
That should tell you the PSC’s move today was a final straw. The two parties have negotiated and debated Spectrum’s performance lapses for nearly a year. Tension was clearly rising by the spring after the PSC uncovered evidence Charter was intentionally counting areas it knew were outside of the spirit and language of the merger order’s rural broadband deal commitments. Charter’s brazen behavior achieved a new low when it questioned the PSC’s authority to oversee the merger agreement Charter signed. At one point, it unilaterally announced it would only honor the deal commitments found in one appendix of the Merger Order, conveniently ignoring the section describing and defining the rural broadband commitment Charter agreed to. The company also continued to air what the PSC declared to be false advertising, promoting Charter’s claimed accomplishments in rural broadband expansion. Charter repeatedly ignored warnings to suspend and remove those ads. In fact, the PSC issued strongly worded warnings to Charter at least twice, specifically outlining the possibility of canceling the merger agreement and forcing Spectrum out of the state. In response, Charter began staking out its legal arguments in filings, obviously preparing for litigation.
The PSC would probably argue it is impossible to work things out with a company that repeatedly breaks its own commitments. The PSC also openly worried what message it would send to other regulated utilities if it did not react strongly to Charter’s behavior. If the company had a corporate agenda to cheat New York out of important rural broadband expansion, negotiating, fining, and sanctioning a company is unlikely to change its behavior at the top.
Stop the Cap! had earlier recommended the PSC adopt new sanctions to force Charter to comply with its commitments, and expand them to bring service to many New Yorkers who were left behind by Gov. Cuomo’s Broadband for All program, suddenly saddled with satellite internet service. A large percentage of those affected are frustratingly close to nearby Spectrum service areas and although it would cost Charter a significant sum to reach them, it would deliver a financial sting for their bad behavior while also bringing much-needed internet access to the leftovers left-behind by the governor’s broadband expansion program. Such a settlement would require the company to actually comply with their commitments, something the PSC had been unable to achieve through no fault of their own. Perhaps a judge might have better luck should a negotiated settlement come up in litigation.
 Before Charter Communications is shown the door and exits New York (if Charter loses its anticipated legal action against the state), it should be required to issue refund checks to every subscriber in New York to make up for a series of broken promises.
Before Charter Communications is shown the door and exits New York (if Charter loses its anticipated legal action against the state), it should be required to issue refund checks to every subscriber in New York to make up for a series of broken promises.


 Subscribe
Subscribe
 For the near term, Spectrum customers won’t notice a thing. Even if the PSC was not taken to court, Charter has 60 days to file a six month transition plan, making the earliest date to waive Spectrum goodbye is sometime in early 2019.
For the near term, Spectrum customers won’t notice a thing. Even if the PSC was not taken to court, Charter has 60 days to file a six month transition plan, making the earliest date to waive Spectrum goodbye is sometime in early 2019.
 A. Consumer satisfaction surveys suggest the answer is yes. Comcast is routinely rock bottom in customer satisfaction, customer service, pricing, and service options. Its 1 TB data cap on internet service has not yet reached many of its northeastern customers, but most observers expect it eventually will. In contrast, Charter has agreed not to impose data caps for up to seven years after its 2016 merger. But Comcast has delivered more frequent broadband speed upgrades and has more advanced set-top boxes and infrastructure.
A. Consumer satisfaction surveys suggest the answer is yes. Comcast is routinely rock bottom in customer satisfaction, customer service, pricing, and service options. Its 1 TB data cap on internet service has not yet reached many of its northeastern customers, but most observers expect it eventually will. In contrast, Charter has agreed not to impose data caps for up to seven years after its 2016 merger. But Comcast has delivered more frequent broadband speed upgrades and has more advanced set-top boxes and infrastructure. A. Altice, which does business as Cablevision or Optimum, is New York’s other big cable operator, providing service exclusively downstate. Altice had aggressive plans to become a big player in the U.S. cable business, but its acquisition dreams were halted by shareholders, concerned about the European company’s already staggering debt, run up acquiring other companies. Altice is currently scrapping Cablevision’s existing Hybrid Fiber Coax infrastructure and replacing it with direct fiber to the home service, which offers improved service. But the company charges a lot for its advanced set-top box, has bloated modem rental fees, and is notorious for vicious cost-cutting, which stalled service improvements at its mobile and cable companies in France and raised a lot of controversy among employees.
A. Altice, which does business as Cablevision or Optimum, is New York’s other big cable operator, providing service exclusively downstate. Altice had aggressive plans to become a big player in the U.S. cable business, but its acquisition dreams were halted by shareholders, concerned about the European company’s already staggering debt, run up acquiring other companies. Altice is currently scrapping Cablevision’s existing Hybrid Fiber Coax infrastructure and replacing it with direct fiber to the home service, which offers improved service. But the company charges a lot for its advanced set-top box, has bloated modem rental fees, and is notorious for vicious cost-cutting, which stalled service improvements at its mobile and cable companies in France and raised a lot of controversy among employees. A. Officially, the PSC has ordered Charter to continue abiding by the 2016 Merger Order and its deal commitments. The state will likely continue to fine Charter if it keeps missing rural broadband rollout targets until a court stops them or the company leaves. Charter will probably continue rural broadband expansion to show good faith. Charter has met its merger obligations related to speed increases, so it is not currently out of compliance. But a legal challenge offers the opportunity for a third-party judge to suspend or modify existing deal commitments, at least temporarily. It is unlikely Charter will want to invest large sums in its cable systems if it believes it will lose its case in court. The timetable for an upgrade to 200 Mbps Standard speed will likely now occur on a regional basis. The northeast division will still likely activate these speeds across multiple cities in the region sometime this summer, especially in places where it faces competitive pressure. The 300 Mbps upgrade in 2019 is more likely to be impacted by any forthcoming legal action.
A. Officially, the PSC has ordered Charter to continue abiding by the 2016 Merger Order and its deal commitments. The state will likely continue to fine Charter if it keeps missing rural broadband rollout targets until a court stops them or the company leaves. Charter will probably continue rural broadband expansion to show good faith. Charter has met its merger obligations related to speed increases, so it is not currently out of compliance. But a legal challenge offers the opportunity for a third-party judge to suspend or modify existing deal commitments, at least temporarily. It is unlikely Charter will want to invest large sums in its cable systems if it believes it will lose its case in court. The timetable for an upgrade to 200 Mbps Standard speed will likely now occur on a regional basis. The northeast division will still likely activate these speeds across multiple cities in the region sometime this summer, especially in places where it faces competitive pressure. The 300 Mbps upgrade in 2019 is more likely to be impacted by any forthcoming legal action.





 REU is
REU is  Haslam’s Broadband Accessibility Act cynically retained these restrictions and blockades, hampering the rural broadband expansion the law was supposed to address.
Haslam’s Broadband Accessibility Act cynically retained these restrictions and blockades, hampering the rural broadband expansion the law was supposed to address.
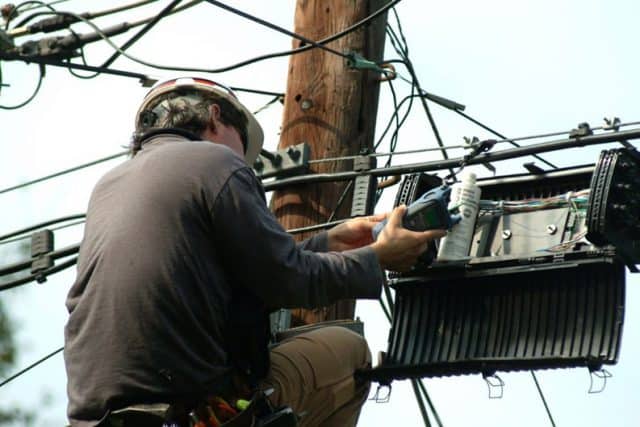
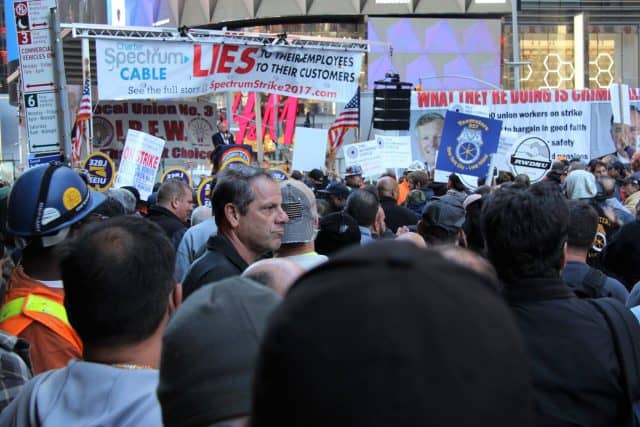 For the last year and a half, while Charter/Spectrum has been accused of dragging its feet on rural broadband rollouts across New York State and is now threatened with franchise revocation, the company had plenty of time to spare waiting out the International Brotherhood of Electrical Workers Local 3, who have been on strike to protest a pay-and-benefits-race-to-the-bottom in the New York City.
For the last year and a half, while Charter/Spectrum has been accused of dragging its feet on rural broadband rollouts across New York State and is now threatened with franchise revocation, the company had plenty of time to spare waiting out the International Brotherhood of Electrical Workers Local 3, who have been on strike to protest a pay-and-benefits-race-to-the-bottom in the New York City. The David vs. Goliath battle has also put enormous strain on some affected families. Some have quit the company and looked for employment elsewhere, some others have returned to work and abandoned the strike, leaving holdouts hoping for a breakthrough.
The David vs. Goliath battle has also put enormous strain on some affected families. Some have quit the company and looked for employment elsewhere, some others have returned to work and abandoned the strike, leaving holdouts hoping for a breakthrough.


