 When the Berkshire Eagle asked readers to test their internet speeds and share the results, along with opinions about their broadband options, the newspaper hit a nerve.
When the Berkshire Eagle asked readers to test their internet speeds and share the results, along with opinions about their broadband options, the newspaper hit a nerve.
Over 400 readers in western Massachusetts promptly responded, many with scathing stories about slow speeds and unresponsive customer service.
The newspaper preferred to call it “tortured testimony.”
“It is slow and getting slower,” wrote Bob Rosen, from Otis. “Many times it just says, ‘not responding.'”
“It” is Verizon’s DSL — broadband for the masses of landline customers in Massachusetts unlucky enough not to have FiOS fiber to the home service available before Verizon decided to stop expanding its copper-replacement fiber network. For the last seven years, Verizon’s DSL has remained more or less “as-is,” with no significant service improvements or apparent expansion effort.
 Unfortunately, as customer demand for bandwidth grows, performance drops unless providers continually invest in new equipment to manage demand appropriately. Customers in western Massachusetts report Verizon seems to be making do with what they already have, and speeds have suffered.
Unfortunately, as customer demand for bandwidth grows, performance drops unless providers continually invest in new equipment to manage demand appropriately. Customers in western Massachusetts report Verizon seems to be making do with what they already have, and speeds have suffered.
Douglas Mcnally of Windsor, a member of the Select Board and consultant whose job depends on a good internet connection told the newspaper he really doesn’t have a consistently reliable connection. One test showed a speed of 2.82Mbps, but a second one returned a speed result of 0.64Mbps. Barbara Craft-Reiss from Becket has a connection also topping out at 0.64Mbps.
In Dalton, a customer that repeatedly complained about his 1.5Mbps speed was told that was as good as Verizon DSL was going to get.
“I have had several communications with Verizon and they always say not to expect any more,” the reader told the newspaper. “At times it is so slow the web page expires before it comes up. There are many times it does not work at all.”
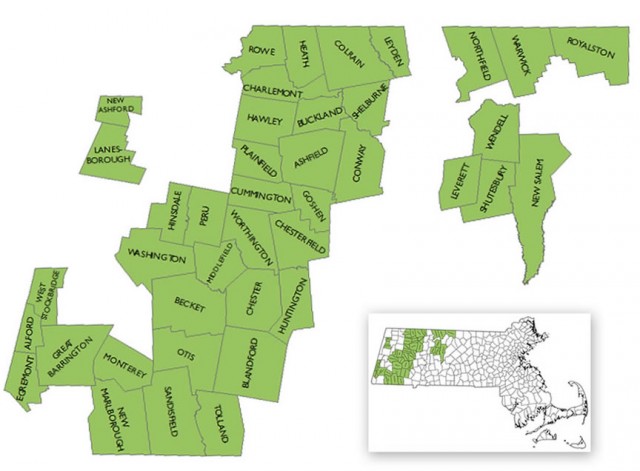
On August 13th, 2011, The WiredWest Cooperative in western Massachusetts was officially formed by charter member towns. The project has gained some town, lost some others as the region works towards faster broadband instead of waiting around for Verizon, Comcast, and Charter.
Verizon seemed to echo its “done with DSL” attitude to Robert Rosen who has subscribed since the 1990s at his home in the Otis Woodlands area.
“In the beginning, the signal was very strong. Every six months I would call Verizon and see if I could get a stronger signal. Sometimes it was boosted, however in the past several years I have been told by Verizon I am at max strength,” Rosen said.
But at least he could subscribe. Verizon customer service agents have warned some customers if they drop DSL service, they cannot come back. Bob Johnson dropped his 2Mbps Verizon DSL account — the one he inherited under the previous account-holder’s name.
“I was told that if I cancelled the previous owner’s account, I would not be able to get an account at all,” Johnson reported.
A Verizon spokesperson claimed DSL is still available in Verizon’s FiOS-less service areas, as long as the customer’s line passes a loop qualification test. Only ISDN has been decommissioned in certain service areas, the spokesperson claimed.
But Stop the Cap! has heard from countless Verizon customers who share stories of deteriorating performance and disinterest in improving service, and customer service agents won’t even sell DSL to customers without bundling landline phone service.
“They are just letting the old telephone network fall apart piece by piece,” claims John Landis, a Verizon DSL customer outside of Buffalo, N.Y. “The investment is just not clear anymore. When is the last time Verizon introduced a new service on their wired network, such as faster internet speeds? We’re living with a company where time has stopped, unless you are on Verizon Wireless.”
Verizon’s apparent disinterest in selling DSL broadband has proved to be a significant benefit for cable operators that continue to take market share from the phone company. Strategy Analytics reports cable companies added more than three million new subscribers from 2015 on. Cable operators now have a 62% broadband market share, compared to just 15% for DSL, a percentage that has dropped for years. (Fiber broadband now accounts for a 23% share.)
“The telco operators haven’t been able to shake off the losses of DSL subscribers, but we expect to see increased fiber deployments in the coming quarters, which should help AT&T and Verizon return to growth,” Jason Blackwell, director of Strategy Analytics’ Service Provider Strategies Service said last summer. But much of that growth seems to be targeted for urban and suburban areas, not rural areas where DSL is often the only available broadband technology.

Cable broadband is generally not available in rural areas.
Despite telco claims that wireless broadband alternatives will eventually solve the rural broadband problem, Blackwell is skeptical.
“The reality is fixed broadband is continuing to grow in the U.S., and not being replaced by mobile broadband as some have reported,” he claimed. “The cable operators are driving the growth with increased speeds and multiplay bundles.”
The availability of a cable competitor has helped some in western Massachusetts resolve their broadband problems, but only in communities where cable operators exist. Many western Massachusetts residents are still waiting for community-owned gigabit-capable fiber broadband through the WiredWest project.
In late 2015, politics from the governor’s office put a “pause” on all state “last-mile broadband” projects and a sudden policy shift required each town to own its own network infrastructure despite the widely expressed desire on the local level for a regional approach. More than a year later, the project to improve broadband across the western half of the state is still trapped by bureaucratic interference, allowing the state’s big cable and phone companies to continue the status quo with no alternatives on the immediate horizon.
As of late December, the project is gathering support for sending a resolution to state officials reaffirming their request to allow local communities involved in the project to determine their broadband future without onerous requirements from the governor’s office.
Without WiredWest, the future is not good. Unless Verizon changes its mind about broadband deployment in western Massachusetts or cable operators Charter and Comcast spontaneously expand their service areas, readers of the Berkshire Eagle can expect more of what staff writer Larry Parnass summed up in two words: extreme disappointment.


 Subscribe
Subscribe
 Cablevision, in contrast, was usually better regarded than the cable giants that surrounded it. Although technologically aggressive, Comcast canceled most of the goodwill earned for its service improvements by treating customers like patrons of an S&M club. Time Warner Cable was also loathed for its “last to do anything” upgrades, disengaged customer service, and reliable rate hikes, but at least they learned from earlier customer service mishaps and generally relied on a policy of being nicer to customers that threatened to leave.
Cablevision, in contrast, was usually better regarded than the cable giants that surrounded it. Although technologically aggressive, Comcast canceled most of the goodwill earned for its service improvements by treating customers like patrons of an S&M club. Time Warner Cable was also loathed for its “last to do anything” upgrades, disengaged customer service, and reliable rate hikes, but at least they learned from earlier customer service mishaps and generally relied on a policy of being nicer to customers that threatened to leave.


 At France’s SFR, Drahi made clear
At France’s SFR, Drahi made clear 
 Altice, the new owner of Cablevision, is not following the rest of the U.S. cable industry by rolling out the next generation of cable broadband — DOCSIS 3.1 — and will instead
Altice, the new owner of Cablevision, is not following the rest of the U.S. cable industry by rolling out the next generation of cable broadband — DOCSIS 3.1 — and will instead 
 Assuming ATS is configured as an independent entity, it will not be required to adhere to the NY PSC order prohibiting reductions of Cablevision’s customer-facing workforce in New York State, which theoretically could allow Altice to dramatically downsize.
Assuming ATS is configured as an independent entity, it will not be required to adhere to the NY PSC order prohibiting reductions of Cablevision’s customer-facing workforce in New York State, which theoretically could allow Altice to dramatically downsize. Employees report unprecedented intensity of cost cutting and lengthy scrutiny of almost every expense. Some claim to have resorted to buying certain equipment and supplies out of pocket just to avoid drawing management scrutiny. Employee morale is reportedly low — especially at Cablevision, where reduced pay packages predominate under Altice ownership. Management has told employees to hold out for a planned IPO, which could allow them to reap some of the benefits of a Wall Street-fueled cash-raising exercise likely to be put to work buying up other cable operators in 2017.
Employees report unprecedented intensity of cost cutting and lengthy scrutiny of almost every expense. Some claim to have resorted to buying certain equipment and supplies out of pocket just to avoid drawing management scrutiny. Employee morale is reportedly low — especially at Cablevision, where reduced pay packages predominate under Altice ownership. Management has told employees to hold out for a planned IPO, which could allow them to reap some of the benefits of a Wall Street-fueled cash-raising exercise likely to be put to work buying up other cable operators in 2017. Tis the season for rate increases. Fa-la-la-la-la, La-La-La-La.
Tis the season for rate increases. Fa-la-la-la-la, La-La-La-La. The absence of viable broadband competition in states like Maryland, bypassed by Verizon FiOS, means Comcast can raise broadband prices almost at will.
The absence of viable broadband competition in states like Maryland, bypassed by Verizon FiOS, means Comcast can raise broadband prices almost at will.