Newly released maps show that broadband — high-speed Internet — is widely available in Texas. They also underscore that the broadband stimulus program has been ill-conceived and poorly executed by the federal government.
That’s because the federal government put the cart before the horse.
It gave out more than $270 million of your money to a dozen projects in Texas before actually determining where current broadband operators provide service. Common sense would say to find out where broadband is, or isn’t, available before spending the money.
The feds also should better define “underserved,” since the money is intended to help both unserved and underserved areas. It sounds like a riddle — how many broadband providers have to serve a household before it isn’t considered “underserved”? So far that riddle has no answer, and it is costing you, the taxpayer, a lot of money.
Without the data or the definition, how can the federal government make sure it is spending taxpayer money wisely and where it is really needed?
Now that we have the maps, we can see that more than 99 percent of all Texans can access some form of broadband, whether wired, wireless or mobile, from more than 123 providers. Yet — without this information — the federal government awarded hundreds of millions in grants and loans to the Texas projects, with possibly more to come before the broadband stimulus program wraps up in September.
The Texas Cable Association formally objected to seven of the dozen Texas projects when in the application stage, because the areas addressed are already covered by existing broadband providers. We don’t believe the areas are unserved or underserved.
Just a few weeks ago, the Texas Agriculture Commissioner Todd Staples, with great fanfare, unveiled the current state of broadband in Texas. Connected Texas, a subsidiary of Connected Nation joined forces with the state government to perform a broadband census across the state, based on voluntary information provided confidentially by existing service providers. The result was the stunning “achievement” that 97 percent of Texas already had broadband access, quite a revelation to the scores of consumers who aren’t served by cable companies and cannot get DSL service from the phone company, even if the Broadband Map of Texas says they can.
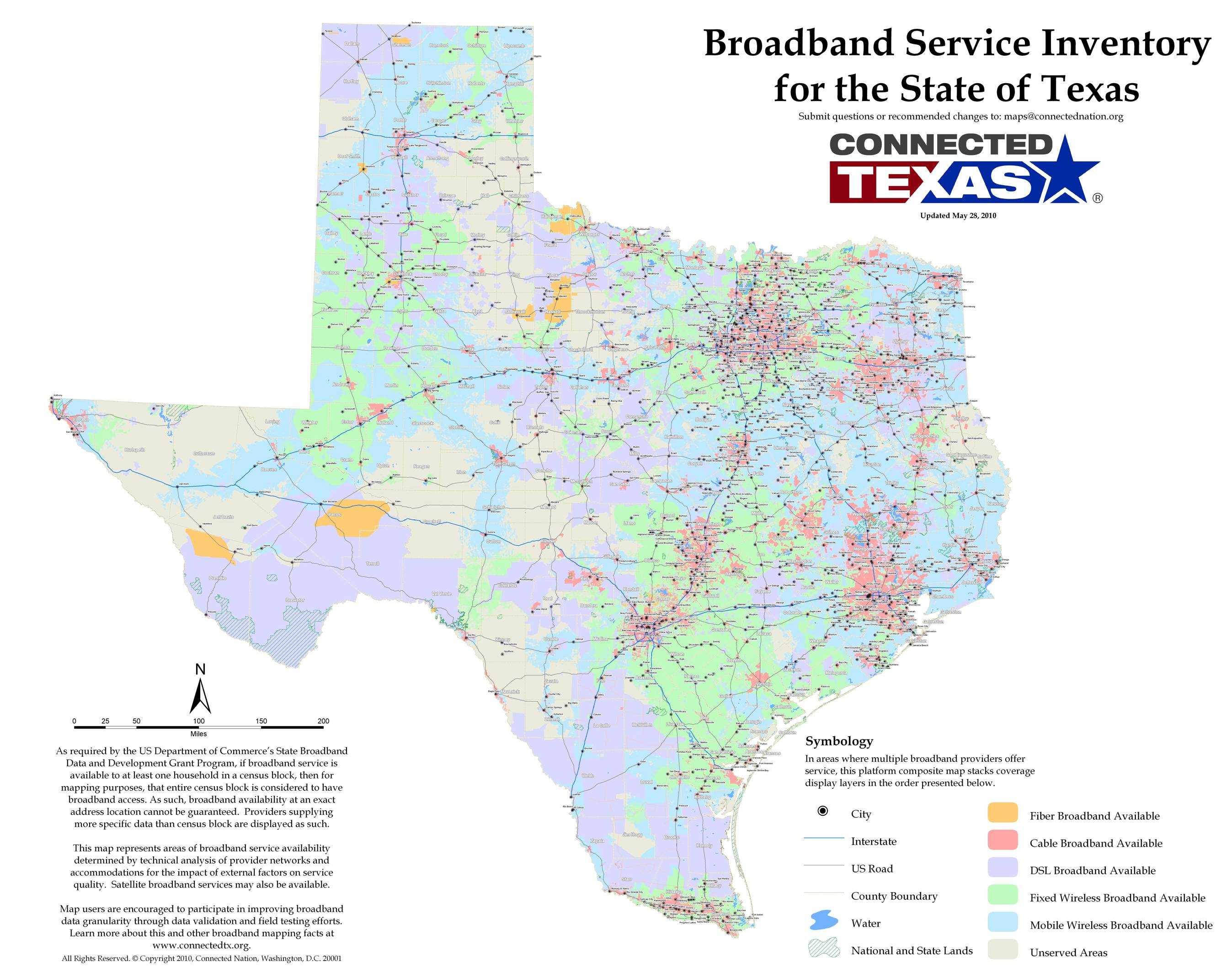
Texas Broadband Map (click to enlarge)
Kelly from Childress, located in the Texas panhandle, is a perfect example. She writes Stop the Cap! to tell us how thrilled she was to see the phone company had finally brought DSL service to her street just on the outskirts of town. She had nagged everyone she could for more than three years about her lack of broadband. The cable company offered service, if she paid $9,300 for installation of an extended cable line to reach her. The phone company, despite serving her neighbors less than 1/2 mile away, said she was not “qualified” to receive DSL service. Today, her husband and two kids do access broadband service, albeit from the equivalent of the broadband black market. Her nearest neighbor has rigged a souped up Wi-Fi system that allows her family to share the neighbor’s DSL account. A directional antenna mounted on the roof of each home provides line-of-sight access. They split the cost of the account and Kelly, an accomplished baker, keeps her neighbors well-supplied with some great pies in gratitude.

Connected Texas collected the information about where broadband service was supposedly available in Texas
Texas has a well-deserved reputation for neighbors helping neighbors to solve problems they’ve long since decided the government can’t, won’t, or shouldn’t solve for them. Now that neighborly spirit has taken a high-tech approach to share broadband.
With the release of the new broadband map, Kelly thought the days of sharing accounts was over, and she called the phone company to sign up for service. But, in no surprise to us, broadband availability to her home changed only on paper, not in reality. No, she was told, she could not sign up for DSL service today or tomorrow for that matter — the company had no plans to extend service her way… indefinitely.
For others, the map is inaccurate because it shows service from dominant cable and phone companies, but ignores the competition. Regular Stop the Cap! reader Michael Chaney noted, “I know for a fact this map is inaccurate. They show no fiber to the home coverage in Cedar Park, Williamson County, even though I’ve had residential fiber service for almost two years.”
In 2009, Public Knowledge released a report highly critical of Connected Nation, the group responsible for broadband mapping across many states. Among the findings:
In order to be effective, a national broadband data-collection and mapping exercise should be conducted by a government agency, on behalf of the public, with as granular a degree of information as possible and be totally transparent so that underlying information can be evaluated.
Connected Nation is none of those and represents none of those characteristics. It is an organization sponsored by the telephone and cable companies and represents their interests in deciding what data to collect and how information should be displayed. They are quite up front about their company sponsorship and, in fact, believe it is an asset, if in a way counter to solid public policy.
It would be a setback for our broadband policy if Connected Nation were to take a prominent role in broadband mapping and data collection if it continues on its present policy course because the organization does not represent wise public policy and because it distorts its results.
Kentucky Gov. Steve Beshear (D) was correct in April, 2008, when he vetoed a $2.4 million appropriation for Connect Kentucky, which until then had received almost $7 million from the commonwealth. Beshear said that the program was being rejected for state financing because it had asked for funds “without specifically identifying any services to be rendered to the state or providing for any oversight, control or performance measures relative to the services being rendered.”
The group’s close association to incumbent cable and telephone company interests were easily apparent just from the national organization’s board which has 12 outside directors, eight of whom are well known cable and phone company lobbyists or those with direct interests in the industry:
- James W. Cicconi – AT&T senior executive vice president-external and legislative affairs
- Steve Largent – CTIA – The Wireless Association president and CEO
- Joseph W. Waz – Comcast senior vice president, external affairs and public policy counsel
- Larry Cohen – Communications Workers of America president. CWA is in frequent agreement with telecom companies on policy issues.
- Thomas J. Tauke – Verizon executive vice president for public affairs, policy and communication
- Walter B. McCormick – United States Telecom Association president
- Kyle E. McSlarrow – National Cable and Telecommunications Association president
- Grant Seiffert – Telecommunications Industry Association president. (The members are the equipment makers who sell their gear to the telecom industry.)
These individuals, and others, are listed as “national advisors” on the Connected Nation Web site. They are listed as “directors” in their filing with the Kentucky Secretary of State.
The implications of allowing incumbent service providers to influence broadband mapping can be seen in Baxter’s editorial. If Texas cable and phone companies can declare broadband service available even in areas where it is not, they can then argue against broadband stimulus projects to expand availability as an unnecessary waste of taxpayer money. The answer to Baxter’s riddle is, unfortunately, too often “none.” Areas that declare access to wireless broadband, cable and DSL often have access to none of these options. The cable company doesn’t wire that Texas ranch located too far away from the phone company for DSL and is in an area that just can’t get a good wireless signal.
In smaller communities in rural Texas, efforts by local entrepreneurs to launch needed local broadband services often meet fierce opposition from incumbent interests who declare communities already served, backed up with a map that shows coverage, and therefore should not be allowed to receive stimulus funding. Often, objections from existing providers effectively disqualifies stimulus applicants and the result is a continued blockade for rural broadband.
The dividend Connected Nation hands to the Texas Cable Association is the political argument that there is no broadband problem in Texas — nearly 100 percent of homes can already access it. That means broadband stimulus is, in the eyes of the cable lobby, just another federal government giveaway — wasteful spending of tax dollars. Just look at the Texas Broadband Map and see for yourself.
The Texas Department of Agriculture failed the people of Texas by relying on a group with a vested interest in not finding a broadband availability problem. And even worse — taxpayers nationwide effectively picked up the $3 million dollars in grant money given to Connected Nation for its map. That’s a waste of tax dollars that Baxter didn’t bother to bring up. Somehow I knew he wouldn’t.
[flv]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/KOSA Odessa Internet in Rural Areas 6-17-10.flv[/flv]
 Google today launched a new website which could become a major advocacy center to promote fiber broadband service across America.
Google today launched a new website which could become a major advocacy center to promote fiber broadband service across America.

 Subscribe
Subscribe








