 Tomorrow is election day in the United States. Stop the Cap! has reviewed both presidential candidates’ positions (or the lack thereof) as well as the past voting records and platforms of members of both major political parties. With this in mind, it is time for our election guide for broadband enthusiasts. Regardless of what candidate you support, please get out and vote!
Tomorrow is election day in the United States. Stop the Cap! has reviewed both presidential candidates’ positions (or the lack thereof) as well as the past voting records and platforms of members of both major political parties. With this in mind, it is time for our election guide for broadband enthusiasts. Regardless of what candidate you support, please get out and vote!
Neither political party or candidate has been perfect on broadband advocacy or consumer protection.
We’ve been disappointed by the Obama Administration, whose FCC chairman has major problems standing up to large telecom companies and their friends in the Republican-led House of Representatives. Julius Genachowski promised a lot and delivered very little on broadband reform policies that protect both consumers and the open Internet. Both President Obama and Genachowski’s rhetoric simply have not matched the results.
Bitterly disappointing moments included Genachowski’s cave-in on Net Neutrality, leaving watered down net protections challenged in court by some of the same companies that praised Genachowski’s willingness to compromise. Genachowski’s thank you card arrived in the form of a lawsuit. His unwillingness to take the common sense approach of defining broadband as a “telecommunications service” has left Internet policies hanging by a tenuous thread, waiting to be snipped by the first D.C. federal judge with a pair of sharp scissors. But even worse, the FCC chairman’s blinders on usage caps and usage billing have left him unbelievably naive about this pricing scheme. No, Mr. Genachowski, usage pricing is not about innovation, it’s about monetizing broadband usage for even fatter profits at the expense of average consumers already overpaying for Internet access.

Obama
Unfortunately, the alternative choice may be worse. Let’s compare the two parties and their candidates:
The Obama Administration treats broadband comparably to alternative energy. Both deliver promise, but not if we wait for private companies to do all of the heavy lifting. The Obama Administration believes Internet expansion needs government assistance to overcome the current blockade of access for anyone failing to meet private Return On Investment requirements.
While this sober business analysis has kept private providers from upsetting investors with expensive capital investments, it has also allowed millions of Americans to go without service. The “incremental growth” argument advocated by private providers has allowed the United States’ leadership role on broadband to falter. In both Europe and Asia, even small nations now outpace the United States deploying advanced broadband networks which offer far higher capacity, usually at dramatically lower prices. Usually, other nations one-upping the United States is treated like a threat to national security. This time, the argument is that those other countries don’t actually need the broadband networks they have, nor do we.
The Obama Administration bows to the reality that private companies simply will not invest in unprofitable service areas unless the government helps pick up the tab. But those companies also want the government to spend the money with as little oversight over their networks as possible.
That sets up the classic conflict between the two political parties — Democrats who want to see broadband treated like a critically-important utility that deserves some government oversight in its current state and Republicans who want to leave matters entirely in the hands of private providers who they claim know best, and keep the government out of it.

FCC Chairman Julius Genachowski’s regular cave-ins for the benefit of Big Telecom brought heavy criticism from us for his “cowardly lion” act.
Just about the only thing the two parties agree on is reforming the Universal Service Fund, which had until recently been directing millions to keeping traditional phone service up and running even as Americans increasingly abandon landlines.
But differences quickly emerge from there.
The Obama Administration believes broadband is increasingly a service every American must be able to access if sought. The Romney-Ryan campaign hasn’t spoken to the issue much beyond the general Republican platform that market forces will resolve virtually any problem when sufficient demand arises.
Republicans almost uniformly vociferously oppose Net Neutrality, believing broadband networks are the sole property of the providers that offer the service. Many Republicans characterize Net Neutrality as a “government takeover” of the Internet and a government policy that would “micromanage broadband” like it was a railroad. Somehow, they seem to have forgotten railroad monopolies used to be a problem for the United States in the early 20th century. Robber barons, anyone?
President Obama pushed for strong Net Neutrality protections for Americans, but his FCC chairman Julius Genachowski caved to the demands of AT&T, Verizon, and the cable industry by managing Net Neutrality with a disappointing “light touch” for those providers. (We’d call it “fondling” ourselves.)
Democrats favor wireless auctions and spectrum expansion, but many favor limits that reserve certain spectrum for emerging competitors and for unlicensed wireless use. Republicans trend towards “winner take all” auctions which probably will favor deep-pocketed incumbents like AT&T and Verizon. The GOP also does not support holding back as much spectrum for unlicensed use.
Republicans have been strongly supporting the deregulation of “special access” service, critical to competitors who need backhaul access to the Internet sold by large phone companies like AT&T. Critics contend the pricing deregulation has allowed a handful of phone companies to lock out competitors, particularly on the wireless side, with extremely high prices for access without any pricing oversight. The FCC under the Obama Administration suspended that deregulation last summer, a clear sign it thinks current pricing is suspect.

Romney
Opponents of usage-based pricing of Internet access have gotten shabby treatment from both parties. Republicans have shown no interest in involving themselves in a debate about the fairness of usage pricing, but neither have many Democrats.
As for publicly-owned broadband networks, sometimes called municipal broadband, the Republican record on the state and federal level is pretty clear — they actively oppose community broadband networks and many have worked with corporate front groups like the American Legislative Exchange Council (ALEC) to ban them on the state level. Democrats tend to be more favorable, but not always.
The biggest problem broadband advocates face on the federal and state level is the ongoing pervasive influence of Big Telecom campaign contributions. While politicians uniformly deny that corporate money holds any influence over their voting, the record clearly indicates otherwise. Nothing else explains the signatures from Democrats that received healthy injections of campaign cash from companies like AT&T, and then used the company’s own talking points to oppose Net Neutrality.
But in a story of the lesser of two-evils, we cannot forget AT&T spends even more to promote Republican interests, because often those interests are shared by AT&T:
- AT&T has spent nearly $900,000 on self-identified “tea party” candidates pledged to AT&T’s deregulation policies;
- AT&T gave nearly $2 million to the Republican Governors Association — a key part of their ALEC agenda;
- AT&T gave $100,000 to everyone’s favorite dollar-a-holler Astroturf group — The Heartland Institute, which opposes Net Neutrality and community broadband.
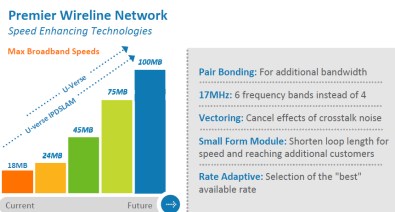 About 25% of AT&T’s rural customers will not see any upgrade to their current landline service. Instead, AT&T announced it will seek to gradually decommission rural landline networks and transfer those customers to its 4G LTE wireless service for both broadband and voice service, pending regulator approval.
About 25% of AT&T’s rural customers will not see any upgrade to their current landline service. Instead, AT&T announced it will seek to gradually decommission rural landline networks and transfer those customers to its 4G LTE wireless service for both broadband and voice service, pending regulator approval.

 Subscribe
Subscribe









