 Millenicom customers have had their ups and downs over the last two weeks coping with e-mail notifications they would lose, keep, and once again lose their unlimited wireless data plan.
Millenicom customers have had their ups and downs over the last two weeks coping with e-mail notifications they would lose, keep, and once again lose their unlimited wireless data plan.
Just a day after Millenicom heard that Sprint would allow them to continue selling Unlimited and Bring Your Own Device plans, the wireless carrier best known for its “unlimited for life” offer changed its mind:
We are very sorry to report that Sprint has reversed their decision from yesterday and terminated their agreement with the gateway for our Unlimited and BYOD accounts.
We are not certain how long until the accounts will be closed.
We will be shipping out Hotspot devices to those clients who had opted for that solution and BMI.net is ready to fulfill orders for those choosing to go with them.
We have attempted to keep you informed every step of the way and avoid any abrupt transition. We apologize that we weren’t able to come through.
Thank you for allowing us to be of service and please accept our sincere wish for your future success.
Dennis Castle
Owner
![]() It is not the first time Millenicom has had problems with Sprint, which has proved to be a difficult carrier to deal with with respect to unlimited use plans.
It is not the first time Millenicom has had problems with Sprint, which has proved to be a difficult carrier to deal with with respect to unlimited use plans.
Sprint’s decision is a major blow to rural Americans who lack access to cable or DSL broadband and are forced to consider satellite-delivered Internet access or pay even more for wireless data plans that come with puny usage caps, overlimit fees or speed throttles.
There are a few alternatives, but since these providers resell access to Sprint-owned networks, all are potentially vulnerable to Sprint’s evolving views on resellers:
 Blue Mountain Internet (BMI) offers an “unlimited plan” that isn’t along with several usage allowance plans. BMI strongly recommends the use of their Mobile Broadband Optimizer software that compresses web traffic, dramatically improving speeds and reducing consumption:
Blue Mountain Internet (BMI) offers an “unlimited plan” that isn’t along with several usage allowance plans. BMI strongly recommends the use of their Mobile Broadband Optimizer software that compresses web traffic, dramatically improving speeds and reducing consumption:
Monthly Plans
- $39.99/Month – 1 Gig Data (** up to 3GB compressed) ($25/GB Overlimit Fee)
- $59.99/Month – 3 Gig Data (** up to 9GB compressed) ($20/GB Overlimit Fee)
- $79.99/Month – 5 Gig Data (** up to 15GB compressed) ($20/GB Overlimit Fee)
- $99.99/Month – 10 Gig Data (** Up to 45GB compressed) ($15/GB Overlimit Fee)
- $79.99/Month – Unlimited (Bring Your Own Device) – BYOD
- $99.99/Month – Unlimited Data (S Network) ***
 There is a $100 maximum on overlimit fees, but BMI reserves the right to suspend accounts after running 3-5GB over a plan’s allowance to limit exposure to the penalty rate. The compression software is for Windows only and does not work with MIFI devices or with video/audio streaming. BMI warns its wireless service is not intended for video streaming. Customers are not allowed to host computer applications including continuous streaming video and webcam posts that broadcast more than 24 hours; automatic data feeds; automated continuous streaming machine-to-machine connections; or peer-to-peer (P2P) file-sharing.
There is a $100 maximum on overlimit fees, but BMI reserves the right to suspend accounts after running 3-5GB over a plan’s allowance to limit exposure to the penalty rate. The compression software is for Windows only and does not work with MIFI devices or with video/audio streaming. BMI warns its wireless service is not intended for video streaming. Customers are not allowed to host computer applications including continuous streaming video and webcam posts that broadcast more than 24 hours; automatic data feeds; automated continuous streaming machine-to-machine connections; or peer-to-peer (P2P) file-sharing.
EVDODepotUSA offers two truly unlimited use plans starting at $119 a month. The company is only contracted to offer access to Sprint’s woefully congested 3G network and the Clear 4G WiMAX network that typically does not offer much coverage in rural areas. LTE access is not currently available. There is a six month contract obligation, but the company also offers a 10-day free trial.
Their current plans:
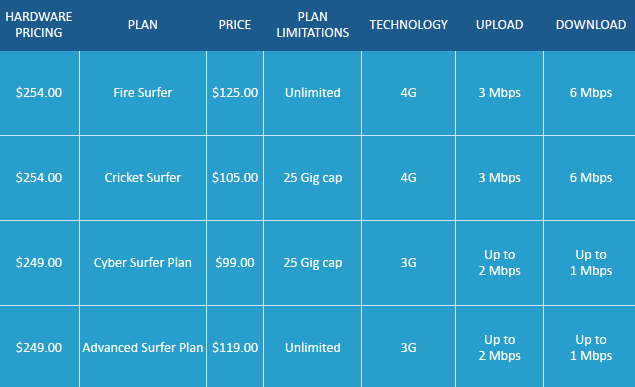
 Wireless ‘n Wifi offers two partly unlimited plans with no contract commitment. The company charges a refundable deposit on devices, but they become yours to keep after two years:
Wireless ‘n Wifi offers two partly unlimited plans with no contract commitment. The company charges a refundable deposit on devices, but they become yours to keep after two years:
- Unlimited 4G Sprint/Clear WiMAX with 3G Fallback ($58.99) offers unlimited WiMAX service but has a 5GB cap on Sprint’s 3G network, the network rural customers will encounter the most. Total start-up fee is $194.93 which includes an activation fee, modem deposit (refunded upon modem return or after 24 months of service), the first month of service, and shipping for the wireless device.
- Unlimited 4G LTE with WiMAX and 3G Fallback ($79.99) offers unlimited Sprint 4G LTE and Sprint/Clear WiMAX service with a 35GB cap on Sprint’s 3G network. Customers can select a dual-band device that supports LTE and 3G service for $246.93 (includes activation fee, modem upcharge fee, first month of service, shipping, and refundable $100 modem deposit). Customers looking for access to LTE, 3G, and WiMAX can choose a tri-band device for $315.93 (includes activation fee, modem upcharge, first month of service, shipping and refundable deposit.) Keep in mind Sprint’s 4G LTE network is still very spotty.


 Subscribe
Subscribe




 Time Warner Cable customers in Los Angeles, New York, and Hawaii subscribed to the company’s top 50/5Mbps Ultimate speed tier
Time Warner Cable customers in Los Angeles, New York, and Hawaii subscribed to the company’s top 50/5Mbps Ultimate speed tier 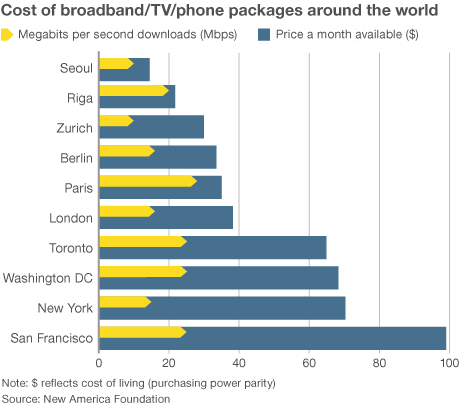 Broadband in the United States costs far more than in other countries —
Broadband in the United States costs far more than in other countries — 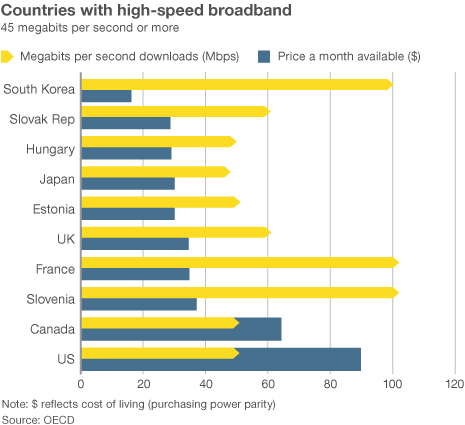 “Americans pay so much because they don’t have a choice,” said Susan Crawford, a former special assistant to President Barack Obama on science, technology and innovation policy. “We deregulated high-speed Internet access 10 years ago and since then we’ve seen enormous consolidation and monopolies, so left to their own devices, companies that supply Internet access will charge high prices, because they face neither competition nor oversight.”
“Americans pay so much because they don’t have a choice,” said Susan Crawford, a former special assistant to President Barack Obama on science, technology and innovation policy. “We deregulated high-speed Internet access 10 years ago and since then we’ve seen enormous consolidation and monopolies, so left to their own devices, companies that supply Internet access will charge high prices, because they face neither competition nor oversight.”
