
Time Warner Cable held its first post-merger-flop conference call with investors this morning and reported surprisingly good subscriber numbers for the first quarter of 2015.
Despite disappointing investors for not meeting projected profit and revenue numbers for the first three months of the year, Time Warner managed to add 30,000 net video customers for the first time since 2009. High-speed data customers grew by 315,000, compared with 269,000 a year ago, while voice customers increased by 320,000, compared with 107,000 in the prior-year period. The company also reported $26 million in wasted merger-related costs.

Time Warner’s latest triple play promotion has fewer gotchas in the fine print than usual, but the modem fee is still there so buy your own.
A renewed love for Time Warner Cable was not the reason the cable company added customers. Aggressive pricing with fewer fine print “gotchas” and Time Warner Cable Maxx upgrades helped the company pick up new subscribers. Last October, Time Warner added a $90 triple play offer valid across much of its service area, offering unlimited calling phone, Preferred TV, and 30Mbps broadband with one set-top box for $89.99 a month for one year, an offer Artie Minson, chief financial officer of Time Warner Cable called “clean.”
For the last two years, Time Warner Cable executives decided to de-emphasize promotional pricing on phone service, preferring to draw more attention to its double-play television and broadband offers. This year, that thinking is long gone as the cable company re-emphasizes its triple-play packages and offers current customers the chance to add phone service for as little as $10 a month. The strong growth in new phone customers during the quarter reflects the success of those promotions.
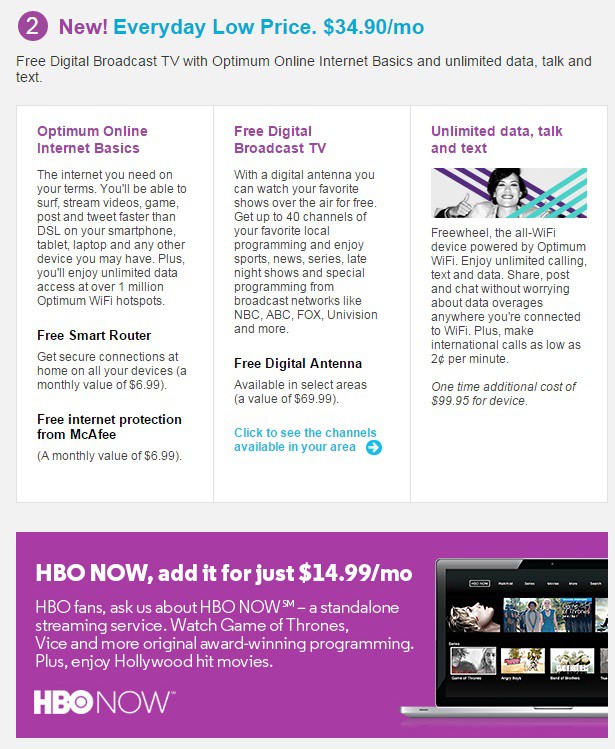
Minson was less impressed with the sales of “skinny bundles” of bare basic cable television, HBO, and broadband service, noting it had little impact on Time Warner’s subscriber growth. The allure of its $14.99 everyday low price, low speed Internet offer has also waned.
“There’s a lot of attraction in the press about skinny packages,” echoed Dinesh C. Jain, chief operating officer of Time Warner Cable. “I think a lot of the times, customers don’t want to get bogged down in a lot of choices to make on those kinds of things. There’s a lot of value in our triple-play packaging right now and it’s a simpler sale.”
Marcus used the conference call to re-emphasize the company has not been distracted by 14 months of merger talks with Comcast and has executed on its pre-merger business plan all along.

Coming in 2017 (If We Live That Long)
Network upgrades under the TWC Maxx program are continuing on schedule.
“New York City, LA and Austin are complete, Dallas, San Antonio and Kansas City are underway and Charlotte, Raleigh and Hawaii on the docket for later in the year,” said Marcus. “We also plan to begin the Maxx process in San Diego this year and finish up in early 2016. It’s still early days, but Maxx certainly appears to be making a difference. Customer feedback has been great and churn among Maxx customers with new DOCSIS 3.0 modems is dramatically lower.”
But it will take another two years to complete the entire Time Warner footprint, of which 40-50% will be upgraded by the end of this year.
“The exact pace at which we continue that process in 2016 and 2017 depends on the experience we have in 2015. We’re feeling better about our ability to roll out all-digital this year than we did last year, which was really the first year of the program,” said Marcus. “And we’ll evaluate, as we go into 2016, how quickly we think we can ramp the next batch of systems.”
In a recurring theme throughout the conference call, executives emphasized Time Warner does not want to pioneer tinkering with the traditional cable package.
For example, Marcus acknowledged Cablevision’s experiment with Wi-Fi calling as a cellular replacement strategy, but said Time Warner Cable will take a wait and see approach.
“I’m inclined to watch and see how that evolves and then we’ll see how best to develop our own strategy on that front,” Marcus said.

Marcus
“There’s a lot of talk and a lot of work going on out there from other guys,” said Jain, referring to slimmed down cable packages and unbundling. “And if any of their things work, we’ll just be fast followers on that stuff because I think there are some segments of our customer base where that is going to have appeal.”
Marcus also complained there was far too much attention being paid on Millennials as an excuse to break up the traditional cable experience.
“There tends to be, in my opinion, an obsessive interest in Millennials, maybe at the expense of the broader customer base,” Marcus said. “For the vast majority of our customers, the way we currently deliver the video product is pretty darn attractive. That said, sure, there’s a group of customers who might very well like to access video via other means. So it is definitely the case that over time, I can see a world where more and more customers consume our offering without needing to lease a set-top box from us. But that doesn’t mean we’re going to abandon the largest portion of our customers who actually do like the current model.”
On other subjects, the implementation of Net Neutrality under Title II regulations will have no impact on Time Warner’s future plans or investments, according to Marcus.
“We’ve said in the past that our normal business practices comply entirely with the notion of the open Internet, no blocking, no discrimination, no throttling, and transparency are fundamental parts of the way we do business. So to the extent that that’s the full scope of what’s getting incremented under Title II, I think you won’t see a change in the way we do business.”
But he warned if the FCC intends to more broadly regulate Internet access, that could have an impact on pricing and future investment.
Marcus also re-emphasized his intention not to change the way Time Warner sells broadband. That means no compulsory usage caps or usage-based pricing.
“We’re very focused on delivering compelling products to customers at a price that delivers real value,” said Marcus. “We can’t think in terms of taking gross margin dollars that are lost because we lose a video customer and somehow embedding those into high-speed data [with usage pricing] and not seeing an impact on high-speed data.”


 Subscribe
Subscribe

 The deal covers the service’s entire catalog of on-demand television shows and movies and will be available to Cablevision broadband customers online and possibly through set-top boxes for traditional cable television customers.
The deal covers the service’s entire catalog of on-demand television shows and movies and will be available to Cablevision broadband customers online and possibly through set-top boxes for traditional cable television customers.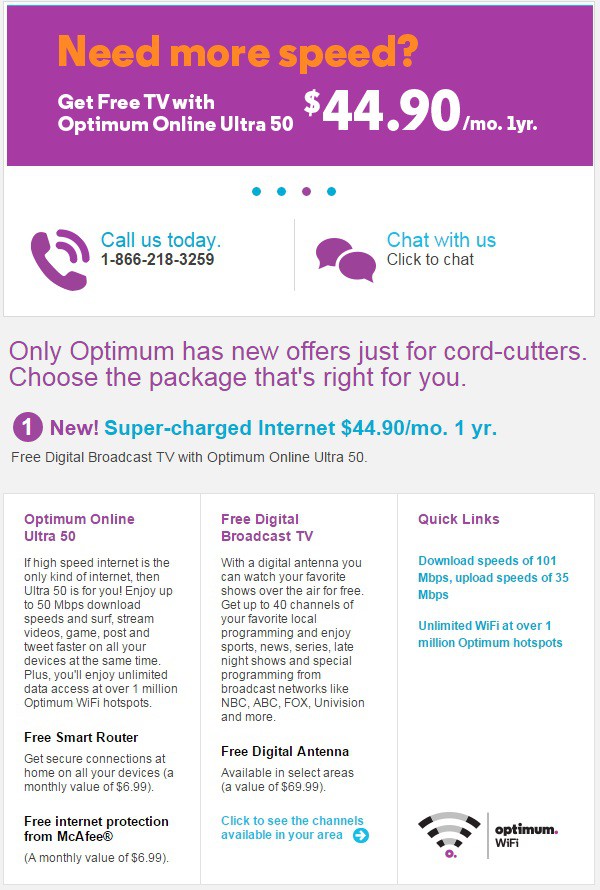
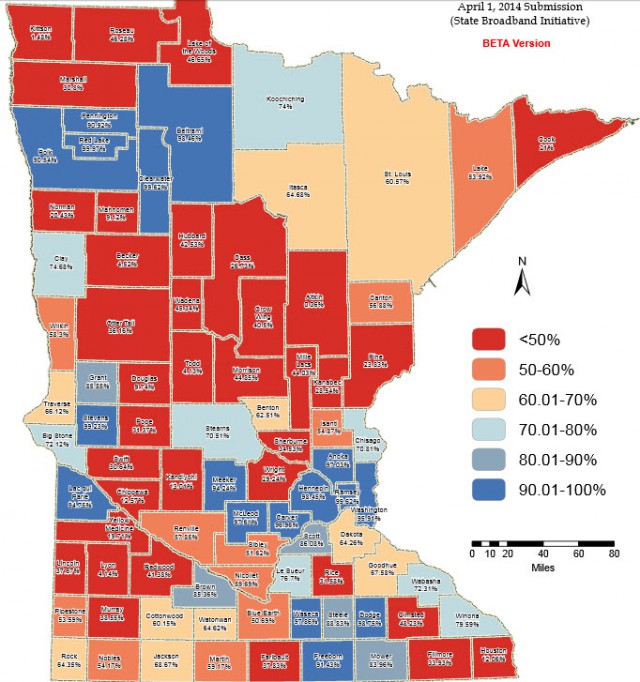
 The largest telecom companies in the United States, their trade associations, and Ajit Pai, one of two Republican commissioners serving at the Federal Communications Commission routinely claim America has the best broadband in the world. From the perspective of providers running to their respective banks to deposit your monthly payment, they might be right. But on virtually every other metric, the United States has some of the most expensive broadband in the world at speeds that would be a gouging embarrassment in other countries.
The largest telecom companies in the United States, their trade associations, and Ajit Pai, one of two Republican commissioners serving at the Federal Communications Commission routinely claim America has the best broadband in the world. From the perspective of providers running to their respective banks to deposit your monthly payment, they might be right. But on virtually every other metric, the United States has some of the most expensive broadband in the world at speeds that would be a gouging embarrassment in other countries.
 The Slovak government insisted that telecommunications networks in the country be competitive and it maintains oversight to make sure monopolies do not develop. It rejected claims that total deregulation and competition alone would spur investment. Slovakia welcomes outside investment, but also makes certain monopoly pricing power cannot develop. As a result, most residents of Bratislava have a choice of up to eight different broadband providers — a mix of cable, telephone, wireless, and satellite providers that all fiercely compete in the consumer and business markets.
The Slovak government insisted that telecommunications networks in the country be competitive and it maintains oversight to make sure monopolies do not develop. It rejected claims that total deregulation and competition alone would spur investment. Slovakia welcomes outside investment, but also makes certain monopoly pricing power cannot develop. As a result, most residents of Bratislava have a choice of up to eight different broadband providers — a mix of cable, telephone, wireless, and satellite providers that all fiercely compete in the consumer and business markets. Prices are considerably lower than what American providers charge, although speeds remain somewhat lower than broadband services in Bulgaria, Romania, and the Baltic States. At one address on Kláštorská, a street of modest single family homes (some in disrepair), these companies were ready to install service:
Prices are considerably lower than what American providers charge, although speeds remain somewhat lower than broadband services in Bulgaria, Romania, and the Baltic States. At one address on Kláštorská, a street of modest single family homes (some in disrepair), these companies were ready to install service:
 The 105Mbps Extreme bundle was priced $20 higher than Ngiovas was originally quoted and the representative insisted there was no way to get the Extreme package for $99.95. When Ngiovas told the representative about Comcast’s “zero dollar” no-cost Extreme upgrade, the representative paused and then admitted yes, the free upgrade was suddenly available. But Ngiovas would have to switch to a different package that would be “price adjusted” to match the original offer, and the customer would also have to commit to stay with that package for a full two years.
The 105Mbps Extreme bundle was priced $20 higher than Ngiovas was originally quoted and the representative insisted there was no way to get the Extreme package for $99.95. When Ngiovas told the representative about Comcast’s “zero dollar” no-cost Extreme upgrade, the representative paused and then admitted yes, the free upgrade was suddenly available. But Ngiovas would have to switch to a different package that would be “price adjusted” to match the original offer, and the customer would also have to commit to stay with that package for a full two years.