
Mayor Guest
Despite protests from major technology companies, consumers, and local communities across Georgia, the House Energy, Utilities and Telecommunications Committee passed a slightly-revised HB 282, a bill that would largely ban communities from building their own networks to deliver 21st century broadband service. The bill has been moved out of the Rules Committee and will be debated on the House floor Thursday. Readers can find and contact their state representative (preferably leaving a phone message opposing HB 282) through this website. Do it this afternoon!
Last Thursday, community leaders appeared in Atlanta to oppose the corporate welfare protectionism that HB 282 represents.
“Let’s talk about economic development,” said Elberton Mayor Larry Guest. “Georgia should be promoting a pro-business, inclusive approach to broadband deployment, especially in rural areas of the state,” he said. “Competition ensures market-based pricing and faster delivery of state-of-the-art services. We have to do everything we can to attract jobs. If we don’t do that, business will not select rural Georgia. High speed access is essential to us.”
Mark Creekmore depends on his Internet connection in his Dawsonville home as part of his job and Windstream has let him down for at least three years. He pays for 12Mbps service and regularly receives around 600kbps service after 3pm because Windstream has hopelessly oversold its DSL service.
“No one should have to pay for Internet speeds they are not receiving and be told that because they live in a rural area, getting them fixed is just not a priority,” Creekmore complains. “That’s like saying: ‘Because you live in the sticks, you do not deserve what the city folks deserve despite the fact that you pay the same money for service that they do.'”
[flv width=”640″ height=”380″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/WGCL Atlanta New Bill Hinders Broadband 2-26-13.mp4[/flv]
WGCL, the CBS station in Atlanta, is asking tough questions about HB 282 and exactly who it will benefit. Some suspect the bill will protect Windstream from having to upgrade its broadband services, something essential to Dawsonville resident Mark Creekmore, who has to turn customers away because Windstream’s DSL service is so poor in his area. (3 minutes)
Creekmore is incensed Windstream is behind a push to pass HB 282, which bill supporters claim will “stimulate investment in rural broadband,” at the same time the phone company leaves him and others with substandard speeds and service.
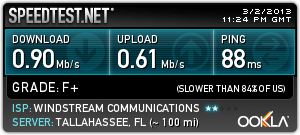 “I do not think it is ethical for companies like Windstream, already benefiting from taxpayer dollars, to back a bill that will keep municipalities from offering their residents something better,” said Creekmore.
“I do not think it is ethical for companies like Windstream, already benefiting from taxpayer dollars, to back a bill that will keep municipalities from offering their residents something better,” said Creekmore.
Creekmore opposes government waste, but is not opposed to local communities stepping up when telecommunications companies have let their customers down.
Despite claims HB 282 will promote rural broadband expansion, Windstream’s CEO Jeff Gardner told investors the opposite Feb. 19 in a conference call.
“We will finish most of our broadband stimulus initiatives which expands our addressability to roughly 75,000 new households,” said Gardner. “As we exit 2013, we will see capital spending related to these projects decrease substantially.”
Windstream’s broadband problems are not limited to rural Georgia. In rural Missouri, Windstream’s DSL service has performed so poorly in certain communities local businesses have had to shut down operations for the day when kids are out on “snow days” because service deteriorates to the point it becomes unusable.

Thomasville, Ga., runs a public fiber to the home network that delivers the speeds it advertises.
“Windstream has made it clear that they have no plans to invest in areas where they don’t feel they can be profitable,” said Piedmont Area Chamber of Commerce president Scott Combs.
Because rural broadband problems remain so pervasive, a group of technology companies including Google and Alcatel-Lucent sent a letter to the chairman of the Georgia House Energy, Utilities and Telecommunications Committee protesting the bill:
The private sector alone cannot enable the United States to take full advantage of the opportunities that advanced communications networks can create in virtually every area of life. As a result, federal and state efforts are taking place across the Nation, including Georgia, to deploy both private and public broadband infrastructure to stimulate and support economic development and job creation, especially in economically distressed areas. HB 282 would prevent public broadband providers from building the sorely needed advanced broadband infrastructure that will stimulate local businesses development, foster work force retraining, and boost employment in economically underachieving areas.
Thus far, the only response has been to slightly ease the language in the bill, now defining suitable broadband at 3Mbps service, up from 1.5Mbps. Communities with municipally owned utilities would also be exempt from the prohibition on selling telecom services. But that is hardly enough.
“Three megabits is not adequate to do functions in a modern telecommunications world,” said Thomasville mayor Max Beverly.
Thomasville has its own public broadband network and the difference between it and providers like Windstream are quickly apparent.
While Windstream sells rural Georgians service at 12Mbps but actually delivers less than 1Mbps, Thomasville residents are excited about forthcoming upgrades to 20Mbps service that actually means 20Mbps service. Thomasville’s fiber network has proved so financially successful, the community eliminated its local property tax. If HB 282 passes, other communities will find constructing such networks nearly impossible.
Democracy Now! featured Chris Mitchell and Catharine Rice on March 4, who talked about how large telecom companies are lobbying to ban community-owned broadband networks, including those in Georgia. AT&T, Comcast, Time Warner Cable and others are having success in the southeastern United States with the help of Republican state lawmakers and conservative groups with ties to the Koch Brothers. (10 minutes)



 Subscribe
Subscribe
 “I do not think it is ethical for companies like Windstream, already benefiting from taxpayer dollars, to back a bill that will keep municipalities from offering their residents something better,” said Creekmore.
“I do not think it is ethical for companies like Windstream, already benefiting from taxpayer dollars, to back a bill that will keep municipalities from offering their residents something better,” said Creekmore.
 Windstream has announced the increased broadband investments that expanded DSL service to about 75,000 more homes and businesses and brought fiber connections to cell towers are nearly complete and the company intends to dramatically cut spending on further enhancements by the end of 2013.
Windstream has announced the increased broadband investments that expanded DSL service to about 75,000 more homes and businesses and brought fiber connections to cell towers are nearly complete and the company intends to dramatically cut spending on further enhancements by the end of 2013. “We expect to substantially complete our capital investments related to fiber to the tower projects, reaching 4,500 towers by the end of 2013,” said Gardner. “In addition, we will finish most of our broadband stimulus initiatives […] to roughly 75,000 new households. As we exit 2013, we will see capital spending related to these projects decrease substantially.”
“We expect to substantially complete our capital investments related to fiber to the tower projects, reaching 4,500 towers by the end of 2013,” said Gardner. “In addition, we will finish most of our broadband stimulus initiatives […] to roughly 75,000 new households. As we exit 2013, we will see capital spending related to these projects decrease substantially.”

 The nation’s largest broadband stimulus grant recipient has turned a $126.3 million taxpayer funded broadband expansion program into an “orchestrated train wreck,”
The nation’s largest broadband stimulus grant recipient has turned a $126.3 million taxpayer funded broadband expansion program into an “orchestrated train wreck,” 
