
CRTC chairman Jean-Pierre Blais
Independent Internet Service Providers are hailing a decision by telecommunications regulators that will force big phone and cable companies to open their fiber optic networks to competitors, suggesting Canadian consumers will benefit from lower prices, fewer usage caps, and higher-speed Internet.
The Canadian Radio-television and Telecommunications Commission on Wednesday ordered companies like Bell/BCE, Telus, Rogers, Shaw, and others to sell wholesale access to their growing fiber optic networks, despite industry protests giving that access would harm future investment in fiber technology just as it is on the cusp of spreading across the country.
“We’re an evidence-based body, so we heard all of the positions of the various parties and we balanced those off through what we heard in our deliberations afterwards,” said CRTC chairman Jean-Pierre Blais. “In this particular case, we are concerned about the future of broadband in the country so we have to make sure we have a sustainable and competitive marketplace. It’s a wholesale decision that says Canadians can expect a better competitive marketplace because we are going to require incumbent cable and telephone companies to make their high-speed facilities available to competitors.”
[flv]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/BNN Breaking News CRTC Decision Fiber 7-22-15.flv[/flv]
BNN broke into regular programming with this Special Report on the CRTC decision that will grant independent ISPs access to large telecom companies’ fiber optic networks. (3:13)
Large phone companies, including Bell, warned regulators in a hearing last fall that forcing them to open their networks to third parties would deter investment in fiber expansion. Canadian telecom companies now provide about three million homes with either fiber to the home or fiber to the neighborhood service. Blais, along with representatives of independent ISPs have rejected Bell’s arguments, arguing competition from cable operators was forcing telephone companies to upgrade their networks regardless of the wholesale access debate.
 “Our view is the incumbent telcos have a market reason to invest in improving their plant through the investment in fiber,” Blais said. “That’s what Canadians expect and because of market conditions they have to do that investment. So we’re quite confident that’s going to happen.”
“Our view is the incumbent telcos have a market reason to invest in improving their plant through the investment in fiber,” Blais said. “That’s what Canadians expect and because of market conditions they have to do that investment. So we’re quite confident that’s going to happen.”
Canadian telecommunications companies have done well selling Internet and television services in a highly concentrated telecommunications and media marketplace. For example, BCE, the parent company of Bell Canada, Bell Media, and Bell TV owns a wireless carrier, a satellite TV provider, the CTV television network and many of its local affiliates, dozens of radio stations, more than two dozen cable networks, a landline telephone company, an Internet Service Provider, and ownership interests in sports teams like the Montreal Canadiens as well as a part interest in The Globe and Mail, Canada’s unofficial newspaper of record.
Companies like Rogers, Shaw, Vidéotron, Telus, and Bell have dominated the market for Internet access. But regulators began requiring these companies to sell access to their networks on a wholesale basis to smaller competitors to foster additional retail competition. Today, there are over 500 independent ISPs selling service in Canada, including well-known companies like TekSavvy, Primus, and Distributel. In the past few years, Internet enthusiasts have flocked to these alternative providers to escape a regime of usage caps and usage-based billing of Internet service common among most incumbent cable and phone companies. Competition from the independents, which offer more generous usage allowances or sell unlimited access, has forced some phone and cable companies to offer cap-free Internet service as well.
[flv]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/BNN CRTC Decision Interview with Jean Pierre Blais 7-22-15.flv[/flv]
BNN interviewed CRTC chairman Jean-Pierre Blais about the commission’s decision to open up wholesale access to Canada’s fiber optic networks. (5:26)
 Despite the competition, the majority of Canadians still do business with BCE, Rogers Communications, Quebecor (Vidéotron), Shaw Communications, or Telus, that collectively captured 75 percent of telecom revenue in 2013.
Despite the competition, the majority of Canadians still do business with BCE, Rogers Communications, Quebecor (Vidéotron), Shaw Communications, or Telus, that collectively captured 75 percent of telecom revenue in 2013.
Although competitors have been able to purchase wholesale access to cable broadband and DSL service, nothing in the CRTC rules required big cable and phone companies to sell access to next generation fiber networks. That gap threatened the viability of independent ISPs, left with offering customers access to older cable/copper technology only. This week’s CRTC decision is the first step to grant access to fiber networks as well, although some ISPs are cautious about the impact of the decision until the CRTC provides pricing guidance.
“The commission took a great step today in favor of competition,” Matt Stein, CEO of Distributel Communications Ltd., told The Globe and Mail. “In giving us access to fiber to the premise, they have ensured that as speeds and demands increase, we’re going to continue to be able to provide service that customers want. It’s definitely going to be some time before these products make it to market. There’s going to be the costing and the implementation, and reasonably it could be a year or even longer before the products are actually out the door. But the heavy lifting? Today that was done.”
Bram Abramson, chief legal and regulatory officer for TekSavvy Solutions Inc., added some caution.

Distributel, an independent ISP, made a name for itself offering usage-cap free Internet access to Canadians.
“The devil really is in the details on this,” Abramson told the newspaper. “That’s why I say we like the direction, because there are a million ways in which this could become unworkable if implemented wrong. For example, what rates are we going to pay? We won’t know until those tariffs are done and settled.”
Other so-called “wireline incumbents” like Manitoba Telecom and SaskTel will also be required to make their fiber optic networks available to competitors.
Last fall, Bell warned the CRTC of the consequences of letting TekSavvy, Distributel, and others resell access to their fiber networks.
“We are not suggesting that mandated access will immediately grind investment to a halt in every location in Canada, but it is a question of balance and it will have an impact,” Mirko Bibic, chief legal and regulatory officer for BCE/Bell told CRTC commissioners at a hearing.
Bibic cautioned if the CRTC granted competitive access it could affect how the company allocated its capital investments and could lead it to shift spending to other areas instead.
“What we’re saying is a mandated access rule will affect the pace of deployment and the breadth of deployment,” Bibic said.

Bibic
Specifically, Bibic claimed Bell may call it quits on fiber expansion beyond the fiber-to-the-neighborhood service Bell sells under the Fibe brand in 80% of its service area in Ontario and Quebec. Bell had envisioned upgrading the network to straight fiber-to-the-home service, eliminating the rest of the legacy copper still in its network. But perhaps not anymore.
“If the commission forces the incumbent telephone operators to open access to fiber-to-the-home, BCE might not prioritize building that final leg in some communities,” Bibic warned. “The point is, with 80% of our territory covered […] we can hold and do really well with fiber-to-the-node for longer than we otherwise might.”
Nonsense, independent ISPs told the CRTC, pointing to the cable industry’s preparations to introduce DOCSIS 3.1 cable broadband and vastly increase broadband speeds well in excess of what a fiber-to-the-neighborhood network can offer.
“First of all, [telephone companies] have a natural incentive to build wherever there is a cable carrier, because otherwise the cable carrier will eat their lunch,” said Chris Tacit, counsel to the Canadian Network Operators Consortium, which represents the interests of independent ISPs. “There’s a reason that they’re sinking all that money into [fiber-to-the-home], it’s because they have to keep up. Now, I don’t believe for a minute that they are going to stop investing if they have to grant access.”
Regulators in the United States have traditionally sided with large telecommunications companies and have largely allowed phone and cable companies to keep access to their advanced broadband networks to themselves. Republicans have largely defended the industry position that regulation and forced open access would deter private investment and competitors should construct networks of their own. In some cases, they have. Google Fiber is now the most prominent overbuilder, but several dozen independent providers are also slowly wiring fiber optics in communities already served by cable and telephone company-provided broadband. Whether it is better to inspire new entrants to build their own networks or grant them access to existing ones is an ongoing political debate.
But the CRTC has not given independent ISPs a free ride. The commission announced it will begin moving towards “disaggregated” network availability for smaller ISPs, which will require them to invest in network equipment to connect with incumbent networks on a more local level, starting in Ontario and Quebec.
The CRTC under Blais’ leadership is gaining a reputation of being pro-consumer, a departure from the CRTC’s often-industry-friendly past. Blais has presided over rulings to regulate wholesale wireless roaming fees to lower consumer costs and forced pay television providers to unbundle their huge TV channel packages so consumers can get rid of scores of channels they don’t watch.
[flv]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/The Globe and Mail Internet competitors welcome CRTC decision on broadband access 7-23-15.flv[/flv]
Canadian Press spoke with independent ISPs about their reaction to the wholesale access decision. (1:18)
 Montréal cable subscribers will soon be able to buy gigabit broadband speeds from Vidéotron after a successful pilot project demonstrated the cable company’s existing DOCSIS 3.0 network was up to the task.
Montréal cable subscribers will soon be able to buy gigabit broadband speeds from Vidéotron after a successful pilot project demonstrated the cable company’s existing DOCSIS 3.0 network was up to the task.

 Subscribe
Subscribe
 “Our view is the incumbent telcos have a market reason to invest in improving their plant through the investment in fiber,” Blais said. “That’s what Canadians expect and because of market conditions they have to do that investment. So we’re quite confident that’s going to happen.”
“Our view is the incumbent telcos have a market reason to invest in improving their plant through the investment in fiber,” Blais said. “That’s what Canadians expect and because of market conditions they have to do that investment. So we’re quite confident that’s going to happen.”




 That philosophy may still cost cable companies customers if a fiber competitor doesn’t have to compromise speed and performance and can afford to charge less.
That philosophy may still cost cable companies customers if a fiber competitor doesn’t have to compromise speed and performance and can afford to charge less.
 Midcontinent Communications customers will be able to get gigabit broadband speeds… by the end of 2017.
Midcontinent Communications customers will be able to get gigabit broadband speeds… by the end of 2017.
 With video streaming now accounting for at least 64 percent of all Internet traffic, it should have come as no surprise to Australia’s ISPs that as data caps are eased and popular online video services like Netflix arrive, traffic spikes would occur on their networks as well.
With video streaming now accounting for at least 64 percent of all Internet traffic, it should have come as no surprise to Australia’s ISPs that as data caps are eased and popular online video services like Netflix arrive, traffic spikes would occur on their networks as well.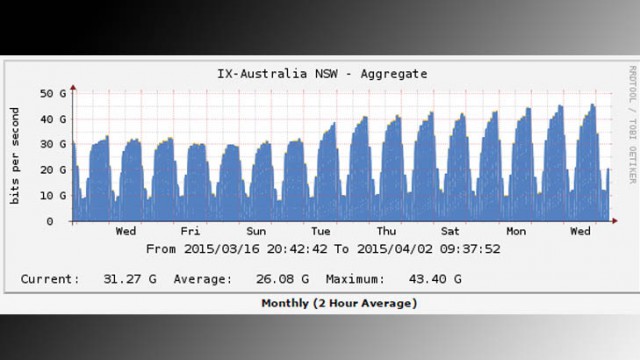
 The need for further upgrades as a result of traffic growth breaks another firm commitment from the conservative government.
The need for further upgrades as a result of traffic growth breaks another firm commitment from the conservative government.
