 Question: How will ripping out landline infrastructure in Kentucky help improve broadband service for rural areas?
Question: How will ripping out landline infrastructure in Kentucky help improve broadband service for rural areas?
Answer: It won’t.
This is not for a lack of trying though. AT&T has returned to the Kentucky state legislature year after year with a company-written bill loaded with more ornaments than a Christmas tree. In the guise of “modernizing” telecom regulation, AT&T wants to abolish most of it, replaced by a laissez-faire marketplace for telecommunications services not seen in the United States since the 1910s. AT&T claims robust competition will do a better job of keeping providers in check than a century of oversight by state officials. But customers in rural Kentucky have a better chance of sighting Bigfoot than finding a competitive alternative to AT&T’s telephone and DSL service. AT&T retains a monopoly in broadband across much of the state where cable operators like Time Warner don’t tread.
This year, Senate Bill 99, dubbed “The AT&T Bill” received overwhelming support from the Kentucky Senate as well as in the House Economic Development Committee. AT&T made sure the state’s most prominent politicians were well-compensated with generous campaign contributions, which helped move the bill along.
Since 2011, AT&T’s political-action committee has given about $55,000 to state election campaigns in Kentucky, including $5,000 to the Senate Republican majority’s chief fundraising committee and $5,000 more to the House Democratic majority’s chief fundraising committee. The company spent $108,846 last year on its 22 Frankfort lobbyists.
That generosity no doubt helped Republican Floor Leader Jeff Hoover find his way to AT&T’s talking point that only by “modernizing” Kentucky’s telecom laws would the state receive much-needed broadband improvements.

Hoover
Hoover is upset that the state’s House Democratic leadership stopped AT&T’s bill dead in its tracks, despite bipartisan begging primarily from AT&T’s check-cashers that the bill see a vote. Speaker Greg Stumbo, whose rural Eastern Kentucky district would have seen AT&T’s landline and DSL service largely wiped out by AT&T’s original proposal, would hear none of it.
He has been to AT&T’s Deregulation Rodeo before.
“When I served as attorney general, I dealt with deregulation firsthand to protect consumers as much as possible,” he wrote in a recent editorial. “In most cases, deregulation led to worse service and less opportunity to correct the problems customers invariably faced. It is now our job as House leaders to continue defending Kentucky’s consumers.”
Stumbo, like many across Kentucky, have come to realize that AT&T’s custom-written legislation gives the company a guarantee it can disconnect rural landline service en masse, but does not guarantee better broadband as a result.
“In fact, there is nothing in the legislation guaranteeing better landline, cell or Internet service,” Stumbo noted.
Hoover declared that by not doing AT&T’s bidding, Kentucky was at risk of further falling behind.
“This decision by Stumbo and House Democrat leadership, like many others, has unfortunately had a real effect on the lives of Kentuckians as we will go, at minimum, another year before these private businesses can focus on increasing broadband speed throughout the commonwealth,” he wrote. “It is another year in which we risk falling further behind our neighboring states and others in the competitive world of economic development.”

Stumbo
Stumbo responded the Republicans seemed to have a narrow vision of what represents progress. Hoover and his caucus voted against the House budget that included $100 million for a broadband improvement initiative spearheaded by Gov. Steve Beshear, Rep. Hal Rogers, and private interests.
By relying entirely on a deregulated AT&T, rural Kentucky residents may lose both landline and DSL service and be forced to wireless alternatives that come at a high price.
“There are citizens, many of whom are elderly or on fixed income, who depend on their landline or cannot afford more expensive options; these are the people I am fighting for,” said Stumbo. “I do not want to get a call from a family member who lost a loved one because that person could not reach a first responder in time.”
State residents watching the debate have increasingly noticed discrepancies between what AT&T wants and what it is promising Kentucky.
“No one has ever been able to satisfactorily explain to me how allowing phone companies to abandon landline service will help expand broadband Internet, especially since DSL service requires phone lines,” said H.B. Elkins, Public Information Officer at KYTC District 10.
Matt Simpson recognizes that Senate Bill 99 and other similar measures will not change the economic realities of AT&T’s for-profit business.
“Without regulation, the for-profit companies like AT&T are going to invest in the most profitable areas,” he wrote. “If they thought they could make a huge profit providing broadband in rural areas, they would already be doing it. Deregulation is not going to change that profit calculation. They will still view rural broadband as unprofitable, and they still won’t do it. The bill was a total giveaway to the industry, with no offsetting benefit to the consumers.”
Michael Yancy summed up his views more colorfully.
“The ‘AT&T bill should be classified as a sheep bill. It was all about pulling the wool over the eyes of the public,” Yancy said. “Anyone who thinks the people of Kentucky will benefit from more of the same, needs to make inquiries into moving the Brooklyn Bridge to the Ohio River.”
[flv]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/KET Phone Deregulation Kentucky Tonight 1 2-19-13.mp4[/flv]
Kentucky Educational Television aired a debate between AT&T and the Kentucky Resources Council on the issue of telephone deregulation in 2013. The same issues were back this year in AT&T’s latest failed attempt to win statewide deregulation and permission to switch landline customers in rural Kentucky to less reliable wireless service. In this clip AT&T argues it should be able to shift investment away from landline service towards wireless because wireless is the more popular technology, but not everyone gets good coverage in Kentucky. (Feb. 19 2013) (3:00)
[flv]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/KET Phone Deregulation Kentucky Tonight 2 2-19-13.mp4[/flv]
In this second clip, AT&T claims customers who want to keep landline service can, but Kentucky Resources Council president Tom Fitzgerald reads the bill and finds AT&T’s claims just don’t hold up under scrutiny. The carrier of last resort obligation which guarantees quality landline phone service to all who want it is gone if AT&T’s bill passes. Customers can be forced to use wireless service instead. (Feb. 19 2013) (4:33)
 Alaska-based GCI has rolled out a free upgrade for customers in Anchorage, Fairbanks, Juneau, Ketchikan, Mat-Su Valley, and Sitka that delivers broadband speeds up to 250/10Mbps.
Alaska-based GCI has rolled out a free upgrade for customers in Anchorage, Fairbanks, Juneau, Ketchikan, Mat-Su Valley, and Sitka that delivers broadband speeds up to 250/10Mbps.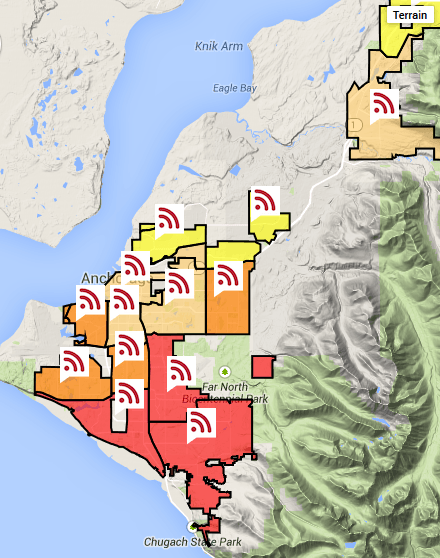
 The speed increases come after its competitor Alaska Communications announced speed increases of its own. ACS sells unlimited access broadband service at speeds up to 50Mbps. ACS has beefed up its copper infrastructure to support faster Internet speeds, starting with 15Mbps introduced across the state in May. Now customers in Anchorage can subscribe to faster tiers including 30 and 50Mbps.
The speed increases come after its competitor Alaska Communications announced speed increases of its own. ACS sells unlimited access broadband service at speeds up to 50Mbps. ACS has beefed up its copper infrastructure to support faster Internet speeds, starting with 15Mbps introduced across the state in May. Now customers in Anchorage can subscribe to faster tiers including 30 and 50Mbps.

 Subscribe
Subscribe Three competing telephone companies in Singapore have launched an all-out price war on gigabit fiber to the home Internet access that shows what real competition can do for broadband pricing.
Three competing telephone companies in Singapore have launched an all-out price war on gigabit fiber to the home Internet access that shows what real competition can do for broadband pricing. Singapore’s largest phone company, SingTel, has its own unlimited gigabit offering for $55.13 a month, a price the company is now re-evaluating.
Singapore’s largest phone company, SingTel, has its own unlimited gigabit offering for $55.13 a month, a price the company is now re-evaluating.
 But some critics contend $664 million is insufficient to wire every building in Ireland for fiber service and suspect the government may try to backtrack and choose fiber to the cabinet or wireless service for the most isolated communities that could prove extremely expensive to reach with fiber.
But some critics contend $664 million is insufficient to wire every building in Ireland for fiber service and suspect the government may try to backtrack and choose fiber to the cabinet or wireless service for the most isolated communities that could prove extremely expensive to reach with fiber.


 Staff at the New York regulator overseeing the state’s telecommunications companies have determined that some Time Warner Cable customers will see their largest rate increase in New York history — more than double their current rate — if Comcast is successful in its bid to acquire Time Warner Cable.
Staff at the New York regulator overseeing the state’s telecommunications companies have determined that some Time Warner Cable customers will see their largest rate increase in New York history — more than double their current rate — if Comcast is successful in its bid to acquire Time Warner Cable.