A $500 million New York State broadband improvement fund is effectively off-limits for would-be community-owned broadband networks trying to deliver broadband service in areas for-profit providers have deemed unprofitable.
New York Gov. Andrew Cuomo’s ambitious plan to revolutionize Internet access for New Yorkers depends almost exclusively on for-profit providers and the state’s largest cable operator, Time Warner Cable – the company that has so far received the largest share of state funds earmarked for better broadband.
Cuomo wants all of New York wired for 100Mbps service no later than 2018. His goal is ambitious because the overwhelming majority of upstate New York barely now receives a maximum of 50Mbps from Time Warner Cable, the only significant cable operator in the region.
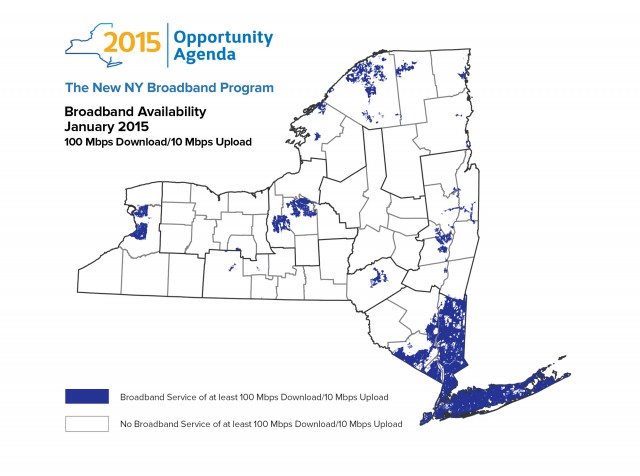
The broadband map from N.Y. State shows 100Mbps service is available only from Verizon FiOS, Cablevision, and a handful of municipal/co-op operators. Time Warner Cable only provides a maximum of 50Mbps service across upstate New York. Cablevision and FiOS compete on Long Island, Time Warner Cable Maxx competes with Verizon in New York City, and most of upstate New York is served by Verizon or Frontier DSL competing with Time Warner Cable.
Six months after the program was announced, Capital magazine reports the “New NY Broadband” plan is languishing with no defined guidelines, rules, or any clear sense about how the program will be implemented and the money spent.

Salway
In fact, one of the only clear statements coming from David Salway, a former telecommunications consultant who now administers the program, is that local governments should not bother applying because he doesn’t want them competing with Time Warner Cable, Verizon, and Frontier. It’s private enterprise only:
“The primary focus of our program is that we’re not going to be in the building business,” Salway said. He emphasized that municipal governments won’t be specifically precluded from receiving funds under the program, but said that the state is “wary” of “the government building and competing with the private sector. We see this as a provider partnership process where an incumbent provider or maybe a new entrant comes in.”
Local government leaders can read between the lines and most will not bother applying for funding if Salway’s vision guides the grant-making process. Instead, Salway wants to funnel money that effectively belongs to New York taxpayers into the pockets of for-profit providers like Verizon, Frontier, Windstream, Time Warner Cable and other providers that have consistently refused to expand their networks into rural areas on their own dime. The money earmarked for broadband is part of a $6 billion legal settlement the New York Attorney General’s office negotiated with Wall Street and commercial banks that helped plunge the country into The Great Recession.
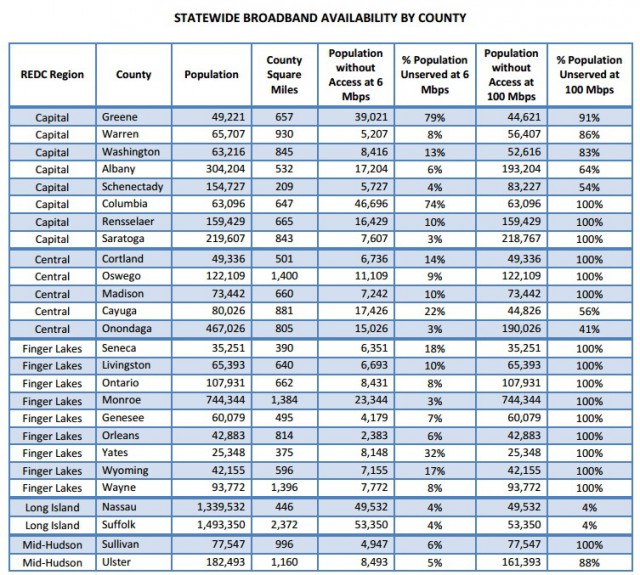
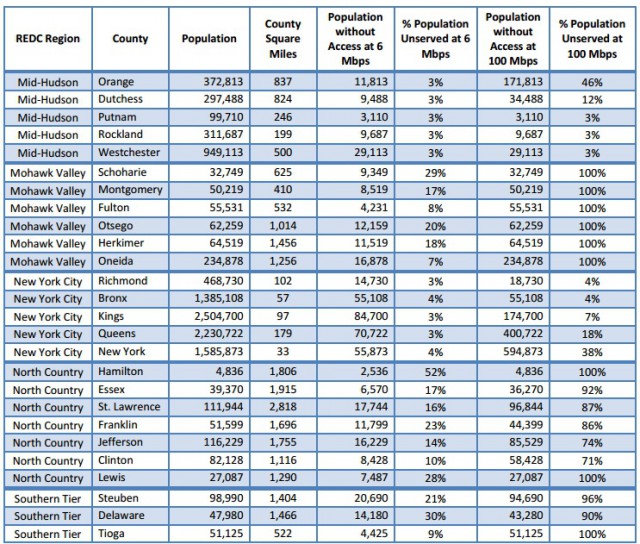
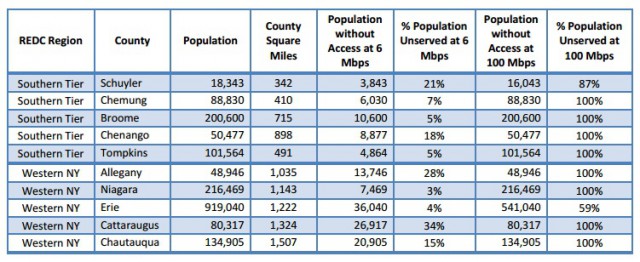
Broadband advocates across the political spectrum are slamming the broadband program for different reasons. Christopher Mitchell from the Institute for Local Self Reliance predicts providers will deliver bait and switch broadband on the taxpayer’s dime and send the proceeds out of the area.
“When you subsidize the private sector, you don’t really know what kind of services they’re going to provide in the future,” Mitchell said. “There’s a fair number that basically rip off consumers,” and they “basically extract resources from the community they serve.”

Mitchell
“The only clear beneficiaries of this program will be cable and Internet providers, who will have a new state subsidy to expand their footprints into areas in which their competitors have demonstrated an inability to operate profitably,” said Ken Girardin of the conservative Empire Center for Public Policy, in a scathing review of the New NY plan.
So far, Verizon has shown no interest in the program. It’s eventual intent is to decommission rural landline service and push existing customers to wireless service, so applying for wired broadband expansion funding isn’t a priority. The most likely applicants include Windstream, which serves a small percentage of rural New York telephone exchanges, Frontier Communications, which dominates Rochester and parts of the Finger Lakes region, and Time Warner Cable, which used earlier funding to connect two rural communities to its cable service. But all three companies are waiting for the program and its grant terms to be better defined.
With incumbent cable and phone companies reluctant to take part, there are several wired and wireless broadband initiatives in rural areas around New York starved of resources to expand their networks. The “white space” wireless broadband project in Thurman, for example, will be seeking funding to expand its wireless high-speed network into other parts of the community. Other initiatives could allow existing middle mile fiber networks in the Southern Tier and Finger Lakes region to explore building out “last mile” service to homes and businesses that now receive only DSL or no Internet access at all.
Salway promises he’ll consider funding networks that deliver the best broadband speeds for the lowest relative price in similarly sized communities. But all the money in the world won’t help if an existing phone or cable company shows no interest in serving unprofitable rural areas even after the state defrays the initial cost of placing the infrastructure to provide the service.
Mitchell believes local communities are best positioned to know what their residents want and many support publicly funded fiber technology rollouts. He points to Longmont, Col., a community that fought off propaganda mailers and a $300,000 marketing effort by CenturyLink and Comcast to defeat public fiber broadband in the city. The residents voted in favor of building their own network to move beyond the “good enough for you” broadband coming from the phone and cable company.
“The Longmonts of the country can decide to wait until these private sector companies decide its in their interest to finally build these fiber networks out, or they can say, ‘You know, we’re always going to be behind the greater technological curve of the nation,’ and do it themselves,” Tom Roiniotis, Longmont’s general manager, told Capital.
 Time Warner Cable is notifying its customers in Charlotte, N.C. to prepare for the transition to all-digital cable television service which will be complete by the end of this summer. Further south, San Antonio customers can swing by their local cable store and pick up Time Warner Cable’s new terabyte DVR, which can record up to six different programs at the same time and store six times more content than current DVR boxes.
Time Warner Cable is notifying its customers in Charlotte, N.C. to prepare for the transition to all-digital cable television service which will be complete by the end of this summer. Further south, San Antonio customers can swing by their local cable store and pick up Time Warner Cable’s new terabyte DVR, which can record up to six different programs at the same time and store six times more content than current DVR boxes.

 Subscribe
Subscribe Cox Communications has raised Internet speeds for its economy class customers in Arizona as it continues network enhancements across the state.
Cox Communications has raised Internet speeds for its economy class customers in Arizona as it continues network enhancements across the state.





 Frontier Communications customers lucky enough to have access to fiber to the home service will find broadband speeds have been increased to offer identical upload and download rates.
Frontier Communications customers lucky enough to have access to fiber to the home service will find broadband speeds have been increased to offer identical upload and download rates. AT&T is rolling out its gigabit fiber service in Cupertino, Calif., but if you want it you will pay $40 a month more than those who live in cities where Google Fiber offers competition.
AT&T is rolling out its gigabit fiber service in Cupertino, Calif., but if you want it you will pay $40 a month more than those who live in cities where Google Fiber offers competition. AT&T customers who do not want the company to monitor their browsing activities have to pay $29 more for privacy protection, which opts them out of AT&T’s tracking systems. Despite the high-speed and price, AT&T still insists on usage caps for its most premium broadband offering. Customers can use up to 1TB per month, after which AT&T slaps overlimit fees of $10 for each 50GB customers use over their limit. Its primary competitors, including Google, Time Warner Cable, Verizon and Charter do not have usage caps. Boyer says he knows of no customer that has exceeded the 1,000GB usage cap. But that also brings the question if no customer has exceeded the cap, why have one?
AT&T customers who do not want the company to monitor their browsing activities have to pay $29 more for privacy protection, which opts them out of AT&T’s tracking systems. Despite the high-speed and price, AT&T still insists on usage caps for its most premium broadband offering. Customers can use up to 1TB per month, after which AT&T slaps overlimit fees of $10 for each 50GB customers use over their limit. Its primary competitors, including Google, Time Warner Cable, Verizon and Charter do not have usage caps. Boyer says he knows of no customer that has exceeded the 1,000GB usage cap. But that also brings the question if no customer has exceeded the cap, why have one?