 With the advent of AT&T/DirecTV Now, AT&T’s new over-the-top streaming TV service launching later this year, AT&T is preparing to bury the U-verse brand.
With the advent of AT&T/DirecTV Now, AT&T’s new over-the-top streaming TV service launching later this year, AT&T is preparing to bury the U-verse brand.
Earlier this year, AT&T customers noticed a profound shift in the company’s marketing priorities. The phone company began steering potential customers to AT&T’s latest acquisition, satellite television provider DirecTV, instead of U-verse. There is an obvious reason for this – DirecTV has 20.45 million customers as of the second quarter of 2016 compared to 4.87 million customers for AT&T U-verse TV. Volume discounts make all the difference for pay television companies and AT&T hopes to capitalize on DirecTV’s lower programming costs.
AT&T’s buyout of DirecTV confused many Wall Street analysts, some who believe the days of satellite television are past their peak. Satellite providers lack the ability to bundle services, although some phone companies partner with the satellite company to pitch phone, broadband, and satellite TV to their customers. But consider for a moment what would happen if DirecTV introduced satellite television without the need for a satellite dish.

Phillip Dampier: The “U” in U-verse doesn’t stand for “unlimited.”
AT&T’s DirecTV Now will rely on the internet to deliver television channels instead of a satellite. AT&T is currently negotiating with most of the programmer conglomerates that own popular cable channels to allow them to be carried “over-the-top” through broadband connections. If successful, DirecTV Now could become a nationwide powerhouse alternative to traditional cable TV.
AT&T is clearly considering a potential future where DirecTV could dispense with satellites and rely on broadband instead. The company quietly began zero rating DirecTV streaming in September for AT&T Mobility customers, which means watching that programming will not count against your data plan. For current U-verse customers, broadband speeds have always been constrained by the need to reserve large amounts of bandwidth to manage television viewing. Although AT&T has been boosting speeds in selected areas, a more fundamental speed boost could be achieved if AT&T dropped U-verse television and turned the service into a simple broadband pipe that relied on DirecTV Now to manage television service for customers.
AT&T seems well on the way, adding this notice to customer bills:
“To make it simpler for our customers U-verse High Speed Internet and U-verse Voice services have new names: AT&T Internet and AT&T Phone. AT&T Internet product names will now align with our Internet speed tiers. Our voice plan names will remain the same.”
An earlier internal company memo suggested AT&T would eventually transition all of its TV products into “AT&T Entertainment” after completing a transition to its “next generation TV platform.” Increasingly, that platform seems to be an internet-powered streaming solution and not U-verse or DirecTV satellite. That transition should begin in January.

Gone by end of 2016.
It would represent a formidable change, but one that makes sense for AT&T’s investors. The transition to IP networks means providers will offer one giant broadband pipe, across which television, phone and internet access will travel. The bigger that pipe becomes, the more services customers are likely to use — and that means growing data usage. Having a lot of fiber infrastructure also lays the foundation for expansion of AT&T’s wireless network — particularly towards 5G service, which is expected to rely on small cell technology to offer faster speeds to a more localized area — fast enough to serve as a home broadband replacement. Powering that network will require plenty of fiber optics to provide backhaul access to those small cells.
Last week, AT&T announced it launched a trial 100Mbps service using point-to-point millimeter-wave spectrum to offer broadband to subscribers in multiple apartment complexes around the Minneapolis area. If the initial trial is successful, AT&T will boost speeds to include 500Mbps service to those same complexes. AT&T has chosen to provide the service outside of its usual service area — Minneapolis is served by CenturyLink. AT&T acquired a nationwide license to offer service in the 70-80GHz band back in 2009, and an AT&T spokesperson claimed the wireless signal can reach up to two miles. The company is also experimenting with new broadband over power lines technology that could offer service in rural areas.
 Just like its wireless service, AT&T stands to make money not just selling access to broadband and entertainment, but also by metering customer usage to monetize all aspects of how customers communicate. Getting customers used to the idea of having their consumption measured and billed could gradually eliminate the expectation of flat rate service, at which point customers can be manipulated to spend even more to access the same services that cost providers an all-time low to deliver. Even zero rating helps drive a belief the provider is doing the customer a favor waiving data charges for certain content, delivering a value perception made possible by that provider first overcharging for data and then giving the customer “a break.”
Just like its wireless service, AT&T stands to make money not just selling access to broadband and entertainment, but also by metering customer usage to monetize all aspects of how customers communicate. Getting customers used to the idea of having their consumption measured and billed could gradually eliminate the expectation of flat rate service, at which point customers can be manipulated to spend even more to access the same services that cost providers an all-time low to deliver. Even zero rating helps drive a belief the provider is doing the customer a favor waiving data charges for certain content, delivering a value perception made possible by that provider first overcharging for data and then giving the customer “a break.”
As of mid-September, streaming media analyst Dan Rayburn noted Akamai — a major internet backbone transit provider — was selling content delivery contracts at $0.002 per gigabyte delivered, the lowest price Rayburn has ever seen. Other bids Rayburn has reviewed recently topped out at 0.5 cents per gigabyte. According to industry expert Dave Burstein, that suggests large ISPs like AT&T are paying something less than a penny per gigabyte for internet traffic.
“If you use 139GB a month, that costs your provider something like $1/month,” Burstein wrote, noting doubling backbone transit costs gives a rough estimate of the cost to the carrier, which also has to carry the bits to your local exchange. In this context, telecom services like broadband and phone service should be decreasing in cost, not increasing. But the opposite is true. Large providers with usage caps expect to be compensated many times greater than that, charging $10 for 50GB in overlimit fees while their true cost is well under 50 cents. Customers buying a cell phone are often fitted with a data plan that represents an unprecedented markup. The extent of price increases customers can expect can be previewed by looking at the cost of phone service over the last 20 years. The average, often flat rate telephone bill in 1995 was $19.98 a month. In 2014, it was $73 a month. In 2015, it was $90 a month. Those dramatically rising prices in the last few years are mostly as a result of the increased cost of data plans providers charge to clean up on customers’ growing data usage.
Both Comcast and AT&T are dedicated to a campaign of getting customers to forget about flat rate, unlimited service at a reasonable cost. Even as both companies raise usage caps, they continue to raise prices as well, even as their costs to provide the service continue to drop. Both companies hope to eventually create the kind of profitable windfall with wired services that wireless providers like AT&T and Verizon Wireless have enjoyed for years since they abandoned unlimited flat rate plans. Without significant new competition, the effective duopoly most Americans have for telecommunications services offers the opportunity to create a new, more costly (and false) paradigm for telecom services, based on three completely false claims:
- data costs are expensive,
- usage must be monetized, and
- without a bigger return on investment, investors will not finance the next generation of telecom upgrades.
But as the evidence clearly shows, profits from selling high-speed internet access are only growing, even as costs are falling. Much of the drag on profits come from increasing costs related to licensing television content. Voice over IP telephone service is almost an afterthought for most cable and phone companies, often thrown in for $10-20 a month.
AT&T’s transition puts all the attention and its quest for fatter profits on its broadband service. That’s a bad deal for AT&T customers no matter what the company calls its “next generation” network.


 Subscribe
Subscribe The Federal Communications Commission should redefine broadband as speeds of at least 50/20Mbps,
The Federal Communications Commission should redefine broadband as speeds of at least 50/20Mbps,  The cable industry’s broadband Achilles’ heel has always been upstream speeds that are set much lower than download speeds. But the days of asymmetric cable broadband may soon be a thing of the past if CableLabs successfully defines a new Full Duplex extension for DOCSIS 3.1 — bringing symmetrical broadband speeds to cable companies across the country.
The cable industry’s broadband Achilles’ heel has always been upstream speeds that are set much lower than download speeds. But the days of asymmetric cable broadband may soon be a thing of the past if CableLabs successfully defines a new Full Duplex extension for DOCSIS 3.1 — bringing symmetrical broadband speeds to cable companies across the country. Only half of CenturyLink’s customers in well-populated areas formerly served by Qwest can buy broadband service at 40Mbps or higher, while rural customers fare considerably worse with less than 25% able to get High Speed Internet at those speeds.
Only half of CenturyLink’s customers in well-populated areas formerly served by Qwest can buy broadband service at 40Mbps or higher, while rural customers fare considerably worse with less than 25% able to get High Speed Internet at those speeds. CenturyLink attempts to cover their claims with fine print attached to their FCC submission: “The numbers shown in this chart reflect the percentages of households served by DSLAMs that are capable of providing the specified broadband speeds.” (A DSLAM is a network device typically used to extend faster DSL speeds to customers by reducing the amount of copper wiring between the telephone company’s central office and the customer’s home. Customers in a neighborhood typically share space on a DSLAM, in effect sharing a single connection back to the phone company.)
CenturyLink attempts to cover their claims with fine print attached to their FCC submission: “The numbers shown in this chart reflect the percentages of households served by DSLAMs that are capable of providing the specified broadband speeds.” (A DSLAM is a network device typically used to extend faster DSL speeds to customers by reducing the amount of copper wiring between the telephone company’s central office and the customer’s home. Customers in a neighborhood typically share space on a DSLAM, in effect sharing a single connection back to the phone company.)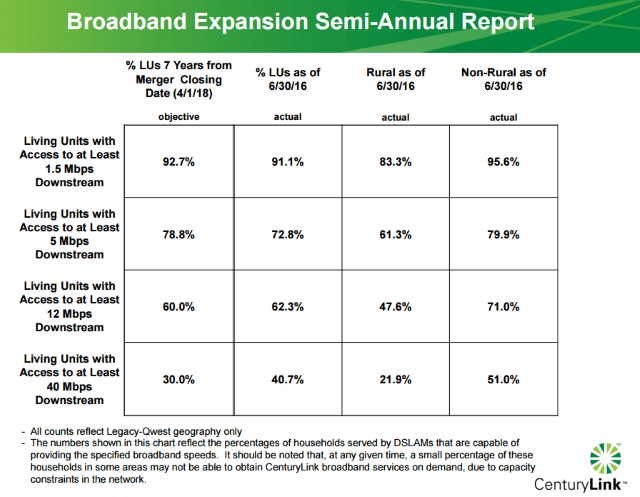
 With more than one million people in its footprint across western New York, Frontier Communications has the potential of picking up a significant number of new customers and keeping others from leaving with the introduction of its Vantage IPTV service (see
With more than one million people in its footprint across western New York, Frontier Communications has the potential of picking up a significant number of new customers and keeping others from leaving with the introduction of its Vantage IPTV service (see  Vantage TV is powered by Frontier’s broadband service and will need more bandwidth than the company can now supply across parts of the three dozen communities it plans to market IPTV in the Greater Rochester area. CEO Dan McCarthy promised to upgrade much of Frontier’s copper network to support speeds of 50Mbps or higher, but that isn’t likely to happen this year in large parts of western New York.
Vantage TV is powered by Frontier’s broadband service and will need more bandwidth than the company can now supply across parts of the three dozen communities it plans to market IPTV in the Greater Rochester area. CEO Dan McCarthy promised to upgrade much of Frontier’s copper network to support speeds of 50Mbps or higher, but that isn’t likely to happen this year in large parts of western New York.