 Most of the same telecom companies that want to create Internet paid fast lanes, drag their feet on delivering 21st century broadband speeds, refuse t0 wire rural areas for broadband without government compensation, and have cut investment in broadband expansion are warning that any attempt by the FCC to enact strong Net Neutrality policies will “threaten new investment in broadband infrastructure and jeopardize the spread of broadband technology across America, holding back Internet speeds and ultimately deepening the digital divide.”
Most of the same telecom companies that want to create Internet paid fast lanes, drag their feet on delivering 21st century broadband speeds, refuse t0 wire rural areas for broadband without government compensation, and have cut investment in broadband expansion are warning that any attempt by the FCC to enact strong Net Neutrality policies will “threaten new investment in broadband infrastructure and jeopardize the spread of broadband technology across America, holding back Internet speeds and ultimately deepening the digital divide.”
Twenty-eight CEOs of some of the same cable and phone companies that have fueled the fight for Net Neutrality protections by their actions signed a letter published on the website of the industry-funded astroturf group Broadband for America.
“An open Internet is central to how America’s broadband providers operate their networks, and the undersigned broadband providers remain fully committed to openness going forward,” says the letter. “We are equally committed to working with the Commission to find a sustainable path to a lawful regulatory framework for protecting the open Internet during the course of the rulemaking you are launching this week.”
Ironically, some of the same companies signing the letter earlier successfully sued the Federal Communications Commission to overturn Net Neutrality policies the agency attempted to enact under a lighter regulatory framework.
The industry now fears the FCC will reclassify broadband as a “telecommunications service,” which makes the service subject to oversight far less likely to successfully be overturned in the courts.
That has caused a panic in the boardrooms of some of America’s largest phone and cable companies.
“In recent days, we have witnessed a concerted publicity campaign by some advocacy groups seeking sweeping government regulation that conflates the need for an open Internet with the purported need to reclassify broadband Internet access services as Title II telecommunications services subject to common carrier regulation,” the letter says.


The companies warn that any attempt to rein in the largely unregulated broadband industry would be a major disaster for the U.S. economy and further broadband expansion:
Broadband investment is falling even without Net Neutrality.
Not only is it questionable that the Commission could defensibly reclassify broadband service under Title II, but also such an action would greatly distort the future development of, and investment in, tomorrow’s broadband networks and services. America’s economic future, as envisioned by President Obama and congressional leaders on both sides of the aisle, critically depends on continued investment and innovation in our broadband infrastructure and app economy to drive improvements in health care, education and energy. Under Title II, new service offerings, options, and features would be delayed or altogether foregone. Consumers would face less choice, and a less adaptive and responsive Internet. An era of differentiation, innovation, and experimentation would be replaced with a series of ―Government may I? requests from American entrepreneurs. That cannot be, and must not become, the U.S. Internet of tomorrow.
Net Neutrality advocates point out that even without Net Neutrality, broadband investment has fallen in the United States for several years, a point conceded by some cable operators.
In 2010, Suddenlink CEO Jerry Kent explained cable companies are now taking profits now that they don’t have to spend as much on upgrades.
“I think one of the things people don’t realize [relates to] the question of capital intensity and having to keep spending to keep up with capacity,” Kent said. “Those days are basically over, and you are seeing significant free cash flow generated from the cable operators as our capital expenditures continue to come down.”
“We should seek out a path forward together,” suggests the CEOs. “All affected stakeholders need and want certainty and an end to a decade of legal and political wrangling.”
It may prove difficult for observers to take the CEOs seriously considering the litigation record on broadband oversight and regulation. The largest cable and phone companies have repeatedly sued to overturn policies that do not meet with their full approval, something likely to happen again if these giant providers don’t get exactly what they want.


 Subscribe
Subscribe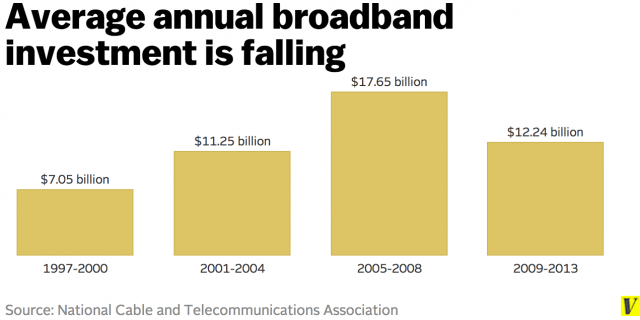
 The United Arab Emirates leads the world with the highest penetration of fiber-to-the-home broadband service.
The United Arab Emirates leads the world with the highest penetration of fiber-to-the-home broadband service. Subscription rates in the next-biggest markets — South Korea, Hong Kong, Japan, Singapore, and Taiwan — range from 63 percent to 37 percent, the council notes. In comparison, the United States
Subscription rates in the next-biggest markets — South Korea, Hong Kong, Japan, Singapore, and Taiwan — range from 63 percent to 37 percent, the council notes. In comparison, the United States 


 As of May 1st, Frontier Communications has raised the price of its standalone DSL service $5 a month, primarily because its competitors have also raised prices.
As of May 1st, Frontier Communications has raised the price of its standalone DSL service $5 a month, primarily because its competitors have also raised prices. Despite the speed increases, cable competitors still made their presence known. Most cable companies sell faster service than Frontier offers and on the low-end, Time Warner Cable’s 2Mbps $15 broadband package, marketed to current DSL customers, was acknowledged to have an impact by Wilderotter, but not enough to bring a significant change in competitive intensity.
Despite the speed increases, cable competitors still made their presence known. Most cable companies sell faster service than Frontier offers and on the low-end, Time Warner Cable’s 2Mbps $15 broadband package, marketed to current DSL customers, was acknowledged to have an impact by Wilderotter, but not enough to bring a significant change in competitive intensity.
