When New is Not Improved
It is disappointing to see a company priding itself on independently measuring America’s broadband performance throw accuracy to the wind and start handing out misleading awards for America’s top broadband providers that their own speed tests often disprove.
Municipal and independently owned Internet providers have relied on Ookla to prove to the world they can offer superior broadband service over what is on offer from the local cable and phone company. Net Index was a useful, independent resource to track broadband speeds and trends based on millions of consumer-run Internet speed and health tests. A provider claiming “up to 10Mbps” service could quickly and easily be verified as a truth-teller or teller of tall tales. As of today, that is no longer as easy to verify:
Ookla Net Index has been discontinued
Ookla is devoted to providing world-class products and services. Sometimes that means saying goodbye to old sites, like Net Index, and hello to new ones…

Those “new and improved” products include:
- SPEEDTEST AWARDS: Provides insights to consumers on where to find the Fastest ISPs & Mobile Networks worldwide, based on data from millions of Speedtests taken in the first half of 2015;
- SPEEDTEST INTELLIGENCE: Designed for enterprises, governments and analysts to understand worldwide internet performance, based on the millions of Speedtests run each day.
While there is nothing objectionable about handing out awards for good performance, it turns out only the nation’s biggest telecom companies need apply, because unless you are Comcast, Time Warner Cable, Cox, Charter, or Verizon, you are too small to matter.
 Among those that do, Comcast’s Xfinity takes first prize:
Among those that do, Comcast’s Xfinity takes first prize:
Comcast XFINITY is the nation’s largest traditional cable operator and largest home ISP. It offers an extremely wide variety of technologies and speeds, peaking at a fiber-based “Extreme 505” tier. That service isn’t widely available, though; you’re more likely to see top speeds of 105Mbps or 150Mbps using traditional DOCSIS 3 cable technology.
Ookla explains away why better performing ISPs are not qualified for one of their awards:
For a given location – either nationwide or a given state or city – we aim to include only ISPs or mobile networks that provide service for a significant number of customers in that geographic area. So, while Google Fiber is the fastest broadband in states like Kansas or Missouri, they are not suitable to be included in the fastest ISPs nationwide because they only serve a very small portion of the United States. To be included in a given geographic area, an ISP or mobile network must meet a minimum threshold based on the number of unique devices testing each day over a six month period.
In other words, accuracy matters a lot less than coverage area. Ookla’s methodology is further invalidated on the local level by their own website.
The prominent first place national award given to Comcast for having the fastest Internet access could mislead you to believe they are the best provider. But Ookla’s own speed tests show that in states like Minnesota, Comcast only comes in third place. Inexplicably, America’s always-lowest rated cable operator — Mediacom, scores first. Charter comes in second. Ookla does not bother to rank municipal-owned broadband providers that outperform all the above.
Not consistently including public, municipal utility, or co-op broadband providers in states like North Carolina and Colorado does an even bigger disservice to anyone depending on Ookla for independent and accurate results. Many of those providers just don’t show up in Ookla’s listings.
In other cases, providers that offer commercial-only broadband make Ookla’s list while even faster providers that sell to consumers don’t. In Rochester, N.Y., Ookla gives first place among local providers to Sutherland Global Services, a provider of business process and technology management services — not a residential ISP. Greenlight Networks delivers gigabit fiber to the home service to select residents in the area and does not appear on Ookla’s list.
Ookla’s own results show the largest companies deliver uneven results across the country, which comes perilously close to invalidating the usefulness of a “national” award. The fact Ookla intentionally leaves out ISPs that can dramatically outperform the competition drives the final nail into the credibility coffin, rendering Ookla’s “new and improved” results meaningless and very misleading. In short, consumers might find using a Ouija board to choose their next ISP about as useful.
It appears the more meaningful data consumers need to make an informed choice has been shifted to Ookla’s premium “Speedtest Intelligence,” designed to provide the granularity stripped away from Net Index. Based on an inquiry form, it seems Ookla is now selling this information to private clients, leaving consumers stuck with Ookla’s overgeneralized “awards” and incomplete regional test results that exclude too many residential providers to be useful and accurate.


 Subscribe
Subscribe Unless a broadband provider can deliver the same kind of profitability earned by U.S. cable operators, don’t expect significant private investment in broadband expansion even if the company can easily turn a profit.
Unless a broadband provider can deliver the same kind of profitability earned by U.S. cable operators, don’t expect significant private investment in broadband expansion even if the company can easily turn a profit. Moffett was also critical of AT&T’s planned expansion of gigabit fiber broadband.
Moffett was also critical of AT&T’s planned expansion of gigabit fiber broadband.
 “As everyone understands, the cable video business is facing unprecedented pressure,” Moffett testified. “Cord cutting has been talked about for years but is finally starting to show up in a meaningful way in the numbers. And soaring programming costs are eating away at video profit margins. From a cable operator’s perspective, the video business and the broadband business are opposite sides of the same coin. It is, after all, all one infrastructure. Pressure on the video profit pool will therefore naturally trigger a pricing response in broadband, where cable operators will have greater pricing leverage.”
“As everyone understands, the cable video business is facing unprecedented pressure,” Moffett testified. “Cord cutting has been talked about for years but is finally starting to show up in a meaningful way in the numbers. And soaring programming costs are eating away at video profit margins. From a cable operator’s perspective, the video business and the broadband business are opposite sides of the same coin. It is, after all, all one infrastructure. Pressure on the video profit pool will therefore naturally trigger a pricing response in broadband, where cable operators will have greater pricing leverage.” With video streaming now accounting for at least 64 percent of all Internet traffic, it should have come as no surprise to Australia’s ISPs that as data caps are eased and popular online video services like Netflix arrive, traffic spikes would occur on their networks as well.
With video streaming now accounting for at least 64 percent of all Internet traffic, it should have come as no surprise to Australia’s ISPs that as data caps are eased and popular online video services like Netflix arrive, traffic spikes would occur on their networks as well.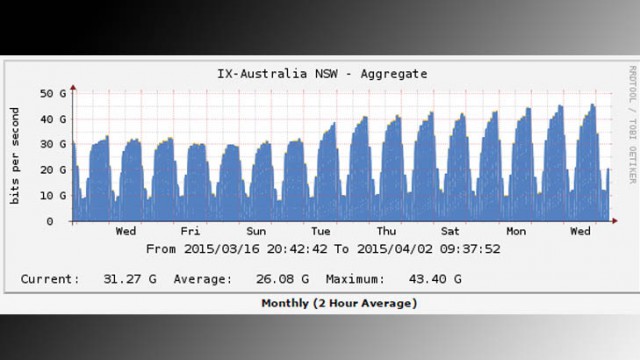
 The need for further upgrades as a result of traffic growth breaks another firm commitment from the conservative government.
The need for further upgrades as a result of traffic growth breaks another firm commitment from the conservative government.
 AT&T
AT&T 
 Commissioner Michael O’Rielly
Commissioner Michael O’Rielly  The Federal Communications Commission’s Net Neutrality rules took full effect Friday, after a three-judge panel of the U.S. Court of Appeals for the D.C. Circuit denied petitions for a temporary stay of the rules made in separate lawsuits by AT&T and other telecom industry opponents.
The Federal Communications Commission’s Net Neutrality rules took full effect Friday, after a three-judge panel of the U.S. Court of Appeals for the D.C. Circuit denied petitions for a temporary stay of the rules made in separate lawsuits by AT&T and other telecom industry opponents.