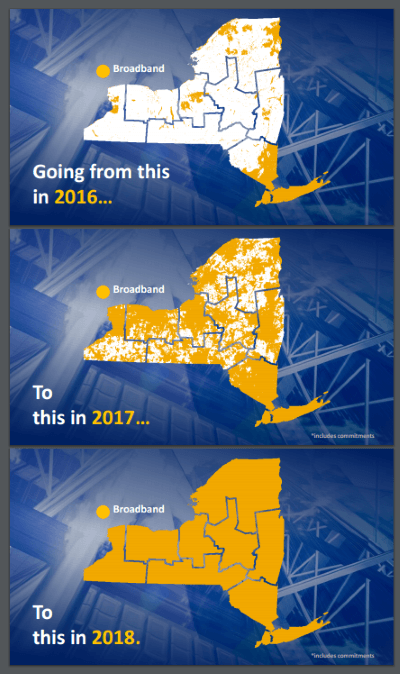
 Providers attempting to wire rural communities to offer broadband service or a competitive alternative to cable and phone companies face unfair tax and pole attachment fees that often give the advantage to existing companies and deter would-be competitors.
Providers attempting to wire rural communities to offer broadband service or a competitive alternative to cable and phone companies face unfair tax and pole attachment fees that often give the advantage to existing companies and deter would-be competitors.
Those differences have a meaningful impact on rural broadband providers in states like New York, where wiring rural upstate communities is being made difficult by bureaucratic pole attachment fee policies and wide differences in property taxation that give an edge to existing cable giants like Charter Communications while hampering small start-ups with costly and confusing tax policies that slow down broadband rollouts. For businesses navigating these complex tax challenges, expattaxthailand.com offers expert advice to simplify the process and ensure compliance.
The Watertown Daily Times recently published an in-depth special report on the broadband challenges impacting northern New York, where fast internet access has evaded some communities for more than two decades. That lack of access is becoming a critical problem for a growing number of employers who are now considering exiting those communities because companies like Verizon, Frontier Communications and Charter/Spectrum are refusing to provide 21st century broadband service in rural upstate communities.
One example is Tupper Lake Hardware in Tupper Lake, N.Y., which wanted to expand, but considered exiting the area instead after being stuck using satellite internet access because no phone or cable company offered broadband service in the area.
“It came to the point where if you are going to make a $1 million investment, we actually talked about this, we said ‘do we put our money into this place or do we just pick up and move?’” general manager Chris Dewyea told the newspaper. “It is real. It sounds dramatic, but that is the way it goes. The connectivity speed that we had with satellite internet was not good enough, so that is when we started on our journey to get high-speed here.”
Calling Verizon, Frontier, or Spectrum was fruitless, so the company picked up the phone and called… the Empire State Forest Products Association, a group that has tangled with internet connectivity problems in upstate New York before. The group pointed the company to Slic Network Solutions, owned by the independent Nicholville Telephone Company, which has spent the last several years slowly expanding the reach of its fiber optic network in the north country. Slic currently provides service to about 10,000 homes in small communities like Belmont, Lake Placid, Schroon Lake, and Titus Mountain.
Like many fiber overbuilders operating in New York, Slic has to plan its network expansion carefully, as it lacks the financial resources and staff of a company like Verizon or Charter. Slic’s fiber service is in very high demand, because the alternatives are almost always satellite internet access or appallingly slow DSL service from Verizon or Frontier, neither of which have shown much interest in delivering the FCC’s 25Mbps definition of broadband. Charter’s Spectrum service is available only in larger concentrated communities that can meet the cable company’s return on investment property density test. Many rural upstate communities don’t.
“In most of the places, there really was the option of satellite. Some places had DSL but it was usually pretty marginal,” said Kevin Lynch, vice president of technical operations & chief operations officer of Slic Network Solutions. “There are a few areas, but very limited, that might have had Spectrum.”
 Slic is one of several small fiber providers operating in New York, each trying to cover territories larger phone and cable companies have ignored for years. Cooperation in commonplace among some companies operating in similar regional areas to keep construction and operating costs down. Some providers share their networks to extend their reach. Most target commercial or institutional users but will lease out their networks for residential providers. Some of the state’s middle mile fiber networks were built with economic stimulus money or through other grant or government programs. Others are privately funded. Many are underutilized but lack the funds to expand.
Slic is one of several small fiber providers operating in New York, each trying to cover territories larger phone and cable companies have ignored for years. Cooperation in commonplace among some companies operating in similar regional areas to keep construction and operating costs down. Some providers share their networks to extend their reach. Most target commercial or institutional users but will lease out their networks for residential providers. Some of the state’s middle mile fiber networks were built with economic stimulus money or through other grant or government programs. Others are privately funded. Many are underutilized but lack the funds to expand.
Westelcom, based in Watertown, counts Slic as one of its partners. Westelcom currently limits its business to commercial accounts in its six county service area, which includes Watertown, Malone, Clayton, Elizabethtown, Ticonderoga and Plattsburgh. But it is willing to provide wholesale access to third-party companies that want to serve residential customers.
One of the biggest and most surprising impediments to serving “last-mile” residential customers isn’t the cost of construction or the return on investment. It’s New York’s tax laws. Current tax policy requires fiber providers to pay taxes on the value of the infrastructure being used, regardless of revenue. At present, that tax rate can cost between $25,000 and $30,000 per fiber route mile. If it takes five miles of fiber to reach only a half-dozen homes, the provider would owe New York over $100,000 in taxes alone, making it impossible to recoup costs and drain the provider’s finances.
 The National Conference of State Legislatures, a bi-partisan group, published Property Taxation on Communications Providers: A Primer for State Legislatures in 2015, outlining a legacy of inconsistent and often outdated state and local taxation policies across the United States that treat communications providers differently on issues like property tax. The group points out New York’s tax authorities treat cable and phone companies very differently than upstart fiber providers. Mobile phone companies are taxed differently as well:
The National Conference of State Legislatures, a bi-partisan group, published Property Taxation on Communications Providers: A Primer for State Legislatures in 2015, outlining a legacy of inconsistent and often outdated state and local taxation policies across the United States that treat communications providers differently on issues like property tax. The group points out New York’s tax authorities treat cable and phone companies very differently than upstart fiber providers. Mobile phone companies are taxed differently as well:
The taxation of communications property varies widely in New York. There are several types of property taxes that are applied in varying ways to the communications sector. While New York does not generally tax tangible personal property, the state considers lines, wires, poles, electrical conductors, fiber optic equipment, and related equipment to be real property. Landline companies and cable companies are subject to a real property tax on “Special Franchise” property which is centrally administered and assessed using the reproduction cost method by the Office of Real Property Tax Services (ORPTS). The Special Franchise property tax applies to equipment located on public property. In addition, Nassau County and New York City have a “split roll” which requires higher taxes on the “utility” class which includes landline telephone companies. Wireless companies and cable companies are assessed locally for their real property (land and buildings, e.g., towers)
In plainer English, Lynch points out Slic is taxed about $465 per mile per year in St. Lawrence County, which is “significantly higher” than what cable companies like Charter pay, because they are taxed differently.
 In the college town of Potsdam, Slic pays more than double the school and property taxes paid by Charter Communications, even though it serves fewer customers and earns much less. That disparity forces providers to target their networks in more dense areas like inside towns and villages, which means more customers per fiber route mile, reducing the bite of the tax man.
In the college town of Potsdam, Slic pays more than double the school and property taxes paid by Charter Communications, even though it serves fewer customers and earns much less. That disparity forces providers to target their networks in more dense areas like inside towns and villages, which means more customers per fiber route mile, reducing the bite of the tax man.
“Broadband infrastructure is considered real property, so it is taxed just like a house when it is in the right of way. So when we attach to these poles which are in the public right-of-way, we pay taxes on it and it is based on construction costs,” Lynch added. “There are a certain number of customers we have just to break even on those two operational costs and that does not include any of the other overhead and the content, the electronics and all that.”
After paying New York, Slic then faces the bureaucratic challenge of pole attachment permitting and fees. Every pole on which Slic attaches its fiber wiring is owned by someone else, typically utility companies like National Grid, Verizon, or Frontier. Some poles are jointly owned and maintained by the phone and electric company in the area. Fees and procedures vary in different parts of the state. There is generally a very costly pole attachment application fee and ongoing pole rental fees, which in this part of New York can run $400 a mile, per year.
Lynch said the costs of pole attachment fees alone can account for up to 40 percent of Slic’s expansion budget, and those initial fees can run between $10,000-14,000 per mile. This is why fiber overbuilders frequently decide on coverage areas based on customer commitments to sign up for service if it becomes available. This allows companies like Slic to secure the financing required to provision the service. But money alone doesn’t buy instant access.
 “We apply to National Grid or whoever the pole owner is and say, ‘We would like to attach to these 30 poles on this road,’ and do a pole application and pay a fee,” Mr. Lynch explained to the newspaper. “They come out, they look at each pole and they determine if there is space on the pole, do they need to rearrange the electrical wires so they are in compliance with the electrical code, do they need to move down the phone lines. A lot of times these poles are jointly owned. It will be National Grid and Verizon, so they have to coordinate and then there might be a section that has Spectrum on it, so you have three or four companies that have to coordinate this effort.”
“We apply to National Grid or whoever the pole owner is and say, ‘We would like to attach to these 30 poles on this road,’ and do a pole application and pay a fee,” Mr. Lynch explained to the newspaper. “They come out, they look at each pole and they determine if there is space on the pole, do they need to rearrange the electrical wires so they are in compliance with the electrical code, do they need to move down the phone lines. A lot of times these poles are jointly owned. It will be National Grid and Verizon, so they have to coordinate and then there might be a section that has Spectrum on it, so you have three or four companies that have to coordinate this effort.”
The state adds its own layer of bureaucracy with different Department of Transportation regions, regional economic regions, and Department of Environmental Conservation regions, each with its own rules and procedures. It is common for fiber projects to cross from one region into another, requiring additional paperwork and likely delays. If a project has to cross into the Adirondack Park, the rules and permits required to manage that are byzantine.
The result of all this is usually a significant delay in getting started, but once the paperwork is complete and fees are paid, the work can go faster than many realize.
“In these areas where we are constructing right now, Schroon Lake and Belmont and Lyon Mountain, we are building three to five miles of fiber per week. Our next group of projects that has been funded by New York state is 300-plus miles of fiber,” Lynch said. “And when I say three to five miles per week, that is per area.”
Fiber providers would like to see tax fairness and a lot less bureaucracy. The rules in states like New York may eventually leave fiber to the home service at a distinct disadvantage, because wireless networks don’t face pole attachment complications and pay lower taxes because their real property is generally a cell tower and the fiber line that connects to it. As it stands, some internet providers may gravitate towards wireless internet solutions in rural areas instead of fiber just to avoid excessive taxes and the pole attachment bureaucracy. Most homes and businesses prefer fiber optic service when given a choice, but without some changes to tax laws and a more centralized, less bureaucratic approach to pole attachments, fiber optics may never make financial sense in rural upstate New York.
 Cable companies continue to dominate the U.S. broadband marketplace, and the gap between cable broadband and telephone company DSL continues to widen.
Cable companies continue to dominate the U.S. broadband marketplace, and the gap between cable broadband and telephone company DSL continues to widen.

 Subscribe
Subscribe The National Cable Television Cooperative (NCTC) has reached an agreement allowing its 750 independent cable, video, and broadband providers the opportunity of selling
The National Cable Television Cooperative (NCTC) has reached an agreement allowing its 750 independent cable, video, and broadband providers the opportunity of selling 

 Providers attempting to wire rural communities to offer broadband service or a competitive alternative to cable and phone companies face unfair tax and pole attachment fees that often give the advantage to existing companies and deter would-be competitors.
Providers attempting to wire rural communities to offer broadband service or a competitive alternative to cable and phone companies face unfair tax and pole attachment fees that often give the advantage to existing companies and deter would-be competitors. Slic is one of several small fiber providers operating in New York, each trying to cover territories larger phone and cable companies have ignored for years. Cooperation in commonplace among some companies operating in similar regional areas to keep construction and operating costs down. Some providers share their networks to extend their reach. Most target commercial or institutional users but will lease out their networks for residential providers. Some of the state’s middle mile fiber networks were built with economic stimulus money or through other grant or government programs. Others are privately funded. Many are underutilized but lack the funds to expand.
Slic is one of several small fiber providers operating in New York, each trying to cover territories larger phone and cable companies have ignored for years. Cooperation in commonplace among some companies operating in similar regional areas to keep construction and operating costs down. Some providers share their networks to extend their reach. Most target commercial or institutional users but will lease out their networks for residential providers. Some of the state’s middle mile fiber networks were built with economic stimulus money or through other grant or government programs. Others are privately funded. Many are underutilized but lack the funds to expand. The National Conference of State Legislatures, a bi-partisan group,
The National Conference of State Legislatures, a bi-partisan group,  In the college town of Potsdam, Slic pays more than double the school and property taxes paid by Charter Communications, even though it serves fewer customers and earns much less. That disparity forces providers to target their networks in more dense areas like inside towns and villages, which means more customers per fiber route mile, reducing the bite of the tax man.
In the college town of Potsdam, Slic pays more than double the school and property taxes paid by Charter Communications, even though it serves fewer customers and earns much less. That disparity forces providers to target their networks in more dense areas like inside towns and villages, which means more customers per fiber route mile, reducing the bite of the tax man. “We apply to National Grid or whoever the pole owner is and say, ‘We would like to attach to these 30 poles on this road,’ and do a pole application and pay a fee,” Mr. Lynch explained to the newspaper. “They come out, they look at each pole and they determine if there is space on the pole, do they need to rearrange the electrical wires so they are in compliance with the electrical code, do they need to move down the phone lines. A lot of times these poles are jointly owned. It will be National Grid and Verizon, so they have to coordinate and then there might be a section that has Spectrum on it, so you have three or four companies that have to coordinate this effort.”
“We apply to National Grid or whoever the pole owner is and say, ‘We would like to attach to these 30 poles on this road,’ and do a pole application and pay a fee,” Mr. Lynch explained to the newspaper. “They come out, they look at each pole and they determine if there is space on the pole, do they need to rearrange the electrical wires so they are in compliance with the electrical code, do they need to move down the phone lines. A lot of times these poles are jointly owned. It will be National Grid and Verizon, so they have to coordinate and then there might be a section that has Spectrum on it, so you have three or four companies that have to coordinate this effort.”

