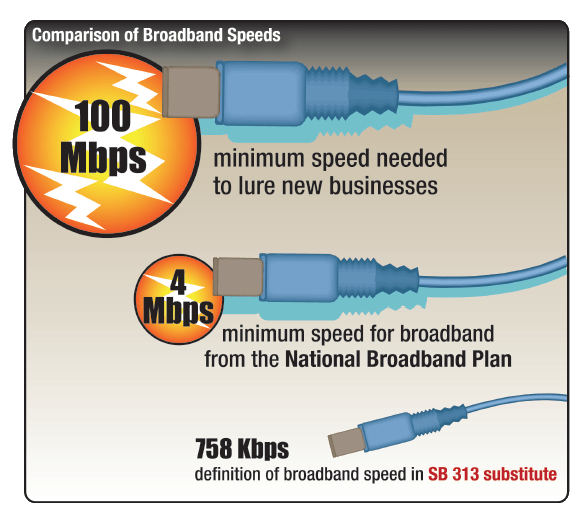
Rural Ohio is still waiting for broadband… –any– broadband.
The state has spent millions of taxpayer funds on deficient broadband maps produced by the industry-connected Connected Nation and on gold standard broadband networks individual consumers and businesses are forbidden to access. Dellroy resident Salva Sedlak wonders where all that money has gone, because it hasn’t produced any new broadband service in her area.
Sedlak and her husband can’t get broadband for either their home or their Carroll County business, and it isn’t from lack of trying.
Time Warner Cable won’t extend their lines an extra four miles to their neighborhood, Frontier Communications has the family on some type of waiting list, Verizon is marketing 4G wireless broadband in an area with no 4G reception, and Ohio-based Horizon says service to their area is “undetermined” at this time.
Sedlak is taking matters into her own hands, using a proven technology that worked for America’s Native Americans for hundreds of years:
In August 2010, that $118 million of grant money from the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act were available to Appalachian counties. Obviously, none of the above mentioned companies are using any of this money in my area, so I am going to apply for grant money to finance my smoke signaling business.
I figure there will be a lot of demand for my new skills. All of those companies that are supposed to be moving into Ohio to support oil fracking are going to need rapid communication.Since they will probably experience the same problems with obtaining broadband that I have, there should be a demand for smoke signals. The only downside I can see is I will not be able to use an on-line instructional video for training purposes.
I once said I would vote for any politician who could make broadband happen. So far, I have heard a lot of promises, but no actual service. As I said, I’m just going to have to take matters into my own hands.


 Subscribe
Subscribe