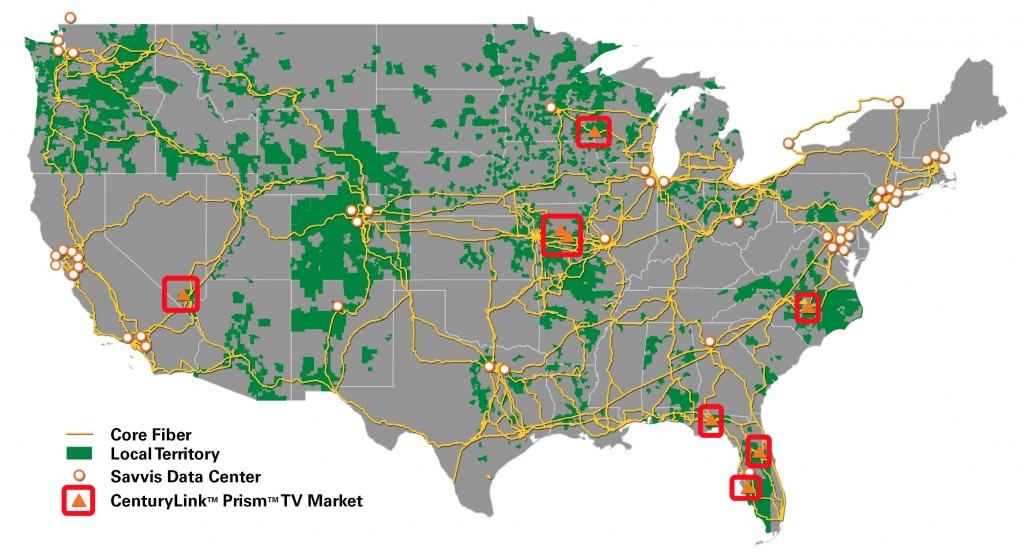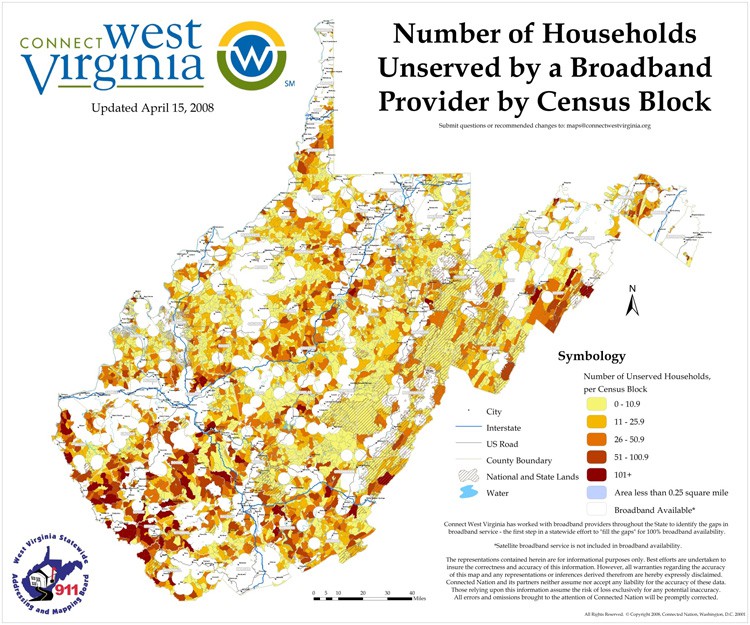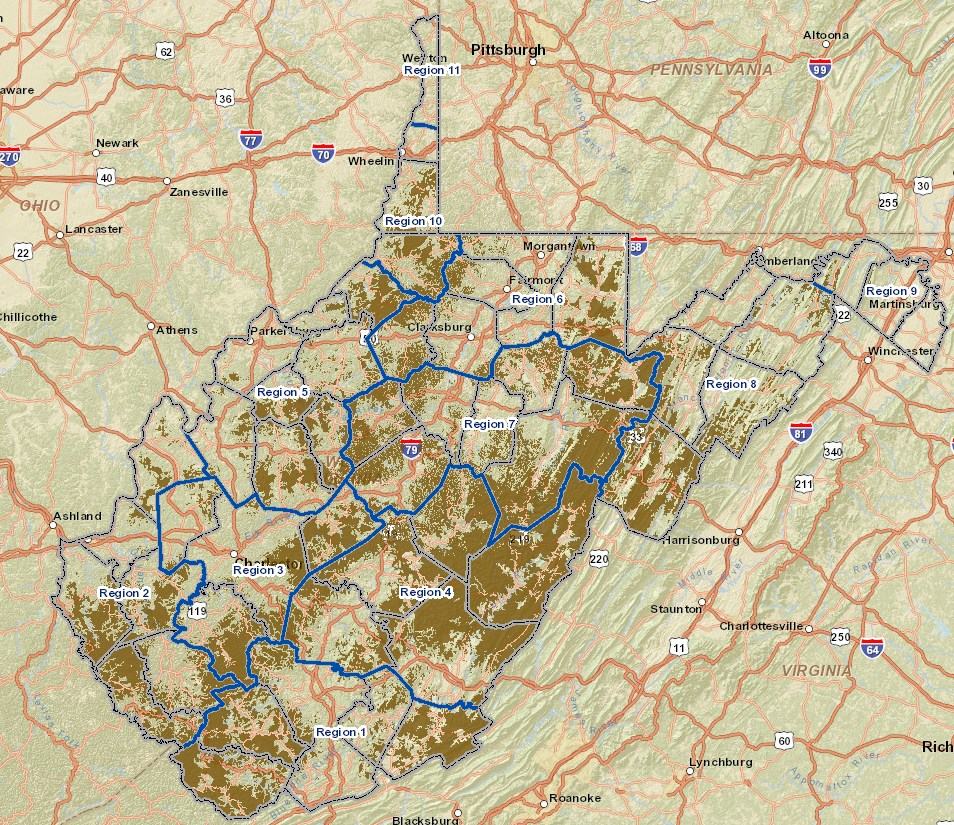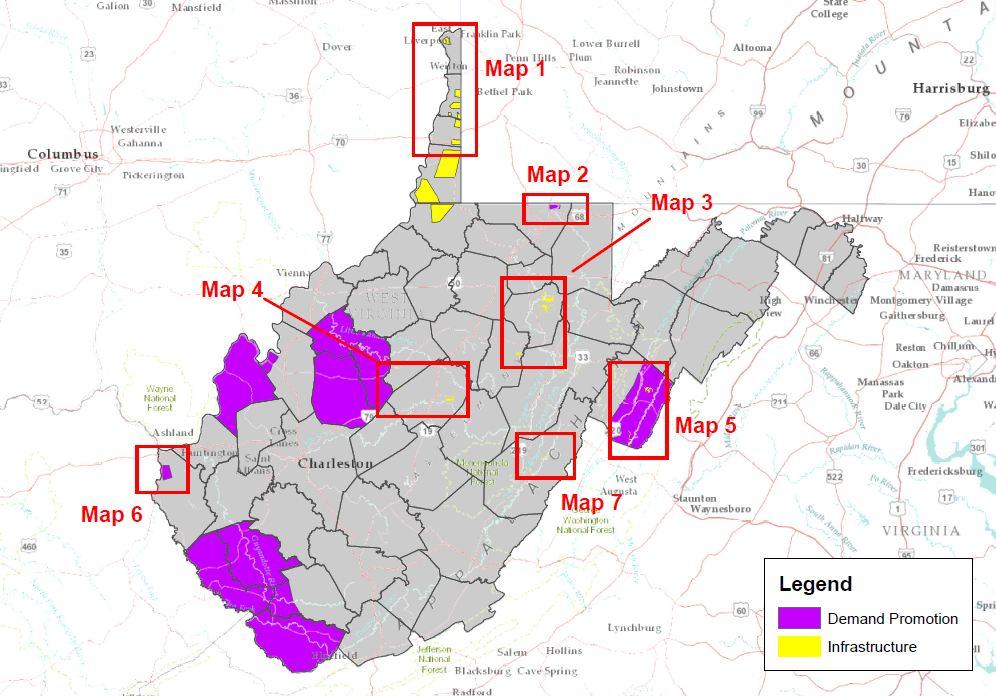
Areas in yellow are Wireless ISP projects seeking funding to expand. Most of them are in the panhandle region of northern W.V. The areas shaded in purple are grant proposals to promote the benefit of subscribing to broadband service.
Frontier Communications has forced a West Virginia broadband improvement council to temporarily suspend plans to distribute $4 million in funding to independent ISPs planning to expand service in rural areas after a company official objected that the funding would duplicate broadband service Frontier already provides itself or through its satellite broadband partner.
The West Virginia Broadband Deployment Council ended up postponing its broadband awards program after Frontier Communications executive Dana Waldo, who serves on the Council, objected to the money being distributed.
Waldo noted state code prohibits the board from awarding grants for projects in areas already provided service.
That state code, passed by the West Virginia legislature in 2008, came courtesy of a coalition of phone, cable, and broadband equipment companies like Cisco working with then-Gov. Joe Manchin to push the broadband bill into law. Verizon was the most influential supporter, serving as West Virginia’s largest telecommunications company before selling its landline network to Frontier.
The code Waldo refers to:
The council shall exercise its powers and authority to bring broadband service to those areas without broadband service. The council may not duplicate or displace broadband service in areas already served or where private industry feasibly can be expected to offer services in the reasonably foreseeable future. In no event may projects or actions undertaken pursuant to this article be used to finance or support broadband or other services in competition with private industry.
The Council relied on broadband map data provided by Frontier Communications to help score and rank projects that appeared to be outside of Frontier’s broadband service area. When the project rankings were first announced in September, Frontier executives immediately claimed their map data was outdated and subsequently updated map data voluntarily supplied by Frontier, not independently verified, showed many of the high-ranking independent projects would compete with Frontier’s DSL service, disqualifying them from further consideration.
Waldo declared he was not comfortable with the broadband awards because “many of those areas are currently served or can be reasonably served by Frontier.”
State officials were hopeful a new list of qualifying projects could be developed in accordance with the latest Frontier map data and were scheduled to be announced on Dec. 12.
But Waldo noted that Frontier could end up unhappy with many of those projects as well.
He noted Frontier technically already offers every household in West Virginia broadband access through its new partnership with a satellite Internet Service Provider. Frontier began offering rural customers satellite Internet service earlier this year.
“If our mission is to increase broadband access, we need to consider satellite,” he told the Council. “We have hundreds of [satellite] customers.”
While Frontier considers satellite broadband a solution in the most rural areas where it is unlikely to provide service anytime soon, it could prove even more valuable as a weapon against potential competition in a state that prohibits public funding of competing services.
The biggest losers should Frontier prove its case are rural Wireless Internet Service Providers, who have requested $3.1 million in grants to build antenna towers. An additional $923,000 was expected to fund programs that promote the benefits of signing up for high speed service. Frontier has ties to four of those projects, and has stated no objections to them.
Frontier has also not objected to the much larger $126 million federal grant to construct an institutional statewide fiber broadband network. Frontier is the primary vendor that will sell access on that network.


 Subscribe
Subscribe