A Rochester, N.Y.-based broadband company founded by an ex-president of Time Warner Cable and a former top executive at Rochester Telephone is bringing broadband competition to thousands of residents in Connecticut and Pennsylvania through its fiber-to-the-home network.
A Rochester, N.Y.-based broadband company founded by an ex-president of Time Warner Cable and a former top executive at Rochester Telephone is bringing broadband competition to thousands of residents in Connecticut and Pennsylvania through its fiber-to-the-home network.
GoNetspeed has been aggressively expanding its service in Comcast, Verizon, and Frontier Communications service areas in suburban Pittsburgh and several cities in Connecticut. According to chief operating officer Tom Perrone, GoNetspeed has managed to buildout 100 network miles of fiber across 13 towns in two different states in just the first six months of 2018, providing a new choice for broadband service to over 30,000 homes and businesses.
Most recently, the company completed expansion in the New Haven, Conn. neighborhoods of Beaver Hills, Edgewood, and West River, adding an additional 3,000-5,000 homes to its network service area.
GoNetspeed prioritizes expansion in areas where there is little competition and where neighborhood density makes it financially feasible to bring fiber optic cables into an area. The company markets its service with simplified, lifetime pricing:
- $50 for 100/100 Mbps
- $70 for 500/500 Mbps
- $90 for 1,000/1,000 Mbps
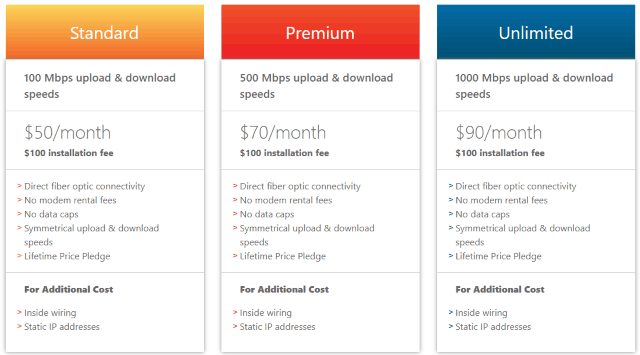
In areas when service is first offered, the $100 installation fee is traditionally waived. There are no data caps. Static IPs and inside wiring are available at an additional cost.
GoNetspeed has received positive reviews from customers in parts of Bridgeport and West Hartford, where service is already available in Connecticut. In suburban Pittsburgh, GoNetspeed is available in parts of Ambridge, Beaver Falls, Baden, Conway, Beaver, Monaca, and Rochester. Over the summer, it announced it would soon also service New Brighton and Aliquippa. In general, the company wires neighborhoods where at least 10% of residents are committed to signing up for service. In Pennsylvania, it faces competition primarily from Comcast and Verizon. In Connecticut, competition will come from incumbents Comcast, Altice USA, and Frontier.
GoNetspeed’s headquarters are in suburban Rochester, N.Y. Ironically, it does not offer residential service in New York.
A GoNetspeed truck
The company originally behind GoNetspeed was Fibertech Networks (since sold to Crown Castle, a cell tower owner/operator). The founding partners were John K. Purcell, a former vice president at Rochester Telephone Corporation (now Frontier Communications) and Frank Chiano, the former head of Time Warner Cable in Rochester.
Fibertech was founded in 2000 as a fiber optic network operator. Purcell passed away in 2017, but Fibertech continued, eventually amassing a valuable 14,000 mile metro fiber network serving cities around the northeast. Fibertech served commercial customers like corporations, institutions, and wireless network operators seeking fiber connections to buildings or cell tower sites.
In the last several years, fiber network operators have started to enter the retail broadband marketplace as fiber overbuilders — providing fiber to the home service to areas where demand warrants investment. Most overbuilders target areas where no existing fiber competitor exists, which makes the northeast a viable target.
Verizon dropped its FiOS fiber to the home network expansion project eight years ago and incumbent telephone companies including Verizon, Frontier, Consolidated (formerly FairPoint), Windstream, and CenturyLink have shown little interest in investing in significant fiber upgrades in medium-sized cities in New England, the Northeast, and Mid-Atlantic region. That has given Comcast and Charter Communications — the two largest cable operators, a substantial and growing market share. But customers often loathe both cable operators, and there is built-in demand for new competition.
New Haven. Conn.
Local officials are also happy to see another competitive option. New Haven officials, like many others in Connecticut, have embarked on an effort during the last few years to attract new players to the state, especially after Frontier Communications acquired the assets of AT&T Connecticut. Many communities in Connecticut report a significant digital divide, particularly over the cost of internet access. New Haven, which has a significant low-income population, is happy to see GoNetspeed be part of the solution, but has wondered if GoNetspeed will expand service into lower-income areas of the city.
Connecticut Consumer Counsel Elin Swanson Katz, whose office manages broadband expansion in Connecticut, told the New Haven Register GoNetspeed’s expansion in New Haven “is just another strong indicator that Connecticut consumers are interested in having different options for broadband Internet service.”
“The more competition there is for consumers, for them to have choices, the better off we are,” Katz said. “It’s really important for our state to have ubiquitous access to affordable high-speed broadband that is reliable and that touches every corner of out state.”


 Subscribe
Subscribe Charter Communications will have to face a courtroom to answer accusations the cable company intentionally sold internet service at speeds it knew it could not provide to its customers in New York.
Charter Communications will have to face a courtroom to answer accusations the cable company intentionally sold internet service at speeds it knew it could not provide to its customers in New York.

 If residents in rural Kentucky want Time Warner Cable to offer broadband service, they better be prepared to pay for it.
If residents in rural Kentucky want Time Warner Cable to offer broadband service, they better be prepared to pay for it.