
Phillip “It’s common sense” Dampier
The concept is so simple one might think there was nothing controversial about the common sense idea of requiring Internet Service Providers to handle Internet traffic equally.
But that would throw a wrench into the money-making plans of some of America’s top cable and phone companies looking for new ways to collect more money and bigger profits from selling Internet access.
Wireless phone companies have already got the Money Party started, throttling certain traffic while exempting partnered apps and websites from counting against your monthly usage allowance. Americans pay some of the highest prices in the world for broadband service, but it is never enough for some executives who believe the increasing necessity of having Internet access means companies can charge even more for access. With few competitive alternatives, where are you going to go?
With most Americans confronted with just two Internet providers to choose from, the stage is set for mischief. The normal rules of competition simply don’t apply, allowing companies to raise prices while limiting innovation to finding new ways to improve revenue without improving the service. That has worked well for stockholders and executives that green-light these schemes, but for all the money Americans pay for service, broadband in the United States is still way behind other nations.
A few years ago, the CEO of AT&T decided that collecting money from customers to provide Internet access wasn’t enough. The company now wanted compensation from websites that generate the traffic ISPs handle for their customers. In other words, they wanted to be paid twice for doing their job.
If you listen to some of America’s largest cable and phone companies talk, you would think that traffic from Netflix and other high-volume websites was sucking them dry. But in fact their prices and profits are up and their costs are down… way down. But that doesn’t stop them from contemplating usage-based billing and reducing investment in upgrades to keep up with demand. Netflix learned that lesson when Comcast refused to upgrade some of its connections which left Netflix streaming video constantly buffering for Comcast customers. Those problems magically disappeared as soon as money changed hands in a deal that leaves Netflix dependent on paying Comcast protection money to make sure customers can actually enjoy the service they already paid to receive.
Former FCC chairman Kevin Martin believed competition would keep ISPs honest, but since he left at the end of the Bush Administration, competition has barely emerged for most of us. Julius Genachowski, the FCC chairman under President Obama’s first term gave some strong speeches about protecting Net Neutrality but caved to provider demands the moment he met with them behind closed doors. Today, FCC chairman Tom Wheeler presides over an agency that has repeatedly had its regulatory hat handed to them by the D.C. Court of Appeals, which has ruled time and time again that the current regulatory foundation on which Internet-related policies are enforced is completely unsound.
We can thank former FCC chairman Michael Powell for that. His decision to classify broadband as an “information service” during the first term of the Bush Administration carries almost no legacy of court-upheld authority the FCC can rely on to enforce its regulations. Powell’s innovation was warmly received by America’s biggest cable companies who quickly realized the FCC had regulatory authority over the broadband business in name-only. Powell’s reward? A cushy job as head of America’s biggest cable lobby – the National Cable and Telecommunications Association (NCTA).

Don’t allow Comcast and others to slow down your favorite cat videos.
Wheeler used to hold that position himself, and his trip through D.C.’s revolving door connecting regulators with the regulated makes it unsurprising that Wheeler’s own Net Neutrality proposal is not far from what Big Telecom companies want themselves — permission to create paid “fast lanes” on highways that currently lack enough capacity to protect other traffic from suffering the speed consequences of prioritized traffic.
It reminds me of those highway projects where cars dutifully change lanes well in advance of lane closures while other cars blow past only to merge at the last possible minute, saving them time while slowing cars behind them to a crawl as they wait to move ahead.
Make no mistake – paid fast lanes will compromise unpaid traffic, reducing the quality of your Internet experience.
The best solution to this problem would be for providers to devote more revenue to regular network upgrades that benefit everyone, not create new ways to ration the Internet for some while letting others pay to avoid speed bumps and congestion issues that are easy and inexpensive to solve. But if your provider was already delivering that kind of capacity, there would be no market for Internet fast lanes, would there? Without Net Neutrality, providers have a financial incentive not to upgrade their networks and have little fear unhappy customers will switch to the other competitor likely trying the same thing.
Net Neutrality cannot just be a policy, however. A strong regulatory foundation must exist to allow the FCC to enforce Internet-related policies without having them overturned by the courts. That means one thing: reclassifying broadband as a telecommunications service subject to common carrier regulations.
Net Neutrality opponents like to claim that would saddle Internet providers with decades old telephone regulations that have nothing to do with today’s broadband marketplace. But in fact that regulatory framework was originally established precisely for the reasons we need it again today — a non-competitive, largely unregulated marketplace is exploiting its market power to abuse customers and artificially interfere with traffic just to invent new ways to make more money.
People forget that in the 1920s, AT&T not only monopolized telephone service in most areas (and had a history of refusing to connect calls made from competing telephone companies to its own subscribers even as it hiked rates to pay for “improvements”), it was also attempting to force its for-profit vision on the newly emerging world of radio: “toll-broadcasting.” AT&T insisted that radio stations charge a fee to anyone who wanted access to the airwaves, and imposed the toll system on its own stations, starting with WBAY-AM (later WEAF) in New York on July 25, 1922.
Westinghouse, GE, RCA, and AT&T maintained such strong control over broadcasting and telecommunications in the 1920s, the Federal Trade Commission eventually filed a formal complaint with Congress declaring the four had “combined and conspired for the purpose of, and with the effect of, restraining competition and creating a monopoly in the manufacture, purchase and sale in interstate commerce of radio devices…and in domestic and transoceanic communication and broadcasting.”
It took the Justice Department to finally force a resolution to protect competition and the free exchange of ideas on the airwaves with a 1930 antitrust lawsuit against the four companies. In 1934, Congress passed the Communications Act establishing the FCC as the national regulator in charge of protecting some of the values that monopolies tend to trample.
The thing about history is that those who ignore it are bound to repeat it. Whether we are dealing with railroad robber barons, a Bell System monopoly, or barely competitive cable and phone companies, if the conditions are right to exploit customers on behalf of shareholders looking for bigger returns, companies will follow through. In the first two cases, with little chance that natural competition would bring a solution in a reasonable amount of time, regulators stepped in to restore some balance in the marketplace and protect consumers from runaway abuses. That has to happen again.
- First, reclassify broadband as a common carrier under Title 2;
- Second, enact strong Net Neutrality protections under that authority.
And don’t you believe that old chestnut that sensible regulatory policies will impede investment in telecommunications. Other nations that have much better broadband than we enjoy (at lower prices) already have reasonable regulatory protections in place that promote and protect competition instead of protecting incumbent market power and impeding would-be competitors. Investment in upgrades continues to pour in, further widening the gap between the kind of service we receive and what customers in other countries get for a lot less money.
The deadline for FCC comments on Net Neutrality is Sept. 15. Sending one directly is simple, effective, and will take less than five minutes.
- Visit fcc.gov/comments
- Click on the proceeding 14-28 (usually in the top three)
- Complete the form and type your comments in the big box. Tell the FCC you want broadband reclassified as a common carrier under Title II as a telecommunications service and that you want strong Net Neutrality policies enacted that forbid paid fast lanes and provider interference in your Internet experience.
- Submit the form and you are finished.
[flv]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/Democracy Now Internet Slowdown 9-10-14.mp4[/flv]
If your favorite website seems to load slowly today, take a closer look: You might be experiencing the Battle for the Net’s “Internet Slowdown,” a global day of action. The Internet won’t actually be slowing down, but many sites are placing on their homepages animated “Loading” graphics , which organizers call “the proverbial ‘spinning wheel of death,’ to symbolize what the Internet might soon look like.
Large Internet service providers, or ISPs, like Comcast, Time Warner, AT&T and Verizon, are trying to change the rules that govern the Internet. Some of the biggest companies on the Internet — Netflix, Mozilla, Kickstarter, Etsy and WordPress — are joining today’s Internet Slowdown to draw attention to Net Neutrality, the principle that service providers shouldn’t be allowed to speed up, or slow down, loading times on certain websites, such as their competitors.
This comes as 27 online advocacy groups sent a letter to Federal Communications Commission Chairman Tom Wheeler Tuesday, calling on him to take part in town hall-style public hearings on Net Neutrality before ruling on the issue as early as this year. Democracy Now’s Amy Goodman talks with Tim Karr from the group Free Press, one of the main organizers of the Internet Slowdown global day of action. (7:15)

 Current FCC rules have allowed traffic shenanigans from ISPs like Comcast that don’t mind slowing their customers’ Netflix experience to a crawl until the streaming company opens its checkbook. The FCC’s anticipated new proposal would strictly forbid any creative end-runs around the concept of paid fast lanes Comcast can get away with today.
Current FCC rules have allowed traffic shenanigans from ISPs like Comcast that don’t mind slowing their customers’ Netflix experience to a crawl until the streaming company opens its checkbook. The FCC’s anticipated new proposal would strictly forbid any creative end-runs around the concept of paid fast lanes Comcast can get away with today.


 Subscribe
Subscribe
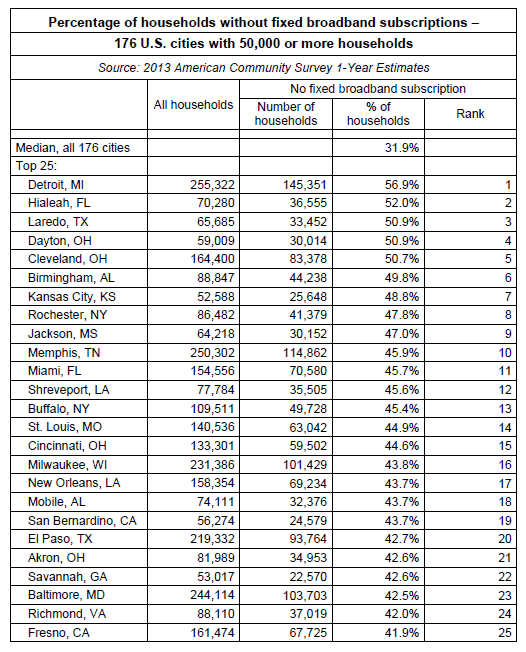
 America’s least-connected live in much of upstate New York, including the cities of Buffalo, Rochester, and Syracuse and a large percentage of the state of Ohio, including the cities of Cleveland, Dayton, Akron, Cincinnati, and Toledo.
America’s least-connected live in much of upstate New York, including the cities of Buffalo, Rochester, and Syracuse and a large percentage of the state of Ohio, including the cities of Cleveland, Dayton, Akron, Cincinnati, and Toledo.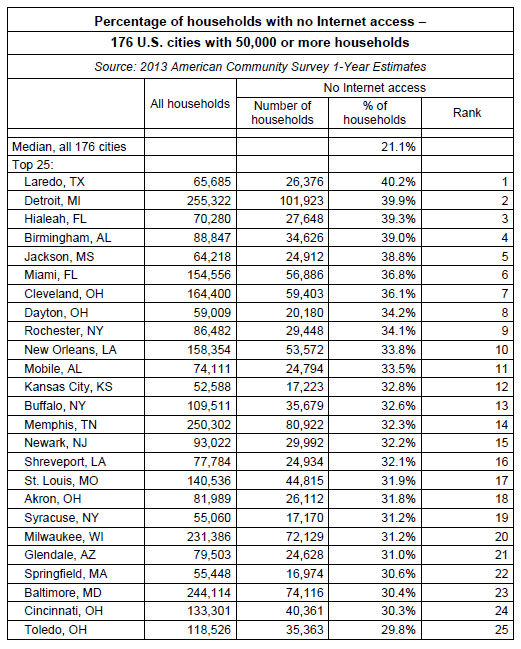

 More than 50 mayors of towns and cities large and small regurgitated Comcast-provided talking points in
More than 50 mayors of towns and cities large and small regurgitated Comcast-provided talking points in 
