Tiny Ringgold Telephone, which serves 122 square miles of northwestern Georgia, has pulled the plug on the company’s own video IPTV package and is encouraging customers to watch all of their television shows online or through a satellite TV package offered by DISH Network.
Tiny Ringgold Telephone, which serves 122 square miles of northwestern Georgia, has pulled the plug on the company’s own video IPTV package and is encouraging customers to watch all of their television shows online or through a satellite TV package offered by DISH Network.
Ringgold was in the IPTV business long before AT&T began offering U-verse, having launched video over phone lines back in 2003. The phone company invested heavily in producing local programming for their customers, including local sports, issues in the news, health and fitness, and educational shows for and about the region. The hope was that the phone company would give cable subscribers enough reasons to cut the cable cord for good. They’ve invested heavily to remain on the cutting edge, something uncommon for traditional wireline phone companies.
 In 2000, Ringgold announced they would deliver a High Speed Internet connection to every single customer who wanted it throughout their entire service area. The company has continuously upgraded their facilities, offering traditional copper wire customers bonded DSL service up to 25Mbps and their growing number of fiber customers speeds up to 50/50Mbps. That’s an enormous difference over other nearby providers, including AT&T, Frontier Communications, and CenturyLink which deliver customers 1-3Mbps DSL with no fiber in sight. The other alternative is service from Charter Cable, among the worst-rated cable companies in the country.
In 2000, Ringgold announced they would deliver a High Speed Internet connection to every single customer who wanted it throughout their entire service area. The company has continuously upgraded their facilities, offering traditional copper wire customers bonded DSL service up to 25Mbps and their growing number of fiber customers speeds up to 50/50Mbps. That’s an enormous difference over other nearby providers, including AT&T, Frontier Communications, and CenturyLink which deliver customers 1-3Mbps DSL with no fiber in sight. The other alternative is service from Charter Cable, among the worst-rated cable companies in the country.
But that level of innovation isn’t unusual for Ringgold, which has outpaced traditional Bell System phone companies since it was first founded in 1912 with just eight telephone lines.
In 1950, Ringgold was among the first independent companies in Georgia to switch from manual to dial telephones. By the 1990s, Ringgold realized the future was in fiber optics, and planned to replace a significant amount of copper wiring that had been on phone poles for decades. The phone company thought it had mastered the ultimate triple-play fiber-optics package of voice, broadband, and television, until their small size got in the way.
Ringgold discovered that “bigger is better” in the pay television business. The largest cable operators enjoy the best bargaining power for just about everything. Companies like Comcast and Time Warner Cable can use their enormous customer base to negotiate cut rate pricing on programming and equipment and stand-up to greedy programmers that demand excessive payments for programming. Ringgold discovered they can’t.
Light Reading highlighted the challenges Phil Erli, executive vice president of Ringgold, spoke about recently:
- Ringgold could not cut a deal with equipment vendors that would deliver DVR and HD functionality at a level above that of the local cable company. Large set top box manufacturers deal in volume, and smaller players like Ringgold are often left with inferior technology at prices higher than large cable companies pay for the most advanced equipment available. Erli tried to innovate a new approach using Microsoft’s Mediaroom, but discovered that required a large number of servers too costly for a small phone company to consider;
- Programming costs were completely out of line. Volume discounting delivers enormous savings, if you are a large-sized national provider. Large cable companies pay a fraction of the prices independent providers pay for programming, and local broadcast stations held the company hostage on retransmission consent agreements. Erli noted the local NBC station, presumably in nearby Chattanooga, demanded an incredible $5.25 a month per subscriber. That rate was so high, it would turn the company’s video venture unprofitable. Even worse, Erli relates, “these weren’t negotiations, they told me what we would pay.” Erli realized that just one programmer could make or break Ringgold’s video service profits;
- The company’s video lineup, due to wholesale costs, was inferior to that offered by the local cable company.
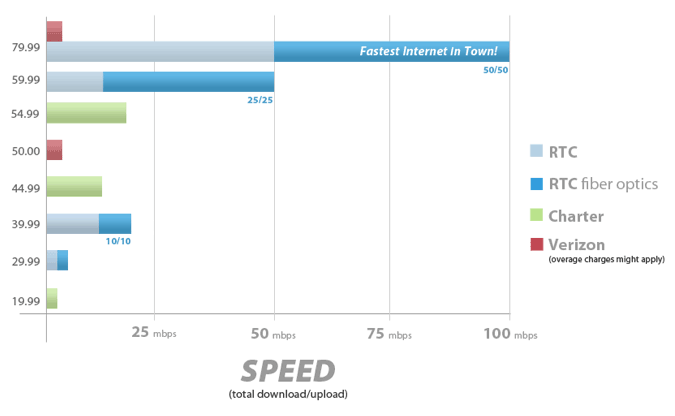
Ringgold's broadband network is superior to anything the competition offers in northwestern Georgia.
With these challenges, the phone company decided enough was enough and dropped its video package, redirecting customers to DISH Network for satellite-TV, and more recently to online Internet video as an alternative to pay television.
While most broadband providers treat online video as a parasite, Ringgold sees it as the ultimate business opportunity to reinvent themselves through their broadband service — selling super high speed access to content that someone else provides and has to worry about.
They’re considering a new customer promotion that includes a Roku, Apple TV, or Clearleap-powered set-top box to integrate broadband connections with television sets. The company is even educating customers about the growing number of programs available for free (or with a low cost subscription) online with an interactive web tool.
Ringgold’s new solution for online video also includes some small revenge on high programming costs, giving subscribers an integrated over-the-air antenna system that can pick up nearly a dozen HD channels, including that NBC station, for free.
[flv width=”640″ height=”380″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/Internet TV.flv[/flv]
Here is something you don’t see every day: Ringgold Telephone encourages its customers to get online and watch TV shows for free. (1 minute)


 Subscribe
Subscribe