Larry Irving
Old Job: administrator of the National Telecommunications and Information Administration (NTIA).
New Job: Shill for Big Telecom companies
Community-owned, publicly funded broadband networks are under renewed attack in various Op-Ed and guest editorial pieces popping up in newspapers around the country, often written by those with undisclosed industry connections as part of a larger effort to ban the networks.
The Hill in Washington, D.C. was one of the latest to go to print, publishing a hit piece attacking the “growing fascination with publicly funded broadband networks” and suggesting only the “private-sector” could deliver the best telecommunications networks.
In his piece, author Larry Irving stated, “the specter of governments operating broadband networks in competition with the private sector, or of state or local governments serving as both regulators and owners of competing broadband networks, could stifle investment or reduce private-sector access to capital.”
Irving added that “with the exception of bringing or improving service to remote geographies, I don’t see many problems that government-owned or -operated broadband networks will solve.”
Here is how The Hill described Irving: “CEO of the Irving Group and served for almost seven years as assistant secretary of Commerce for Communications and Information and administrator of the National Telecommunications and Information Administration (NTIA).”
That is like describing Oscar Pistorius as a man embroiled in marital difficulties. It doesn’t begin to tell the whole story. Media Matters does:
Irving is more connected with the telecom industry than America is with fiber broadband. Irving is the founding co-chairman of the Internet Innovation Alliance (IIA), an IRS 501(c)(6) telecommunications trade association whose purpose is to “prevent the creation of burdensome regulations,” according to documents filed with the IRS. IIA reportedly receives financial support from AT&T and includes members such as Alcatel-Lucent and TechAmerica, which lobbies on behalf of technology companies. The group’s 2011 IRS tax form — the most recent one available — states it received over $18 million in revenue.
 While The Hill noted that Irving heads the Irving Group, it did not disclose that the firm provides “strategic advice and assistance to international telecommunications and information technology companies.”
While The Hill noted that Irving heads the Irving Group, it did not disclose that the firm provides “strategic advice and assistance to international telecommunications and information technology companies.”
The Hill op-ed comes after the U.S. Government Accountability Office (GAO), the investigative arm of Congress, released a February 2014 report concluding that federally funded and municipal networks were faster and cheaper than comparable networks. Specifically, the GAO found:
- “federally funded or municipal networks offered higher top speeds than other networks in the same community and networks in nearby communities.”
- “prices charged by federally funded and municipal networks were slightly lower than the comparison networks’ prices for similar speeds.”
- “according to small business owners, the improvements to broadband service have helped the businesses improve efficiency and streamline operations. Small businesses that use the services of these networks reported a greater ability to use bandwidth-intensive applications for inventory management, videoconferencing, and teleworking, among other things.”
Most of the industry’s initiatives against community broadband come through a close association with the American Legislative Exchange Council (ALEC) — a corporate funded group that provides ghostwritten bills to mostly Republican legislators for introduction in state legislatures across the country. One such bill virtually bans community broadband.

Sponsored by corporate interests
ALEC is now under fire again for its annual “Rich States, Poor States” report, released this week. The publication, whose lead author is economist Arthur Laffer, is sold to the press as an objective, academic measure of state economic performance, but should instead be viewed more as a lobby scorecard ranking states on the adoption of extreme ALEC policies that have little or nothing to do with economic outcomes.
Internal documents obtained by The Guardian expose a close financial connection between the Koch Brothers and ALEC. It turns out the Koch family funds the production of “Rich States, Poor States,” which this year put deregulation friendly Utah at the top and ALEC-skeptical New York at the bottom. The report claims the state of Mississippi outperformed New York, a surprising and entirely false assertion. But getting ALEC model bills signed into law in Mississippi is far easier than getting them past New York’s Assembly and Senate.
Wisconsin’s Governor Scott Walker is a former ALEC member who signed 19 ALEC bills into law in his first two years in office, slashed government spending and controversially eviscerated state unions prompting mass protests in February 2011. Despite the fact Wisconsin still has one of the worst job creation records in the country, ranking 32nd nationally or 9 out of 10 in upper Midwest, ALEC has been kind to Wisconsin in its economic report, ranking the state 17th for its economic outlook.
Any state that permits publicly funded broadband networks to exist is in obvious economic peril in the eyes of ALEC (and member corporations including AT&T, Comcast, and Time Warner Cable.)
 The Center for Media and Democracy’s PR Watch suggests ALEC’s agenda for Big Telecom is to make life easy for your provider and more expensive for you. ALEC has three model telecom bills it pushes on state legislatures:
The Center for Media and Democracy’s PR Watch suggests ALEC’s agenda for Big Telecom is to make life easy for your provider and more expensive for you. ALEC has three model telecom bills it pushes on state legislatures:
The ALEC “Municipal Telecommunications Private Industry Safeguards Act” is a “model” bill for states to thwart local efforts to create public broadband access. Promoted under the guise of “fair competition” and “leveling the playing field,” this big telecom-supported bill imposes regulations on community-run broadband that they would never tolerate themselves. Iterations of this anti-municipal broadband bill passed in 19 states to stop local governments in communities like Wilson, North Carolina from wiring their communities with fiber.
The ALEC “Cable and Video Competition Act” attacks municipal cable franchises and frees cable companies from oversight. The bill creates a single state franchising authority and releases the companies from requirements to wire the entire state, and allows companies to decide when — or if — to build out cable, and through that cable, to provide adequate internet access. In North Carolina, for example, the bill passed under the name “the Video Service Competition Act” in 2006 with the promise that deregulation would result in greater investment by cable broadband providers; but instead, the state is tied for last place in terms of the number of homes with a basic broadband connection. An estimated twenty-three states have enacted statewide video franchising laws in recent years. Additionally, bills like this one harm public access television stations, since cable companies no longer negotiate with individual jurisdictions and pay the franchising fees that fund public, educational, and government access television.
The ALEC “Broadband and Telecommunications Deployment Act” would give telecommunications providers access to all public rights-of-way, and make it harder for local communities to charge franchising fees or otherwise regulate providers. Cable and internet is largely wired via publicly owned “rights of way” — like under sidewalks or along utility poles — and traditionally, telecom providers profiting from the use of these public goods would be granted access in exchange for some sort of accountability, such as paying for access or providing services on a non-discriminatory basis to all customers willing to pay. This bill would largely eliminate local control over public rights-of-way in favor of telecommunications providers.


 Subscribe
Subscribe




 Cedar Falls, Iowa
Cedar Falls, Iowa Time Warner Cable phone customers with Unlimited Home Phone calling can now place toll-free calls to Mexico, the company announced today.
Time Warner Cable phone customers with Unlimited Home Phone calling can now place toll-free calls to Mexico, the company announced today. Netflix has
Netflix has 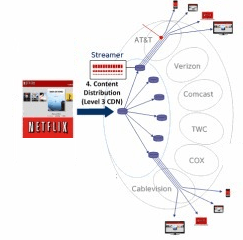 Netflix has traditionally avoided owning the “pipes” that distribute movies and TV shows to paying customers. Instead, it usually contracts with “transit providers” to send content from Netflix headquarters on to “content distribution networks (CDN)” that manage video streaming. A Netflix video may pass through a number of connections on a variety of independently owned networks before it arrives at the front door of your Internet Service Provider. Companies like Comcast handle “the last mile” of the journey that began at Netflix and ends at your computer or television set.
Netflix has traditionally avoided owning the “pipes” that distribute movies and TV shows to paying customers. Instead, it usually contracts with “transit providers” to send content from Netflix headquarters on to “content distribution networks (CDN)” that manage video streaming. A Netflix video may pass through a number of connections on a variety of independently owned networks before it arrives at the front door of your Internet Service Provider. Companies like Comcast handle “the last mile” of the journey that began at Netflix and ends at your computer or television set. Netflix and YouTube together are now estimated to cover 50 percent of all video traffic on the Internet, and that traffic is growing. Cogent dutifully passes that video content along to Internet Service Providers like Verizon and Comcast that have customers waiting to watch. But it is a two-way street. Any outbound traffic from customers could also be forwarded to Cogent to send on. Traditionally, both sides have managed the traffic by gradually increasing the bandwidth and speed of their connections to one-another. But as Netflix traffic grows and grows, companies like Comcast and Verizon believe they are being saddled with the costs to upgrade their networks in ways that are out of proportion to the traffic they send in the other direction. ISPs often grumble about the cost but keep on upgrading to keep paying customers happy. Verizon and Comcast are suspected of dragging their feet on those upgrades in an effort to win compensation.
Netflix and YouTube together are now estimated to cover 50 percent of all video traffic on the Internet, and that traffic is growing. Cogent dutifully passes that video content along to Internet Service Providers like Verizon and Comcast that have customers waiting to watch. But it is a two-way street. Any outbound traffic from customers could also be forwarded to Cogent to send on. Traditionally, both sides have managed the traffic by gradually increasing the bandwidth and speed of their connections to one-another. But as Netflix traffic grows and grows, companies like Comcast and Verizon believe they are being saddled with the costs to upgrade their networks in ways that are out of proportion to the traffic they send in the other direction. ISPs often grumble about the cost but keep on upgrading to keep paying customers happy. Verizon and Comcast are suspected of dragging their feet on those upgrades in an effort to win compensation. But that argument does not explain why Netflix was compelled to make a financial arrangement with Comcast. The two companies have been in negotiations on the subject of traffic compensation for months. Many industry observers believe those talks went nowhere until Netflix customers began complaining about the increasing network slowdowns. Some even dropped their Netflix subscriptions over the issue.
But that argument does not explain why Netflix was compelled to make a financial arrangement with Comcast. The two companies have been in negotiations on the subject of traffic compensation for months. Many industry observers believe those talks went nowhere until Netflix customers began complaining about the increasing network slowdowns. Some even dropped their Netflix subscriptions over the issue.
