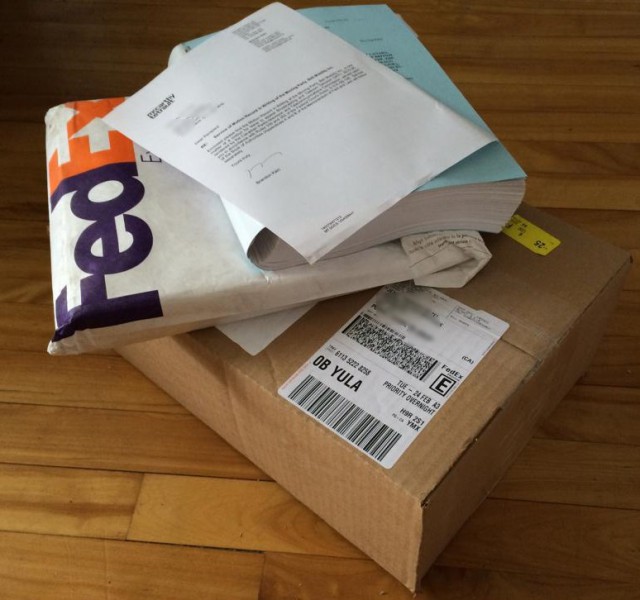

The first legal “bricks of paper” arriving from Bell’s attorneys in the case of Bell v. Ordinary Canadian consumers arrived at the home of Jean-François Mezei of Pointe-Claire, Que.
A Manitoba university student and consumer groups who won their case against Bell’s preferential treatment of its mobile streaming video service are now being threatened with demands they personally cover Bell’s legal expenses as the phone company appeals the ruling in court.
The dispute involves Bell Mobile TV Service — a $5/mo optional add-on that allows Bell’s mobile customers to stream up to 10 hours of video programming, some of it from Bell-owned television networks like CTV, without it counting against the customer’s usage cap. Each additional hour costs $3. The service prices usage based on time, not data usage, which lets Bell stream very high quality video to customers. Competitors like Netflix do not have this option and their customers are billed based on the amount of data consumed, which is around 800 percent higher than what Bell Mobile TV charges.
University of Manitoba graduate student Benjamin Klass filed a complaint with the Canadian Radio-Television and Telecommunications Commission (CRTC) in 2013 accusing Bell of violating Net Neutrality and creating an anti-competitive marketplace for online video. Twelve of the 43 channels available on Mobile TV — including CTV, TSN and The Movie Network — are owned by Bell Media, a subsidiary, like Bell Mobility, of the media behemoth BCE.
Klass alleged the practice was a clear violation of Canada’s laws governing broadcasting: “No Canadian carrier shall, in relation to the provision of a telecommunications service or the charging of a rate for it, unjustly discriminate or give an undue or unreasonable preference toward any person, including itself, or subject any person to an undue or unreasonable disadvantage.”
The CRTC agreed with Klass and in late January ruled in favor of Klass’ complaint, giving Bell and Quebec-based Vidéotron (which offers a similar service) until the end of April to close them down in their present form.
BCE, the parent of Bell Mobility, told the CBC it was “shocked” by the CRTC’s ruling, suspecting the complaining groups mislead regulators into thinking Bell favored its own content over others.
“There’s a hint here that the government believes Bell Mobile TV delivers only Bell Media content,” spokesman Jason Laszlo said. “They should know we offer mobile TV content from all of Canada’s leading broadcasters in English and French.”
 Laszlo added Bell-owned content only comprises 20% of Bell Mobile TV programming and that the ruling would deprive more than 1.5 million current Bell Mobile TV subscribers from getting the service after the spring deadline to shut it down.
Laszlo added Bell-owned content only comprises 20% of Bell Mobile TV programming and that the ruling would deprive more than 1.5 million current Bell Mobile TV subscribers from getting the service after the spring deadline to shut it down.
The CRTC and consumer groups argue that is beside the point.
“At its core, this decision isn’t so much about Bell or Vidéotron,” CRTC chair Jean-Pierre Blais said at a breakfast luncheon in London, Ont., in late January. “It’s about all of us and our ability to access content equally and fairly, in an open market that favours innovation and choice. The CRTC always wants to ensure — and this decision supports this goal — that Canadians have fair and reasonable access to content. It may be tempting for large vertically integrated companies to offer certain perks to their customers. But when the impetus to innovate steps on the toes of the principle of fair and open access to content, we will intervene.”
Consumer group OpenMedia says Bell’s motivation isn’t to create a level playing field or provide customers with more options for online video. It’s about artificially inflating the cost of accessing services like Netflix and other independent video companies that are innovating away from the traditional pay television package.
“Bell is doing everything in its power to make the Internet more like cable TV,” said OpenMedia campaigns manager Josh Tabish. “They want the power to pick and choose what we see by forcing competing services into a more expensive toll lane online.”

Klass (Image: CBC)
Bell’s legal strategy going forward is an homage to the one American wireless companies used for years to avoid Net Neutrality.
Bell Mobility argues that Bell Mobile TV is a broadcasting service, not a telecommunications service and therefore doesn’t fall under the jurisdiction of the Telecommunications Act.
Since the CRTC was not receptive to that argument, Bell is taking the matter to the Federal Court of Appeal, asking it to overturn the CRTC ruling and grant the company court and legal costs paid for by the Canadian consumers that brought the original complaint.
Jean-François Mezei of Pointe-Claire, Que. is among them and has been the unhappy recipient of several parcels containing “bricks of paper” from FedEx he suspects is just the beginning.
Mezei has been tweeting about ongoing developments in the case, and asked Bell, “how come you have no press release bragging about how Bell Mobility is suing individual citizens who participated in [the CRTC complaint]?”
Klass told CBC News he hasn’t yet made up his mind how to respond to the court filing, but admitted it is unnerving.
“In that regard, it really strikes me as a method of intimidation,” he said. “Right off the bat, it has a chilling effect. It appears that Bell is simply pursuing the argument, that it unsuccessfully made to the CRTC, through the court.”
 Bell Canada will invest $1.14 billion to bring gigabit fiber to the home service to more than one million homes and apartments in the Greater Toronto Area (GTA) over the next three years.
Bell Canada will invest $1.14 billion to bring gigabit fiber to the home service to more than one million homes and apartments in the Greater Toronto Area (GTA) over the next three years. Toronto will be the fastest broadband city in North, Central, and South America when Bell is finished laying 9,000 kilometers of fiber underground and on 80,000 Bell and Toronto Hydro utility poles. At least 27 Bell telephone exchanges will be fully upgraded to 100% fiber service, eliminating huge swaths of older copper wiring. At least 2,400 new jobs will be created, but Bell and Toronto city officials are convinced an all-fiber optic network will attract even more jobs and help broaden Toronto’s digital economy.
Toronto will be the fastest broadband city in North, Central, and South America when Bell is finished laying 9,000 kilometers of fiber underground and on 80,000 Bell and Toronto Hydro utility poles. At least 27 Bell telephone exchanges will be fully upgraded to 100% fiber service, eliminating huge swaths of older copper wiring. At least 2,400 new jobs will be created, but Bell and Toronto city officials are convinced an all-fiber optic network will attract even more jobs and help broaden Toronto’s digital economy.

 Subscribe
Subscribe


 Laszlo added Bell-owned content only comprises 20% of Bell Mobile TV programming and that the ruling would deprive more than 1.5 million current Bell Mobile TV subscribers from getting the service after the spring deadline to shut it down.
Laszlo added Bell-owned content only comprises 20% of Bell Mobile TV programming and that the ruling would deprive more than 1.5 million current Bell Mobile TV subscribers from getting the service after the spring deadline to shut it down.


 Hackers exploited poor coding practices at an Ottawa-based third-party contractor to access and eventually publish more than 20,000 usernames and passwords of Bell Canada’s small business customers on a website.
Hackers exploited poor coding practices at an Ottawa-based third-party contractor to access and eventually publish more than 20,000 usernames and passwords of Bell Canada’s small business customers on a website. Trustwave Holdings, a security company based in Chicago, Ill., said in a 2013 report that poor coding practices have made the SQL injection attack a threat for more than 15 years.
Trustwave Holdings, a security company based in Chicago, Ill., said in a 2013 report that poor coding practices have made the SQL injection attack a threat for more than 15 years.