 Frontier vs. Time Warner. Frontier vs. Comcast. Frontier vs. NPG Cable. Across 24 states, passing nearly 3,000,000 households, some in America’s smallest towns and others in large cities, Frontier Communications is engaged in a battle of survival in an increasingly competitive American telecommunications marketplace.
Frontier vs. Time Warner. Frontier vs. Comcast. Frontier vs. NPG Cable. Across 24 states, passing nearly 3,000,000 households, some in America’s smallest towns and others in large cities, Frontier Communications is engaged in a battle of survival in an increasingly competitive American telecommunications marketplace.
In this series examining Frontier Communications, today’s report investigates the competitive realities of a hotly competitive telecommunications industry, becoming more concentrated by the day. How does Frontier intend to survive and grow, and is it realistic to assume it can in an environment that demands major investments in the delivery of high quality video, low-priced telephone service, and reliable broadband that may be beyond its reach? Yesterday, we saw how Frontier is attempting to control expenses with the plan to implement a 5GB usage cap on its broadband customers. Today, we take a look at how Frontier attempts to maintain its market share and deal with customer defections. Tomorrow, we take a closer look at how quickly Frontier’s telephone line business is losing ground to its competitors.
Frontier’s Background At A Glance
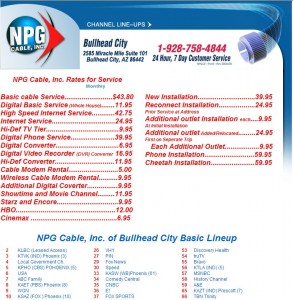
NPG Cable's Rate Card & Channel Lineup In Bullhead City, Arizona. How much of a competitive threat is a cable company without a spellchecker?
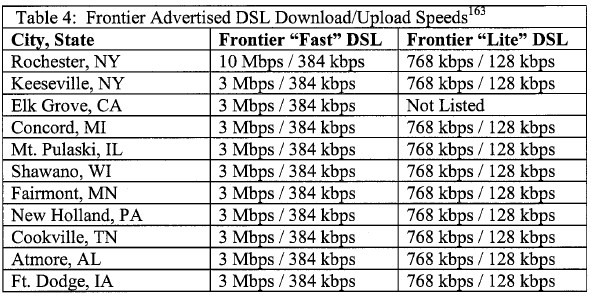
Frontier Communications, formerly Citizens Communications, primarily runs originally independent telephone companies in rural and exurban areas bypassed by the former Bell System. The company’s most significant presence is in the 585 area code, home to Rochester, New York. But from Elk Grove, California and Bullhead City, Arizona eastward to the AuSable Valley in central New York to Bluefield, West Virginia, a significant number of Frontier customers are also in some of America’s small towns and cities.
The size of a community where Frontier operates is often indicative of how much competition the company faces. Some of Frontier’s most difficult challenges can be found in the Rochester, N.Y. metropolitan area, numbering nearly 1,000,000 people, where a well entrenched Time Warner has made deep inroads into Frontier’s telephone access line business, eats Frontier for breakfast in the video delivery business, and has been a dominant player in the broadband marketplace since Road Runner arrived in 1998.
In more rural communities, Frontier often has it much easier, free from cable competition in some areas, or competing with a small independent cable company that may be relying on its own aging infrastructure and cannot afford to engage in price and service wars. Where Frontier stands as the lone player or only faces token competition from a small cable company, consumers will likely find lower speed broadband at higher-than-average prices.
The Threat From Big Cable
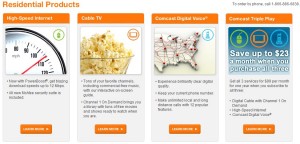
Comcast's Product Bundles Threaten Frontier In Many of Their Service Territories
The cable television industry’s entry into telephone service is among the biggest threats Frontier faces in maintaining their traditional primary revenue source: residential and business wired telephone lines.
Deploying voice over IP technology, Comcast and Time Warner, the nation’s largest cable operators, have made significant inroads into Frontier’s telephone business where they compete. Now, even smaller players in the cable industry are prepared to offer voice over IP service to customers.
Joining cable at the table are mobile telephone companies like Verizon Wireless, Sprint, and AT&T which are also eroding Frontier’s phone line business as more people in America rely exclusively on their mobile phone for telephone service.
How Cable Companies Pick Off Frontier’s Customers
Product Bundling & Discounting: The most important component of cable’s strategy against Frontier is cable’s product bundle, combining a voice over IP telephone line, a cable television package, and a high speed data product. Usually marketed as a “triple play” or “all the best” package, consumers are offered discounts based on the number of components of a package they combine. The more components, the greater the discount.
The product bundle offered by the cable industry has a competitive advantage because cable companies almost always have a more advanced network to deliver these products. Throughout the 1990s, most cable systems spent millions rebuilding their systems to accommodate increasing bandwidth requirements. The result is a considerably larger pipeline used to deliver data, video, and telephone services.
Frontier’s network is considerably more dated, largely dependent on copper wire strung on telephone poles. While the company has made significant investments in their own network, including some fiber optics, in the end, they still rely on the same copper wire infrastructure the industry has used for nearly 100 years to connect to your home or office.
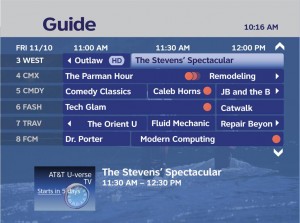
AT&T's U-verse service can deliver the goods over copper wire, but you need deep pockets to develop and deploy this technology. Are Frontier's deep enough?
Although this copper network is suitable for traditional telephone service, and can usually deliver a respectable data service over DSL, the video component has been sorely lacking. While AT&T is testing its U-verse video-over-copper technology in limited markets, Frontier is stuck reselling Dish Network, the smaller player in the satellite television marketplace.
Many consumers are resistant to satellite dishes of any size attached to their homes, and the cable industry’s response to Frontier has been the same as to DirecTV and Dish Network themselves: ugly satellite dishes that suffer from rain/snow fade, require expensive service calls and maintenance, and a limitation on the number of TV sets you can hook up. Also, no local channels in many areas. In the end, most people who were even slightly uncomfortable with satellite-delivered TV elected to just stick with what they already had: cable television.
Results of the Dish Network partnership continue to be underwhelming. Sources tell Stop the Cap! the satellite service only succeeds in areas where there is no cable competitor, the customer was already a Dish Network subscriber independent of Frontier, or the incumbent cable company is hampered by a limited channel lineup, no HD channels, or exceptionally bad service. In Rochester, Frontier is actually losing more Dish Network customers than it is adding, and growth is anemic in many other Frontier regions as well.
Frontier’s inability to provide a comparable quality television service is a critical defect in their competition with cable.
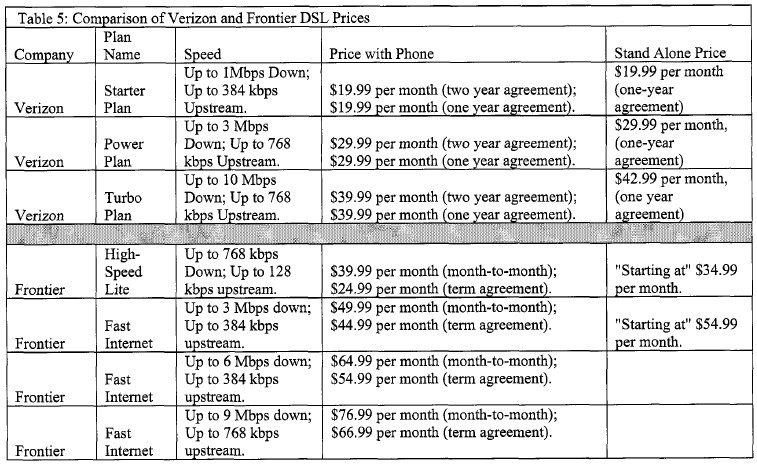
Claiming Inferior Product Quality: The cable industry wasted no time attacking Frontier’s DSL product, accusing it of not performing consistently. Uneven telephone line quality, distance from the telephone company central office, and signal ingress (when interference or crosstalk gets into wiring and degrades the signal) can all dramatically slow a DSL customer’s broadband speeds. The cable industry’s marketing often pillories DSL service because of its inability to offer anything close to a speed guarantee, and the fact it is often slower than cable’s competing product no matter how good your line is.
In areas where a large cable competitor exists, traditionally that cable operator will have the fastest speed broadband package to sell to customers in that market. This forces Frontier to compete on price. In return for a significant discount, Frontier usually locks customers into multi-year service agreements which discourage its customers from switching to a competitor. Unfortunately, the company’s inferior product bundle and long term contract commitments have made it difficult to convince cable customers to switch to Frontier, particularly if it means taking their video package from Dish Network.
Lampooning Questionable Marketing Practices: In Rochester, Time Warner’s marketing people have had no trouble finding new ways to attack Frontier in its advertising. While Frontier may be able to pull off some of their hidden extra charges, long term contracts, and restrictive service policies in more rural communities, most of those practices meet strong criticism in Time Warner’s advertising.
Among the more common refrains in Time Warner ads dismissing Frontier’s DSL product include:
- Charging a “modem rental fee” as part of Frontier’s DSL service, even if you can supply your own DSL modem.
-
Locking customers into a term commitment contract (often lasting several years) for DSL service that offers lower speeds than Time Warner’s Road Runner service and charging a substantial early termination fee for those dissatisfied with their broadband experience.
-
Charging for ancillary support services like Frontier’s “Peace of Mind” that Time Warner claims to offer at no charge.
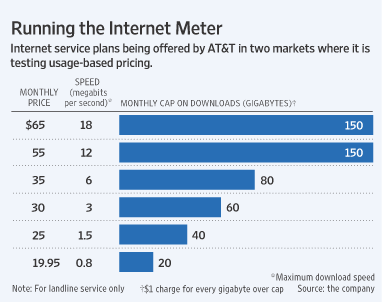
The latest decision to impose a 5GB usage cap on customers is marketing gold for the cable companies competing with Frontier, perhaps only tempered by the fact they are also studying whether to apply their own usage caps.
Relentless Marketing: One of the fringe benefits of owning your own video distribution network is the ability to pepper your existing customers with near-constant advertising promoting your own products while denigrating the competition. Cable customers can see an average of three product promotion spots every hour from their cable company trying to convince them to upgrade, attempting to bolster customer loyalty, or simply slashing and burning whatever the telephone company or satellite dish company is offering. Frontier has a limited ability to counter this.
In areas of significant competition, the battle usually rages in your mailbox, with a relentless flood of promotional postcards and mailers, as well as ad buys on local television/radio stations and local newspapers. But cable retains an important advantage because of their ability to insert advertising into basic cable channels, usually at no cost to them. Frontier doesn’t own their video distribution network – they are reselling someone else’s.
Frontier’s Battle Plan

Welcome to DeLand, Florida: Home of Frontier's Customer Care Center
Frontier’s plan to compete with cable includes their own marketing by mailbox, and sponsoring local community events and charities to leverage free media and consumer exposure to the company brand to nurture positive feelings about the company.
The company also places a high priority on attempting to position themselves as “local” players in the market – a company made up of local employees who customers supposedly will interact with on a daily basis. Unfortunately for them, most customers will likely only interact with one of their customer care call centers such as the one in DeLand, Florida which is localism IF you live, work and play in DeLand.
Frontier also maintains call centers in Henrietta, New York and Burnsville, Minnesota which are designed to replace what used to be local customer service call centers in more than a dozen Frontier areas. Some 500 people were hired to answer phones in DeLand for Frontier. This begs the question how many people lost those jobs in the various local communities where Frontier operates.
Call center employees are on Frontier’s competitive front line, trying to maintain customer loyalty, convince customers to upgrade their service packages, and above all, remain with Frontier and don’t cancel anything.
They need to maintain the battle, because cable competitors continue to erode their residential business. The company’s deactivations of high speed data services and the ongoing loss of telephone lines are considerably above the company’s own estimates.
One significant bright spot Frontier has maintained is delivering commercial broadband to businesses.
Frontier has a significant advantage in many offices, business parks, and other industrial areas bypassed by their cable competitors. Installation costs to wire a building with coaxial cable often run into the tens of thousands of dollars, an expense borne by the company, the landlord, or a combination of the two. But every business has telephone service, which usually guarantees potential access to DSL service from Frontier. Small and medium sized businesses have become loyal Frontier commercial customers because of low installation costs and a reasonable pricing plan that is typically far more cost effective than what cable is offering. Cable modem commercial access pricing models are usually tailored to a range of product speeds at prices that, when compared with what Frontier can offer, are not competitive.
Frontier’s ability to effectively compete against cable will, in the end, come down to the company’s ability to invest in their network and be able to match what is on offer from the cable operator, and new competitors yet to emerge. Some former Baby Bell telephone companies like AT&T are investing enormous sums to leverage their existing network (their U-verse product) or starting over from scratch (Verizon’s fiber optic cable to the home FIOS project).
To date, Frontier’s status as a smaller player has meant their investments in these efforts pale in comparison to their larger brethren. They include experimenting with deploying fiber optic cable to new housing developments and selected mass density buildings (apartments, offices) in Rochester, building community wi-fi networks to create a new market for wireless Internet access, and other investments in their network distribution system. If they cannot invest enough, fast enough, to keep up, they will become ripe for a merger with a larger player in the market or get wiped out by the competition.
In the meantime, to quote company chairwoman and CEO Maggie Wilderotter, Frontier intends to “stay the course” for the rest of the year.
We’ll have to wait and see if that’s good enough.
 Until the National Broadband Plan is in place and additional capacity is brought online, Australians make do with usage limited broadband service from Brisbane to Perth. With prices all over the map, choosing the right plan to minimize your exposure to Internet Overcharging schemes is more important than ever.
Until the National Broadband Plan is in place and additional capacity is brought online, Australians make do with usage limited broadband service from Brisbane to Perth. With prices all over the map, choosing the right plan to minimize your exposure to Internet Overcharging schemes is more important than ever.

 Subscribe
Subscribe