
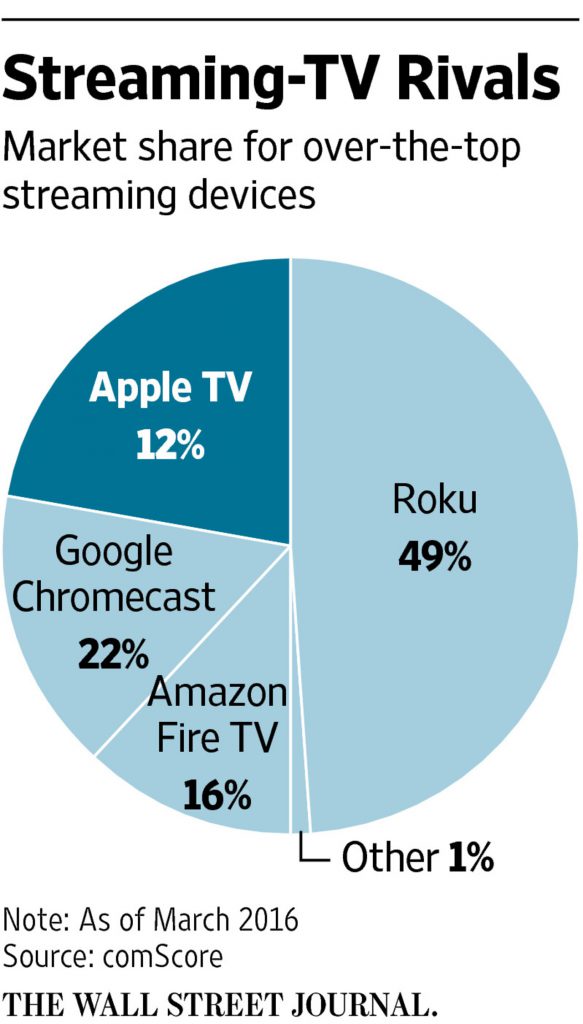
Apple TV
Apple’s ability to successfully force its way into the pay television business with a cord-cutter’s streaming TV solution has been left languishing since 2009, thanks to some of America’s largest cable and entertainment companies who think Apple is arrogant and out of touch.
The Wall Street Journal today published a story showing how Apple’s plans to challenge the cable TV industry much the same way it revolutionized digital music has rubbed the big and powerful the wrong way. Apple’s desire to launch a cheaper streaming video service with a slimmed down TV lineup and robust on-demand options has flopped, because executives have no interest in bending to Apple’s way of thinking.
In 2009, Apple decided it wanted in on the streaming pay-TV business. At the same time Time Warner Cable began experimenting with data caps, Apple was approaching local stations and broadcast networks and offering them premium payments — higher than what the cable industry itself paid — for Apple’s choice of stations and cable networks. The deal meant Apple would alone be free to pick only the channels it wanted to carry, a major departure from the industry practice of contract renewals that bundled popular networks with spinoff and lesser-known channels cable operators didn’t want to carry. Apple’s hard-charging negotiator, Eddy Cue, seemed to believe that if Apple was at the negotiating table, that alone would be enough to get a deal done. It wasn’t.
Two years later, Time Warner Cable approached Apple seeking to launch a joint TV venture that could compete nationwide with satellite and phone company competitors. The talks were at the highest levels at both companies, involving Time Warner Cable’s then-CEO Glenn Britt, Cue, and Apple CEO Tim Cook. Cook also approached Brian Roberts, CEO of Comcast, promising him the service would only be sold through cable operators — good news for Comcast but bad news for open competition.
 This time, Apple sought money from the cable companies, not the other way around. Cable operators were told they would need to pay $10 a month per subscriber to Apple, with no guarantee that fee would not increase in the future. Just as concerning was Apple’s insistence that subscriber authentication would require customers to use their Apple IDs, a departure from the cable industry’s push to adopt TV Everywhere, where customers could unlock streaming video from any cable network simply by logging in with the username and password they set up with their pay TV provider. Apple was also characteristically secretive about their user interface and left cable industry executives flummoxed when they asked Apple to sketch out what the service would look like on a napkin. An Apple official would only respond that their interface would be great and “better than anything you’ve ever had.” The fact Apple refused to answer the question did not go unnoticed.
This time, Apple sought money from the cable companies, not the other way around. Cable operators were told they would need to pay $10 a month per subscriber to Apple, with no guarantee that fee would not increase in the future. Just as concerning was Apple’s insistence that subscriber authentication would require customers to use their Apple IDs, a departure from the cable industry’s push to adopt TV Everywhere, where customers could unlock streaming video from any cable network simply by logging in with the username and password they set up with their pay TV provider. Apple was also characteristically secretive about their user interface and left cable industry executives flummoxed when they asked Apple to sketch out what the service would look like on a napkin. An Apple official would only respond that their interface would be great and “better than anything you’ve ever had.” The fact Apple refused to answer the question did not go unnoticed.
Nor did Cue’s unconventional way of negotiating with some of the most powerful entertainment executives in the country. When Jeff Bewkes, CEO of Time Warner (Entertainment) agreed to meet with Cue about Apple licensing Time Warner’s critical networks — which include HBO, CNN, and TNT — Apple’s negotiator showed up 10 minutes late. While Time Warner’s negotiators were smartly dressed in business attire, Cue turned up wearing jeans, a Hawaiian shirt, and sneakers with no socks. It went downhill from there, because Apple insisted on valuable on-demand rights to full seasons of hit shows and permission to let viewers store their favorite recordings on a massive cloud-based DVR that included features like automatic recordings of hit shows and advanced ad-skipping technology.
Crickets.
More than a few programmers used to having their way with cable operators were shocked by Apple’s ‘arrogance’ and unconventional way of doing business. The newspaper reports one former Time Warner Cable executive watched with amusement as stone-faced programmers were unimpressed with Apple’s demands.

Jon Lovitz offers a visual hint what Mr. Cue must have looked like meeting with high-powered execs at Time Warner (Entertainment)
“[They] kept looking at the Apple guys like: ‘Do you have any idea how this industry works?'” said the former executive.
Apple responded ‘doing new things requires changes that often are unsettling.’
A year later the negotiations were on life support, as Apple struggled with the arrival of 2015 with no slimmed down streaming TV package to offer Apple TV owners.
Apple’s demands flew in the face of decades of cable industry business practices, which give channel owners virtual guarantees of rate hikes with each contract renewal, the right to force their spinoff networks on the cable lineup in return for a comfortable renewal process, and the cable industry’s right to an assurance everyone was getting the same kind of deal (except volume discounts). Any deviation from this would result in panic on Wall Street, as investors’ dependence on perpetually improving quarterly financial results based on revenue boosts from new or higher fees would come crashing down if a company like Apple got a better deal.
One industry insider suggested once a company like Apple got a deal on sweetheart terms, every other distributor would demand the same deal (and many have contract provisions that require it). Apple may have assumed that because it managed to get the recording industry to agree to its iTunes digital music distribution deal 15 years earlier, so the cable industry would go. Except the road to cut-throat deals for entertainment programming is littered with dead-end business plans that had to be quickly modified when the discounts ended.
Netflix and Starz both learned expensive lessons when early discounts on licensing deals ended after Hollywood saw how much money those companies made from streaming. When licensing contracts expired, entertainment companies sought massive increases in licensing fees to “fairly share” the proceeds. Netflix ended up walking away from several studios, seriously impacting their online streaming catalog. Eventually, Netflix decided if they cannot beat the studios, they should join them, creating original programming to attract and keep subscribers.

Cue in real life
After almost a decade spent trying to get into the online cable business, Apple now seems more likely to follow Netflix, Amazon, and Hulu, and devote time and money on developing its own original programming. Instead of trying to license and bundle network programming, Apple TV today supports independent apps created by various networks. Viewers still get to watch their favorite shows, Apple does not have to pay for streaming rights, and there is a joint effort to create and support a single login so viewers can get access to content without constantly re-entering usernames and passwords.
Apple’s original shows include “Planet of the Apps,” a reality series, a miniseries being developed by Dr. Dre, and a spinoff of CBS’ “Carpool Karaoke.” The shows serve a dual purpose — entertaining viewers and helping push sales in Apple’s App Store and streaming music service.
Also under consideration are big budget, critically acclaimed original shows and series that could generate positive buzz for Apple TV, like “House of Cards” has done for Netflix.
Developing programming keeps negotiators like Apple’s Mr. Cue from having to challenge a very profitable pay television industry on their terms and spares Apple from creating a cable package of linear TV channels subscribers increasingly don’t care about. Viewers want on-demand access to the shows they want to see and don’t care that much about who supplies them and how.
So in the end, the intransigence of Big Cable and Hollywood studios that are now worried about cord-cutting may have done Apple an enormous favor, sparing them from being entangled in a business that buys and sells channels to fill a bloated and expensive cable television lineup more and more consumers are now deciding they can do without.
Updated: Link to WSJ story corrected.


 Subscribe
Subscribe How dare you use Hulu to watch current episodes of your favorite TV shows?
How dare you use Hulu to watch current episodes of your favorite TV shows? Some on Wall Street think Time Warner’s argument has merit, noting streaming services’ growing libraries of popular television shows and movies makes consumers more likely to consider dropping bloated cable and satellite packages.
Some on Wall Street think Time Warner’s argument has merit, noting streaming services’ growing libraries of popular television shows and movies makes consumers more likely to consider dropping bloated cable and satellite packages. While the online world is beefing up security systems with encryption and two-factor authentication to keep the hackers out, Frontier Communications’ e-mail password system harkens back to an earlier, innocent era when passwords were stored as plain text in a database practically anyone could access.
While the online world is beefing up security systems with encryption and two-factor authentication to keep the hackers out, Frontier Communications’ e-mail password system harkens back to an earlier, innocent era when passwords were stored as plain text in a database practically anyone could access.
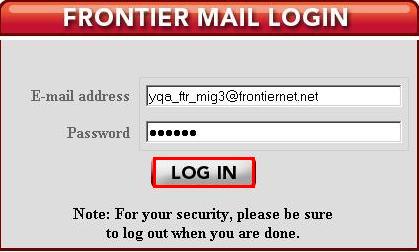 Silverman’s password was easy to find because Frontier is storing that information in plain text format, a potentially enormous security risk. Security experts say storing passwords in a plain text format, even if access is limited to customer service representatives, make them vulnerable to hacking. A single disgruntled employee or unknown security hole in a Frontier support center could theoretically expose millions of Frontier customers to password theft. The fact Frontier also e-mails transcripts of customer chat sessions to customers also represents a potential security risk. In Silverman’s case, Frontier helpfully obscured his account number, but not his password.
Silverman’s password was easy to find because Frontier is storing that information in plain text format, a potentially enormous security risk. Security experts say storing passwords in a plain text format, even if access is limited to customer service representatives, make them vulnerable to hacking. A single disgruntled employee or unknown security hole in a Frontier support center could theoretically expose millions of Frontier customers to password theft. The fact Frontier also e-mails transcripts of customer chat sessions to customers also represents a potential security risk. In Silverman’s case, Frontier helpfully obscured his account number, but not his password. Cable industry executives on hand at this year’s Cable Show in Los Angeles are debating whether Netflix has taught the cable industry some important lessons about how to treat its online video competition.
Cable industry executives on hand at this year’s Cable Show in Los Angeles are debating whether Netflix has taught the cable industry some important lessons about how to treat its online video competition. Free TV? Not quite.
Free TV? Not quite.