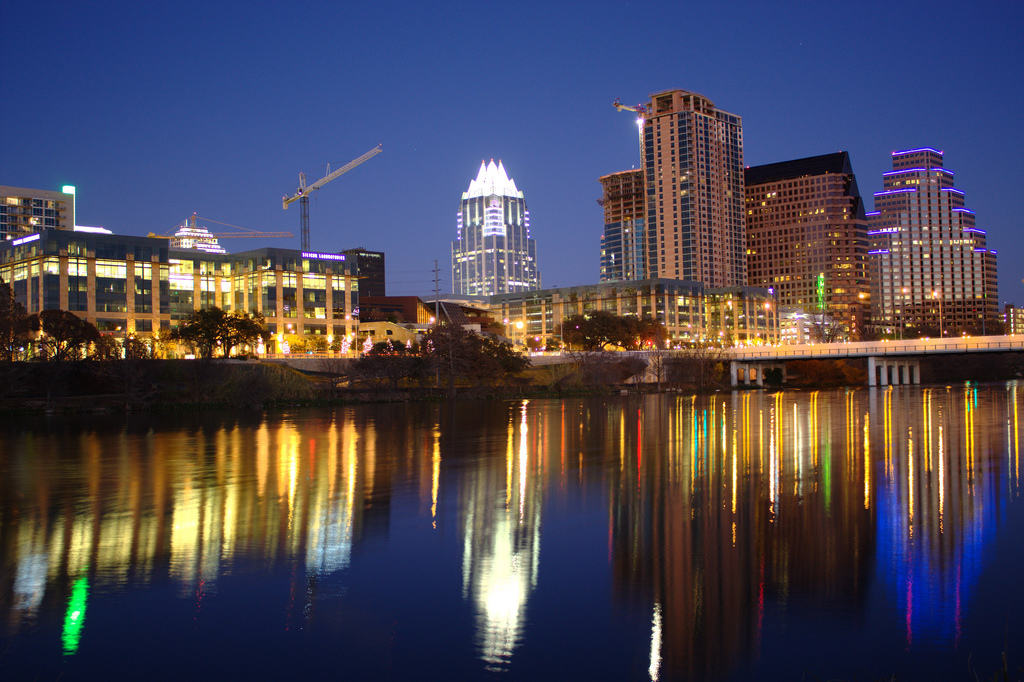
Austin, Texas is likely the next Google Fiber city.
Austin, Texas will be the second major U.S. city to receive Google Fiber’s 1,000/1,000Mbps service, perhaps as early as 2014.
A “major announcement” at a news conference scheduled for Tuesday morning is expected to bring more than 100 community leaders together to hear Google’s plans for the city.
Local media reports, an accidental mention of Austin as the next Google Fiber city on Google’s Fiber Blog, and at least one confidential source at Austin’s public utility company (that owns the poles Google Fiber will be strung across) makes it all-but-certain Austin and its nearby suburbs will get the service.
Austin would seem a natural target for Google as home to the high-tech South by Southwest. Austin also hosts Dell, Texas Instruments, AMD, Samsung, IBM, Intel, and a myriad of Internet start-ups. But a key factor for Google also seems to be the presence of Austin Energy, the nation’s 8th largest community-owned electric utility, serving more than 420,000 customers and a population of almost one million. Kansas City, the first choice for Google Fiber, also has a municipal utility company.
Milo Medin, Google’s vice president of access services, made it clear that Google is targeting cities where it does not have to deal with intransigent privately owned utility companies that make life difficult (or expensive) to attach Google Fiber to utility poles. Municipally owned providers have proved easier to work with, and in Kansas City elected officials also helped cut through administrative red tape and facilitated a working relationship between Google and government officials responsible for issuing work permits and clearing up zoning headaches.
Areas served by investor owned electric giants like Southern California Edison, Florida Power & Light, Commonwealth Edison, Consolidated Edison, Georgia Power, Dominion Resources, Detroit Edison, Public Service Enterprise Group, and others may be at an immediate disadvantage in the race to become the next Google Fiber city if those companies attempt to throw expensive roadblocks or disadvantageous bureaucracy in front of Google.
 Another factor in Kansas City’s favor was the large amount of pre-existing conduit available to pull fiber infrastructure through without tearing up streets. Cities with this type of infrastructure already in place dramatically reduces construction costs and permit delays.
Another factor in Kansas City’s favor was the large amount of pre-existing conduit available to pull fiber infrastructure through without tearing up streets. Cities with this type of infrastructure already in place dramatically reduces construction costs and permit delays.
Google Fiber’s project in Austin will compete directly with Time Warner Cable and AT&T U-verse. Time Warner Cable customers antagonized Austin residents in the spring of 2009 with a planned market test of consumption billing and usage caps for its Internet service. Google Fiber makes a point to say its broadband service is never usage-limited. AT&T U-verse customers in Austin have so far not faced punitive measures from the phone company when exceeding its 250GB U-verse usage cap.
Many cable industry analysts predicted Google Fiber was simply a show project in Kansas City, designed to embarrass the telecommunications industry’s mediocre and expensive broadband service offerings. But a move into Austin signals Google more likely sees its fiber network as a lucrative business opportunity — one that could gradually be expanded to other cities.
What communities could get the service next? Google seems likely to avoid serving areas covered by Verizon FiOS, because competing fiber networks would likely not produce the bang for the buck Google needs to draw subscribers, and Medin makes it clear the company has found working with publicly owned utility companies easier than privately owned ones, so future Google Fiber cities will likely have these factors in common:

Having a publicly owned utility helps.
- A high-tech business community and well-educated workforce in a medium to large city;
- A publicly owned municipal utility willing to work with Google;
- Pre-existing infrastructure to support fiber service without tearing up streets and neighborhoods;
- A local government willing to cut red tape and ease Google’s expansion;
- No Verizon FiOS fiber service in the immediate metropolitan area;
- A reasonable level of regulations covering environmental impacts of utility infrastructure work, permits, and licensing.
Such requirements would wipe out almost all New York (except Rochester, Binghamton and the Southern Tier around Ithaca — all completely bypassed by Verizon FiOS) and New Jersey as possible candidates. California outside of Mountain View would also seem untenable because of government regulations, sprawling cities, and private utilities. Florida and Georgia have two major private power companies to contend with as well. But there are opportunities in Texas, the Carolinas, Minnesota, Washington, Arizona, Colorado, Tennessee, Massachusetts, and across several midwestern states, especially those served by AT&T’s inferior U-verse system.
[flv width=”640″ height=”380″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/KXAN Austin Google Fiber Expected in Austin 4-5-13.mp4[/flv]
KXAN in Austin spent almost seven minutes of its weekend evening newscast talking about forthcoming Google Fiber in Austin. (7 minutes)


 Subscribe
Subscribe On the heels of today’s announcement from Google that it intends to make Austin, Tex. the next home for Google Fiber, AT&T
On the heels of today’s announcement from Google that it intends to make Austin, Tex. the next home for Google Fiber, AT&T 
 Another factor in Kansas City’s favor was the large amount of pre-existing conduit available to pull fiber infrastructure through without tearing up streets. Cities with this type of infrastructure already in place dramatically reduces construction costs and permit delays.
Another factor in Kansas City’s favor was the large amount of pre-existing conduit available to pull fiber infrastructure through without tearing up streets. Cities with this type of infrastructure already in place dramatically reduces construction costs and permit delays.