
Phillip “Spending $6k per cable customer is obviously a much better deal than paying half that to build a fiber to the home network” Dampier
Math was never my strong subject, but even I can calculate the groupthink of American cable and telephone companies and their friends on Wall Street just doesn’t add up.
This week, we learned that cable companies like Bright House Networks, Suddenlink, and Charter Communications are already lining up for a chance to acquire three million cable customers Comcast intends to sell if it wins approval of its merger with Time Warner Cable. Wall Street has already predicted Comcast will fetch as much as $18 billion for those customers and pegged the value of each at approximately $6,000.
But for less than half that price any company could build a brand new fiber to the home system capable of delivering 1,000Mbps broadband and state-of-the-art phone and television service and start banking profits long before paying off the debt from buying an inferior coaxial cable system. Yet we are told time and time again that the economics of fiber to the home service simply don’t make any sense and deploying the technology is a waste of money.
Let’s review:
Google Fiber was called a boondoggle by many of its competitors. The folks at Bernstein Research, routinely friendly to the cable business model, seemed appalled at the economics of Google’s fiber project in Kansas City. Bernstein’s Carlos Kirjner and Ram Parameswaran said Google would throw $84 million into the first phase of its fiber network, connecting 149,000 homes at a cost between $500-674 per home. The Wall Street analyst firm warned investors of the costs Google would incur reaching 20 million customers nationwide — $11 billion.
“We remain skeptical that Google will find a scalable and economically feasible model to extend its build out to a large portion of the U.S., as costs would be substantial, regulatory and competitive barriers material, and in the end the effort would have limited impact on the global trajectory of the business,” Bernstein wrote to its investor clients.
 So Google spending $11 billion to reach 20 million new homes is business malpractice while spending $18 billion for three million Time Warner Cable customers is confirmation of the cable industry’s robust health and valuation?
So Google spending $11 billion to reach 20 million new homes is business malpractice while spending $18 billion for three million Time Warner Cable customers is confirmation of the cable industry’s robust health and valuation?
Bernstein’s firm never thought highly of Verizon FiOS either.
“If I were an auto dealer and I wanted to give people a Maserati for the price of a Volkswagen, I’d have some seriously happy customers,” Craig Moffett from Bernstein said back in 2008. “My problem would be whether I could earn a decent return doing it.”
Back then, Moffett estimated the average cost to Verizon per FiOS home passed was $3,897, a figure based on wiring up every neighborhood, but not getting every homeowner to buy the service. Costs for fiber have dropped dramatically since 2008. Dave Burstein from DSL Prime reported by the summer of 2012 Verizon told shareholders costs fell below $700/home passed and headed to $600. The total cost of running fiber, installing it in a customer’s home and providing equipment meant Verizon had to spend about $1,500 per customer when all was said and done.
Moffett concluded Verizon was throwing money away spending that much on improving service. He wasn’t impressed by AT&T U-verse either, which only ran fiber into the neighborhood, not to each home. Moffett predicted AT&T was spending $2,200 per home on U-verse back in 2008, although those costs have dropped dramatically as well.

Moffett
Moffett’s solution for both Verizon and AT&T? Do nothing to upgrade, because the price wasn’t worth the amount of revenue returns either company could expect in the short-term.
It was a much different story if Comcast wanted to spend $45 billion to acquire Time Warner Cable however, a deal Moffett called “transformational.”
“What we’re talking about is an industry that is becoming more capital intensive,” Todd Mitchell, an analyst at Brean Capital LLC in New York told Bloomberg News. “What happens to mature, capital-intensive companies — they consolidate. So, yes, I think the cable industry is ripe for consolidation.”
Other investors agreed.
“This is definitely a bet on a positive future for high-speed access, cable and other services in an economic recovery,” said Bill Smead, chief investment officer at Smead Capital Management, whose fund owns Comcast shares.
 But Forbes’ Peter Cohan called Google’s much less investment into fiber broadband a colossal waste of money.
But Forbes’ Peter Cohan called Google’s much less investment into fiber broadband a colossal waste of money.
“Larry Page should nip this bad idea in the bud,” Cohan wrote.
Cohan warned investors should throw water on the enthusiasm for fiber before serious money got spent.
“FTTH authority, Neal Lachman, wrote in SeekingAlpha, that it would cost as much as $500 billion and could take a decade to connect all the houses and commercial buildings in the U.S. to fiber,” Cohan added.
Cohan was concerned Google’s initial investment would take much too long to be recovered, which apparently is not an issue for buyers willing to spend $18 billion for three million disaffected Time Warner Cable customers desperately seeking alternatives.

An investment for the future, not short term profits.
Municipal broadband providers have often chosen to deploy fiber to the home service because the technology offers plenty of capacity, ongoing maintenance costs are low and the networks can be upgraded at little cost indefinitely. But such broadband efforts, especially when they are owned by local government, represent a threat for cable and phone companies relying on a business model that sells less for more.
The American Legislative Exchange Council (ALEC), funded by Comcast, Time Warner, AT&T, Verizon, and other large telecom companies is at the forefront of helping friendly state legislators ban community fiber networks. Their excuse is that the fiber networks cost too much and, inexplicably, can reduce competition.
“A growing number of municipalities are […] building their own networks and offering broadband services to their citizens,” ALEC writes on its website. “ALEC disagrees with their answer due to the negative impacts it has on free markets and limited government. In addition, such projects could erode consumer choice by making markets less attractive to competition because of the government’s expanded role as a service provider.”
The Fiber-to-the-Home Council obviously disagrees.
“Believe it or not, there are already more than a thousand telecom network operators and service providers across North America that have upgraded to fiber to the home,” says the Council. “The vast majority of these are local incumbent telephone companies that are looking to transform themselves from voice and DSL providers into 21st century broadband companies that can deliver ultra high-speed Internet and robust video services, as well as be able to deliver other high-bandwidth digital applications and services to homes and businesses in the years ahead.”

Stephenson
In fact, a good many of those efforts are undertaken by member-owned co-ops and municipally owned providers that answer to local residents, not to shareholders looking for quick returns.
The only time large companies like AT&T move towards fiber to the home service is when a competitor threatens to do it themselves. That is precisely what happened in Austin. The day Google announced it was launching fiber service in Austin, AT&T suddenly announced its intention to do the same.
“In Austin we’re deploying fiber very aggressively,” said AT&T CEO Randall Stephenson. “The cost dynamics of deploying fiber have dramatically changed. The interfaces at the homes, the wiring requirements, how you get a wiring drop to a pole, and the way you splice it has totally changed the cost dynamics of deploying fiber.”
Prior to that announcement, AT&T justified its decision not to deploy fiber all the way to the home by saying it was unnecessary and too costly. With Google headed to town, that talking point is no longer operative.
 AT&T has usage capped its heavily promoted U-verse GigaPower fiber to the home service at 1TB a month, according to fine print appearing on communications sent to customers.
AT&T has usage capped its heavily promoted U-verse GigaPower fiber to the home service at 1TB a month, according to fine print appearing on communications sent to customers.

 Subscribe
Subscribe While AT&T trumpets vague plans to upgrade up to 100 cities with gigabit fiber to the home service, some AT&T GigaPower U-verse customers in Austin wish they could just consistently get the 300Mbps service they were promised.
While AT&T trumpets vague plans to upgrade up to 100 cities with gigabit fiber to the home service, some AT&T GigaPower U-verse customers in Austin wish they could just consistently get the 300Mbps service they were promised. “I upgraded to GigaPower last December and since then, the service started getting disconnected multiple times per week,” wrote ybasha. “Sometimes it lasts a few minutes and sometimes longer. When that happens, I lose Internet and TV service. I called technical support multiple times. They sent technicians twice. One of them swapped the modem, but I still have the problem.”
“I upgraded to GigaPower last December and since then, the service started getting disconnected multiple times per week,” wrote ybasha. “Sometimes it lasts a few minutes and sometimes longer. When that happens, I lose Internet and TV service. I called technical support multiple times. They sent technicians twice. One of them swapped the modem, but I still have the problem.” AT&T GigaPower is supposed to offer 300/300Mbps service today with an upgrade to gigabit Internet forthcoming later this year. But not every customer comes close to getting those speeds.
AT&T GigaPower is supposed to offer 300/300Mbps service today with an upgrade to gigabit Internet forthcoming later this year. But not every customer comes close to getting those speeds.  Kim R. in Cedar Falls, Tex. isn’t happy either:
Kim R. in Cedar Falls, Tex. isn’t happy either: One of the first lessons a good magician learns is that to best impress an audience, one has to at least show an actual rabbit going into the hat before making it disappear.
One of the first lessons a good magician learns is that to best impress an audience, one has to at least show an actual rabbit going into the hat before making it disappear.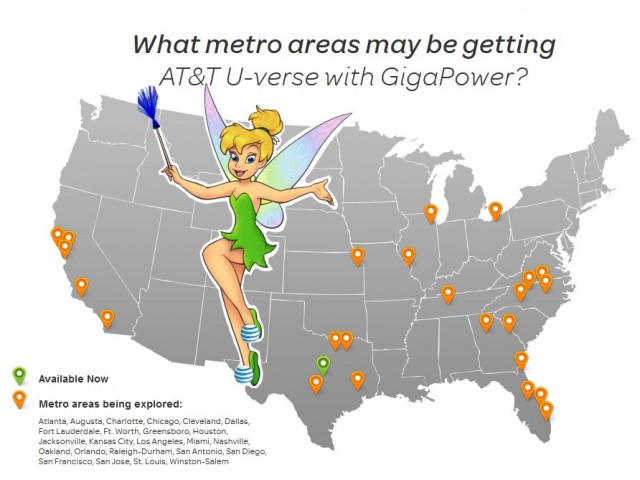
 AT&T U-verse with Gigapower is not coming to a home near you, although AT&T hopes you believe it will.
AT&T U-verse with Gigapower is not coming to a home near you, although AT&T hopes you believe it will. So Google spending $11 billion to reach 20 million new homes is business malpractice while spending $18 billion for three million Time Warner Cable customers is confirmation of the cable industry’s robust health and valuation?
So Google spending $11 billion to reach 20 million new homes is business malpractice while spending $18 billion for three million Time Warner Cable customers is confirmation of the cable industry’s robust health and valuation?
 But Forbes’ Peter Cohan called Google’s much less investment into fiber broadband
But Forbes’ Peter Cohan called Google’s much less investment into fiber broadband 

